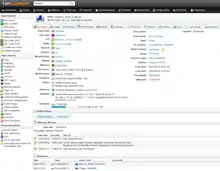
 Lansweeper Windows asset overview | |
| Initial release | 2005 or earlier[1][lower-alpha 1] |
|---|---|
| Stable release | 10.6.2.0[2]
|
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows |
| Type | IT Asset Management |
| Website | www |

Lansweeper stands as a comprehensive IT Discovery & Inventory Platform, delivering reliable, valuable, and precise insights into the status of users, devices, and software within any IT environment. This sophisticated platform seamlessly discovers and inventories all IT devices, enabling organizations to centrally manage and gain comprehensive knowledge about their IT infrastructure. Lansweeper's automated processes effortlessly identify and compile a comprehensive list of connected devices, including computers, routers, servers, and printers. It furnishes detailed, device-specific information covering installed software, applied updates & patches, user details, serial numbers, warranty specifics, printer toner levels, and a wealth of additional data.
History
Description
The main purpose of Lansweeper derives from a discovery phase of sweeping round a local area network (LAN) and maintaining an inventory of the hardware assets and software deployed on those assets.[5] Reports from the inventory enable complete hardware and software reports on the devices and can be used to identify problems.[6] Lansweeper can collect information on all Windows, Linux and Mac devices and can also IP-addressable network appliances.[5]
The software incorporates an integrated ticket-based Help Desk module that can be used to assist issues to be captured and tracked through to completion.[7] There is also a software module that allows Lansweeper to orchestrate software updates on Windows computers.[7]
The Lansweeper central inventory database must be located on either an SQL Compact or SQL Server database on a Microsoft Windows machine.[8] In 2019 Lansweeper was discovered to be vulnerable to an SQL injection vulnerability.[9] Lansweeper claims while a minimum default configuration can be supported by placing all its components on a single server the application has the capability to scale up to hundreds of thousands of devices.[10] While Lansweeper can be set up agentless it may be recommended to use agents for more complex configurations.[11]
Lansweeper has a freeware version of the product but it is limited in the number of devices available and functionality provided unless appropriate commercial licenses are purchased.[12][13][14]
Criticisms
A PC World review in 2010 claimed the interface rendered less rapidly than Spiceworks.[12]
Lansweeper itself does not directly provide a network intrusion system; however, Lansweeper claims it is able to partner with an addition tool to address that area.[15]
Notes
- ↑ The domain lansweeper.com was first registered 4 June 2004
References
- 1 2 Schulman, Jerold (23 February 2005). "JSI Tip 9094. LanSweeper is a free solution to make a software/hardware inventory of your windows clients, but you may donate". ITPro Today. Archived from the original on 25 October 2019. Retrieved 25 October 2019.
- ↑ "Lansweeper Changelog | Lansweeper | IT Discovery Software Software". Lansweeper | IT Discovery Software. Retrieved 9 December 2022.
- ↑ "About".
- ↑ "Lansweeper secures €130m investment from Insight Partners to accelerate further growth". Business Leader.
- 1 2 "IT-Asset-Management: Lansweeper - Netzwerkressourcen überprüfen und inventarisieren" [Lansweeper - review and inventory network resources]. www.tecchannel.de (in German). Archived from the original on 22 October 2019. Retrieved 22 October 2019.
- ↑ Rux, Eric B (9 February 2009). "Lansweeper". Windows IT Pro. No. 175. p. 47. Archived from the original on 25 October 2019. Retrieved 25 October 2019.
- 1 2 Blum, Erik (24 April 2017). "Lansweeper review - amazing tool for IT Service desk". ITSMDaily.com. Archived from the original on 22 October 2019. Retrieved 22 October 2019.
- ↑ "About Lansweeper". cherwellsupport.com. Archived from the original on 10 March 2014. Retrieved 22 October 2019.
- ↑ Dalili, Soroush (25 July 2019). "Technical Advisory: Unauthenticated SQL Injection in Lansweeper". nccgroup. Archived from the original on 25 October 2019. Retrieved 25 October 2019.
- ↑ "Lansweeper component overview". Lansweeper | IT Discovery Software. Archived from the original on 14 October 2019. Retrieved 14 October 2019.
- ↑ Paul, Andy (21 October 2014). Citrix XenApp® 7.5 Desktop Virtualization Solutions. Packt Publishing Ltd. ISBN 9781849689694.
- 1 2 Jacobi, Jon L. (4 June 2010). "Lansweeper". PCWorld. Archived from the original on 23 October 2016. Retrieved 22 October 2019.
- ↑ Williams, Mike. "Lansweeper 7.2.100.23 - Networking Tools - Downloads". Tech Advisor. Archived from the original on 27 October 2019. Retrieved 27 October 2019.
- ↑ Przemyslaw, Klys (14 July 2019). "Using Lansweeper with PowerShell to your advantage – Evotec". Archived from the original on 22 October 2019. Retrieved 22 October 2019.
- ↑ Pelletier, Mikel (25 July 2018). "Clearing the Mine Field: Scrutinizer & Lansweeper for Network Monitoring". Plixer. Archived from the original on 22 October 2019. Retrieved 22 October 2019.