| Kyhytysuka | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Skull of K. sachicarum in the Paleontological Museum in Villa de Leyva, Colombia | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | †Ichthyosauria |
| Node: | †Ophthalmosauria |
| Genus: | †Kyhytysuka Cortés et al., 2021 |
| Type species | |
| Kyhytysuka sachicarum (Páramo, 1997) | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
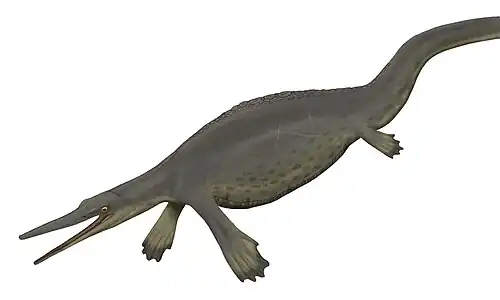
Kyhytysuka (IPA: [kɨhɨtɨˈsuka][1]) is an extinct genus of ophthalmosaurian ichthyosaur from Early Cretaceous Colombia. The animal was previously assigned to the genus Platypterygius, but given its own genus in 2021. Kyhytysuka was a mid-sized ophthalmosaurian with heterodont dentition and several adaptations suggesting that it was a macropredatory vertebrate hunter living in shallow waters. It contains a single species, Kyhytysuka sachicarum.[2]
Discovery and naming
The first definitive ichthyosaur remains in Colombia were discovered in the 1970s in the Paja Formation of Villa de Leyva. This fossil, a three dimensionally preserved skull discovered by local Jorge Cárdenas, was described as a new species of Platypterygius, P. sachicarum, by María Páramo-Fonseca in 1997.[3] However the taxon went largely ignored in the following years or was unofficially considered to be synonymous with the Argentinian Platypterygius hauthali. Further research on ichthyosaurs since its discovery have rendered the original description inadequate and furthermore found the genus of Platypterygius as taxonomically problematic. Further discoveries were made including postcranial material assigned to P. sachicarum and partial forelimbs considered to be Platypterygius sp. In 2021 Cortés et al. published a redescription of the holotype skull, finding it to represent a distinct genus they named Kyhytysuka sachicarum. The holotype, specimen DON-19671, is currently held at the Museo Geológico Nacional José Royo y Gómez, Colombian Geological Survey.[2]
The name Kyhytysuka derives from two words of the indigenous Muisca language. The name is composed of the verb "kyhyty" and the particle "suka", in combination meaning "the one that cuts with something sharp" in reference to the animal's unique dentition. The species name "sachicarum" was coined in 1977 and was originally conceived to refer to a "Sáchicas" indigenous community. Instead it refers to the town of Sáchica, despite the fact that the holotype was discovered in Villa de Leyva.[2]
Description
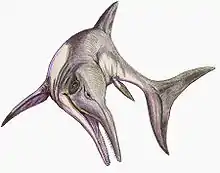
Kyhytysuka was a medium-sized ichthyosaur, with the largest specimen CIP-GA-01042014 measuring around 5 metres (16 ft) in length.[4] Its entire skull measures 940 mm in length from the tip of the premaxilla to the posterior end of the mandible. The premaxilla is relatively robust when compared to other ophthalmosaurs and slightly convex in shape. The premaxilla makes up most of the rostrum and houses a shallow alveolar groove that's deepest at the premaxillary-maxillary contact and grows wider and shallower towards the tip of the snout. The contact to the maxilla is poorly preserved; however, the contact to the nasal is clearly visible as it overlaps the premaxilla posterodorsally. The maxilla measures 320 mm in length and contacts the lacrimal and jugal, but not the prefrontals. The maxilla has delicate striations on its dorsolateral surface and a smooth groove on the last 2/3 of the lateral surface. The subcircular external nares are surrounded by the maxilla, lacrimal and over most of its dorsal surface the nasal. The nasal is 50 cm long and makes up 2/3 of the rostrum's dorsal surface. The areas closest to the tip of the snout are dorsally slightly convex and become more squared towards the posterior of the bone. The lacrimal is longer than high with a broad contact to the maxilla. The bone has three projections, a subnarial, suborbital and an ascending process, the later two of which crescent shaped. The jugal is dorsoventrally compressed with ridges at the end of the maxilla suggesting that the two bones made broad contact. The bone forms the ventral margin of the orbits and connects to the postorbital bone behind the eyes. The frontal is narrow and saddle shaped behind the orbits and widens towards its contact with the prefrontals before growing narrower again as it drives a wedge between the nasal bones. The parietal makes up the bulk of the dorsal skull roof, is broad and dorsoventrally thick and weakly convex. The orbits were large and oval, however the external sclerotic ring is not preserved. There are however several disarticulated sclerotic fragments present in the fossil.[2]
The dentary is the longest bone in the fossil, measuring a total of 720 mm, and makes up the majority of the mandible. It contains a long tooth groove with space for 47 dentary teeth that ends approximately at the anterior boundary of the narial fossa. The mandibular symphysis makes up 40% of the mandible, with 2/3 of it being made up by the extensive splenial bone. In lateral view the surangular contributes more to the surface of the mandible than the angular.[2]
The left lower jaw of the Kyhytysuka holotype may even preserve connective tissue similar to a Stenopterygius quadriscissus specimen from Holzmaden. However these elements are not well preserved and may also represent teleost fish bones or plant remains with carbonate replacement.[2]
Dentition

The most noteworthy trait of Kyhytysuka is its unique dentition. The teeth are seated in long, continuous grooves in the premaxilla, maxilla and dentary. In the dentary this groove ends around 20 mm before the orbit. However, the posterior most dentary teeth are located outside the groove on a shallow alveolar table posterior to the external nares. The dentary toothrow ends before that of the maxilla, leaving the last seven maxillary teeth unopposed. The teeth are slightly recurved lingually and posteriorly, however this may be caused by taphonomy. They are conical with an oval to rounded cross section and the anterior and posterior most teeth are notably smaller than those in the middle of the jaws. An alternating wave-like pattern of tooth replacement can be observed in Kyhytysuka's anterior and posterior teeth, showing either fully erupted functional teeth or non-functional teeth that wouldn't have been erupted in life. The teeth vary between 8 and 26 mm in total size (from the root to the crown), with most of the variation stemming from the root size (crown size varies between 5 and 12 mm). The anterior most teeth are pointed and show little wear, while further back in the jaw teeth are blunt with wear on their apice. Cortés et al. managed to identify 5 different dental zones differentiated through size and morphology.[2]
Dental Zone I encompasses the first 3 premaxillary teeth, which are slender and closely packed, forming a terminal rosette at the beginning of the jaw. They occlude lingually to the dentary, creating a differentiated tooth region. These teeth most likely served to catch fish and other small prey.
Dental Zone II includes the following 10 premaxillary teeth as well as their opposing dentary teeth. They are over 5 mm shorter than the preceding premaxillary teeth and appear in an alternating patter between functional erupted and non-functional teeth. Like the teeth of dental zone I, they have pointed apices.
Dental Zone III includes the large teeth of the posterior premaxilla and anterior maxilla. They are closely packed together forming a nearly continuous saw-tooth ridge of fully erupted teeth opposed by smaller dentary teeth. Typically ichthyosaurs possess interlocking teeth in stark contrast to the robust cutting edge formed by the teeth of this area. Based on their morphology they most likely served to shear prey.
Dental Zone IV is made up from most of the remaining maxillary teeth, diminished in size compared to the previous set and like those of dental zone II again alternating between functional and non-functional.
Dental Zone V is the last of the five tooth regions, hosting tightly packed teeth with robust morphology and short crowns.[2]
According to calculations based on Cohen et al. (2020), the relative stress throughout the upper dentition follows a relatively linear path throughout the first four dental zones, not following the different zones based on their size and morphology. Instead the stress is evenly distributed with the differences between tooth zones mitigating the dramatic difference in stress across the dentition. The highest stress was determined in the last dental zone due to their close proximity to the jaw joint. This, combined with their short and robust crowns means that they were most likely used for crushing.[2]
Phylogeny
Ophthalmosaurs have a long and complex taxonomic history dating back to 1887 and going through a multitude of revisions and changes over the years. One problem in ophthalmosaur taxonomy is presented by Platypterygius, with the type species Platypterygius platydactylus suffering from a description insufficient by modern standards. To complicate matters both the holotype and referred specimen have been destroyed in World War 2, preventing it from being redescribed. This has led to the genus becoming a wastebasket taxon for a variety of Cretaceous ichthyosaurs. This is not only problematic for the genus, but also for the family Platypterygiinae, which uses "P." hercynicus as its anchor, a taxon potentially quite distant from P. platydactylus. To stabilize ophthalmosaurian phylogeny, Cortés et al. propose node-stem-triplet approach, redefining Ophthalmosauria and the families part of it. As part of this revision they reject Platypterygiinae as a name due to the problematic nature of the genus Platypterygus, instead coining Brachypterygiidae in its place, composing of all ophthalmosaurians closer to Brachypterygius than to Ophthalmosaurus. In their phylogeny Cortés et al. recover Kyhytysuka as a derived member of Brachypterygiidae.[2]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Paleobiology

Kyhytysuka's large body size, robust skull, putative gular soft tissue and heterodont dentition all give important clues to the animal's ecology and feeding habits. The front most teeth are long and slender, built to grip smaller prey, while the more saw-toothed dentition of the maxilla is built to shear prey. The hind most teeth on the other hand are short and robust and may have been used for crushing. The connection between quadrate and braincase is reinforced in Kyhytysuka, which may be an indication for increased biteforce. The medial-lateral cartilage in the holotype is reduced, suggesting tight joints and preventing the animal from moving its jaws in a lateral motion. However, the ichthyosaur would have been able to open its jaws to a gape of 70 to 75°. This massive gape is consistent with other ichthyosaurs, such as the more basal Guizhouichthyosaurus being capable of even swallowing very large prey. Furthermore, Cortés et al. suggest that the mandibular joint would have been very mobile at wide gape angles and more constrained at low gape angles, perhaps an adaptation to resist jaw opening. The large gape and peculiar dentition suggest that Kyhytysuka was a macropredatory animal, hunting large vertebrates and possibly being aided by ligament-like connective tissue supporting a gular expansion while swallowing. Based on the relatively small orbits and linear jaw line, the authors furthermore propose that the animal inhabited shallow waters. Lastly, the skull is strengthened along its axis and the mandibular symphysis is heavily reinforced, which can also be seen in the jurassic macropredatory Temnodontosaurus.[2]
References
- ↑ "Phonetic transcription of Kyhytysuka, the first Cretaceous hypercarnivorous ichthyosaur". YouTube.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Cortés, D.; Maxwell, E.E.; Larsson, H.C.E. (2021). "Re-appearance of hypercarnivore ichthyosaurs in the Cretaceous with differentiated dentition: revision of 'Platypterygius' sachicarum (Reptilia:Ichthyosauria, Ophthalmosauridae) from Colombia". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 19 (14): 1–34. doi:10.1080/14772019.2021.1989507. S2CID 244512087.
- ↑ Páramo, M. E. (1997). "Platypterygius sachicarum (Reptilia, Ichthyosauria) nueva especie del Cretácico de Colombia". Revista Ingeominas (in Spanish). 6: 1–12.
- ↑ Maxwell, Erin E.; Cortés, Dirley; Patarroyo, Pedro; Ruge, Mary Luz Parra (2019). "A new specimen of Platypterygius saharicum (Reptilia, Ichthyosauria) from the Early Cretaceous of Colombia and its phylogenetic implications". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 39 (1). e1577875. doi:10.1080/02724634.2019.1577875. S2CID 146059015.