Kubota Beisen | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Born | March 15, 1852 |
| Died | May 19, 1906 (aged 54) |
| Nationality | Japanese |
| Education | Suzuki Hyakunen |
| Known for | Nihonga, pictorial |
Kubota Beisen (久保田 米僊, 1852 – May 19, 1906) was a Japanese artist and art instructor in the Meiji period.
Although his style remained recognisably Japanese, his knowledge of Western principles and methods is also reflected in his work.[1] Beisen trained under Suzuki Hyakunen (1825–1891).[2] The way in which he integrated Western perspective and techniques in his work was a self-taught skill.
Biography
Kubota was a teacher at the Kyoto Prefectural School of Painting, which was founded in 1878 by Kubota and others.[1] Among his colleagues in establishing the school was the artist Kōno Bairei (1844–95).[2]
- 1886: Kubota was ordered to decorate the ceiling and doors of one of the rooms in the Imperial palace, which was then newly constructed in Tokyo.[1]
- 1889: Kubota visited Paris, where he made a study of European masters.[1]
- 1890: Kubota began working for the Kokumin Shimbun, which was among the daily newspapers in Tokio.[1]
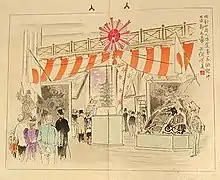
- 1893: Kubota was sent to the World's Columbian Exposition at Chicago by a newspaper, Kokumin Shimbun; and his drawings were published for its subscribers in Tokyo and elsewhere in Japan[1] Kubota's paintings were collected in a multivolume set of soft cover books in Japan that same year under the title Kakuryū sekai hakurankai bijutsu hin gafu (閣龍世界博覧美術品画譜) by Okurashoten. The illustration to the right appears in volume one, available for free download as a PDF through Getty Images, the Internet Archive, and Hathi Trust.
- 1897: A painting by Kubota was amongst the gifts from Japan which were presented to Queen Victoria on the occasion of her Diamond Jubilee.[1]
As war artist for Kokumin Shimbun, he accompanied the Japanese army at the time of the war with China in 1894 through 1895.[1] His vivid illustrations of battlefield scenes of the First Sino-Japanese War were widely distributed in the Japanese population.
When Kubota returned from the front, he was summoned to General Headquarters where he was ordered to create drawings in the presence of the Emperor.[1]
Kubota's artwork was published in Nisshin Sentou Gahou (A Pictorial Record of the Sino-Japanese War). The eleven volumes were published at irregular intervals between October 1894 and June 1895. The volumes are a visual chronicle of the war, beginning with the outbreak of hostilities in the summer of 1894.[3] Kubota created images of Japan's sea-victories. He also published a visual account of Japan's advance into Manchuria. The peace treaty signed between Japan and China was also illustrated as part of this series of drawings.[3]
Amongst the honours he received are the Paris Exposition, Gold Medal, 1889.[4] and at the Columbian Exposition, First Class Medal, 1893.[4]
Works

Kubota's published work in Japanese is encompassed in 24 works in 25 publications in 53 library holdings.[5] His one work in English was published in six editions and is found in 84 libraries worldwide.[6]
- 1921 — 洗張浮世模漾 (Araihari ukiyo moyō) OCLC 029340693
- 1905 — The New theory of Aesthetics (美感新論, Bikan shinron) OCLC 037632804
- 1901 — 米僊畫談 (Beisen gadan). OCLC 037418923
- 1895 — Sino-Japanese Campaign at the Front (日清戦役陣中, Nisshin sen'eki jinchu no zu)
- 1894 — 圖案服紗合 (Zuan fukusa awase) OCLC 027754896
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Diósy, Arthur. (1900). The New Far East, p. xvii., p. xvii, at Google Books
- 1 2 British Museum, Kubota Beisen and others
- 1 2 Nisshin Sentou Gahou (A Pictorial Record of the Sino-Japanese War, 1894-1895
- 1 2 Tokutomi, Ichiro et al. (1896). The Far East: an Exponent of Japanese Thoughts and Affairs, Vol. 1, p. 29., p. 29, at Google Books
- ↑ WorldCat Identities Archived 2010-12-30 at the Wayback Machine: 久保田米僊 1852-1906
- ↑ WorldCat, Beisen, Kubota 1852-
Further reading
- Diósy, Arthur. (1900). The New Far East. London: Cassell. OCLC 1368973
- Okamoto, Shumpei and Donald Keene. (1983). Impressions of the front: woodcuts of the Sino-Japanese War, 1894-95. Philadelphia: Philadelphia Museum of Art. OCLC 179964815
- Tokutomi Ichiro and Y. Fukai. (1896). The Far East: an Exponent of Japanese Thoughts and Affairs, Vol. 1. Tokyo: Office of the Kokumin-no-tomo. OCLC 17255487
External links
- British Museum, "Myriad Fish," a handscroll painting by Beisen and others
- Victorian & Albert Museum, "The Japanese left wing fire off cannon against the Chinese camp."
- Nisshin sen'eki jinchu no zu, digitized version, Waseda University Library