| Kunama | |
|---|---|
| Baada, Baazayn, Diila | |
 | |
| Native to | Eritrea, Ethiopia |
| Region | western Eritrea, northern Ethiopia |
| Ethnicity | Kunama |
Native speakers | 240,000 (2020)[1] |
| Dialects |
|
| Latin | |
| Official status | |
Recognised minority language in | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | kun |
| Glottolog | kuna1268 |
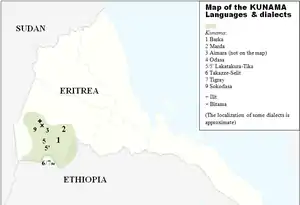
Map of the Kunama Languages
The Kunama language has been included in the proposed Nilo-Saharan language family, though it is distantly related to the other languages, if at all. Kunama is spoken by the Kunama people of the Gash-Barka Region in western Eritrea and just across the Ethiopian border. The language has several dialects including: Barka, Marda, Aimara, Odasa, Tika, Lakatakura, Sokodasa, Takazze-Setit and Tigray. Ilit and Bitama are not mutually intelligible and so may be considered distinct languages.
There have been some use of the Kunama language in publications. "The first Bible translation product in Kunama was the Gospel of Mark prepared by Andersson and published in 1906."[2]
Phonology
Consonants
| Labial | Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stop | voiceless | t | tʃ | k | ||
| voiced | b | d | dʒ | g | ||
| Fricative | f | s | ʃ | (h) | ||
| Nasal | m | n | ɲ | ŋ | ||
| Rhotic | r | |||||
| Lateral | l | |||||
| Approximant | w | j | ||||
- /h/ is only of marginal status.
- /k, ɡ/ are labialized as [kʷ, ɡʷ] after back vowels.
- /k/ is heard as aspirated [kʰ] in syllable-initial position.
Vowels
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i iː | (ɨ) | u uː |
| Mid | e eː | (ə) | o oː |
| Open | a aː |
- /i, e/ can be heard as [ɨ, ə] when in unstressed syllable position.[3]
See also
- Kunama word list (Wiktionary)
References
- ↑ Kunama at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022)

- ↑ Andemariam, Senai Woldeab (2020). "The Polygon of the Bible Translation Efforts in Eritrea 1880–2012". Journal of Translation. 16 (1): 1–16. doi:10.54395/jot-d389t.
- ↑ Getachew, Anteneh (2018). Segmental and Non-Segmental Phonology of Kūnámá. Addis Ababa University.
Relevant literature
- Bender, M. Lionel. 1996. Kunama. Languages of the World/Materials 59. München: Lincom Europa.
- Bender, Marvin Lionel. 2001. English-Kunama lexicon. Afrikanistische Arbeitspapiere 65: 201–253.
- Idris, Nikodimos.1987. The Kunama and their language. Addis Ababa University BA thesis
- Thompson, E. D. 1983. "Kunama: phonology and noun phrase" in Bender, M. L. (ed.): Nilo-Saharan Language Studies. East Lansing: African Studies Center, Michigan State University. pp. 280–322.
- Thompson, E. David. 1989. "Kunama Verb Phrase" in Bender, M. Lionel (ed.): Topics in Nilo-Saharan Linguistics. Hamburg: Helmut Buske Verlag. pp. 305–346.
- Tucker, A. N. and Bryan, M. A. 1966. "Kunama" in Linguistic Analyses: the Non-Bantu Languages of North-Eastern Africa. London: Oxford University Press.
External links
- World Atlas of Language Structures information on Kunama
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.