
Philips LM358D
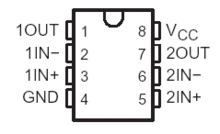
LM358 pinout

LM358 die photo
The LM358 is a low-power dual operational amplifier integrated circuit, originally introduced by National Semiconductor.[1]
It supports an operating voltage of +3 to +32 volts (single power supply) or ±1.5 to ±16 volts (dual power supplies).
Input voltage can range from −0.3 to +32 volts with single power supply. Small negative input voltages below ground are acceptable because the bipolar junction transistors at the input stage are configured such that their base-emitter junction voltage provides just enough voltage differential between the collector and base for the transistors to function.[2]
References
- ↑ http://www.ti.com/product/lm358
- ↑ Elliott, Rod (2016). "Voltage Followers". sound-au.com. Figure 5. Archived from the original on 2021-08-01. Retrieved 2022-07-27.
Further reading
The LM358 is now an industry-standard part manufactured by multiple companies, all of which publish datasheets:
- Diodes Incorporated: datasheet, webpage
- Fairchild Semiconductor: datasheet, webpage
- ON Semiconductor: datasheet, webpage
- ST Microelectronics: datasheet, webpage
- Texas Instruments: datasheet, webpage
- National Semiconductor: datasheet, supporting materials for MIT course 6.115.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.