| Country/ies of origin | People's Republic of China |
|---|---|
| Type | Military, Commercial |
| Status | Operational |
| Coverage | Global |
| Constellation size | |
| Nominal satellites | 24 MEO, 3 GEO, 3 IGSO (BeiDou-3)[1] |
| Current usable satellites |
|
| First launch | 30 October 2000 |
| Last launch | 26 December 2023 |
| Total launches | 62 |
| Orbital characteristics | |
| Regime(s) | Geostationary orbit Inclined geosynchronous orbit Medium Earth orbit |
| Orbital height | Various |
| Docking with Shijian-21 done by Compass G2 | |
| Docking date | Late December 2021[2] |
| Undocking date | Late January 2022[3] |
This is a list of past and present satellites of the BeiDou/Compass navigation satellite system. As of December 2023, 44 satellites are operational: 7 in geostationary orbits (GEO), 10 in 55° inclined geosynchronous orbits (IGSO) and 27 in Medium Earth orbits (MEO). Furthermore, 8 satellites (4 in Medium Earth orbit, 2 in geostationary orbit and 2 in inclined geosynchronous orbit) are undergoing testing or commissioning.
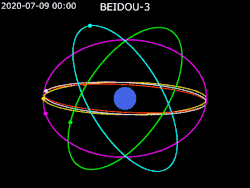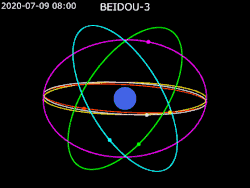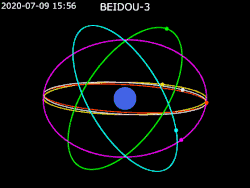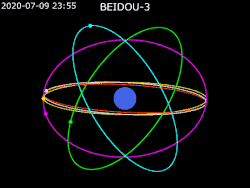
Constellation design
For BeiDou-1, the system consists of 4 GEO satellites (3 active + 1 spare).[4]
For BeiDou-2, the nominal constellation consists of 35 satellites (27 MEO, 5 GEO for BeiDou-1 compatibility, 3 IGSO).[5]
For BeiDou-3, the nominal constellation consists of 30 satellites (24 MEO, 3 GEO, 3 IGSO).[1] The constellation was declared "complete" on 23 June 2020.
Satellites
Summary table
| Constellation | Launch period |
Launches | Status | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Success | Failure | Planned | Operational | Testing/Reserve | Unhealthy/Spare | Retired | ||
| 1 | 2000–2006 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 2 | 2007–2019 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 3S | 2015–2016 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 1 |
| 3 | 2016–present | 33 | 0 | 0 | 29 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 62 | 0 | 0 | 44 | 8 | 0 | 10 | |
Note: 3S is the experimental / validation constellation for BeiDou-3. Although these satellites may be functional, their message format differs slightly from BD-3.
Full list
| # | Satellite[6] | Launch date (UTC) |
Launch site | Carrier rocket[7] | PRN[8] | Orbit[9] | Status[8][9] | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | BeiDou-1A | 30 October 2000 16:02 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3A | N/A | GEO 140° E | Retired December 2011 |
BeiDou-1, first generation experimental satellite |
| - | BeiDou-1B | 20 December 2000 16:20 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3A | N/A | GEO 80° E | Retired December 2011 |
BeiDou-1, first generation experimental satellite |
| - | BeiDou-1C | 24 May 2003 16:34 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3A | N/A | GEO 110.5° E | Retired December 2012 |
BeiDou-1, first generation experimental satellite |
| - | BeiDou-1D | 2 February 2007 16:28 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3A | N/A | GEO 86° E | Retired February 2009 |
BeiDou-1, first generation experimental satellite |
| 1 | Compass-M1 | 13 April 2007 20:11 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3A | N/A | MEO ~21,500 km | Retired | BeiDou-2, second generation validation satellite |
| 2 | Compass-G2 | 14 April 2009 16:16 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3C | N/A | GEO drifting | Retired | BeiDou-2 - Sent to GEO graveyard Orbit by Shijian-21 space Debris mitigation satellite or orbital servicing vehicle in January 2022.[10] |
| 3 | Compass-G1 | 16 January 2010 16:12 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3C | N/A | GEO 140.0° E | Retired | BeiDou-2 |
| 4 | Compass-G3 | 2 June 2010 15:53 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3C | N/A | GEO 79.5° E | Retired September 29, 2018 |
BeiDou-2, retired on 29 September 2018 |
| 5 | Compass-IGSO1 | 31 July 2010 21:30 |
Xichang, LC-3 | Long March 3A | C06 | 55° inclination IGSO 118° E | Operational | BeiDou-2 |
| 6 | Compass-G4 | 31 October 2010 16:26 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3C | C04 | GEO 160.0° E | Operational | BeiDou-2 |
| 7 | Compass-IGSO2 | 17 December 2010 20:20 |
Xichang, LC-3 | Long March 3A | C07 | 55° inclination IGSO 118° E | Operational | BeiDou-2 |
| 8 | Compass-IGSO3 | 9 April 2011 20:47 |
Xichang, LC-3 | Long March 3A | C08 | 55° inclination IGSO 118° E | Operational | BeiDou-2 |
| 9 | Compass-IGSO4 | 26 July 2011 21:44 |
Xichang, LC-3 | Long March 3A | C09 | 55° inclination IGSO 95° E | Operational | BeiDou-2 |
| 10 | Compass-IGSO5 | 1 December 2011 21:07 |
Xichang, LC-3 | Long March 3A | C10 | 55° inclination IGSO 95° E | Operational | BeiDou-2 |
| 11 | Compass-G5 | 24 February 2012 16:12 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3C | C05 | GEO 58.75° E | Operational | BeiDou-2 |
| 12 | Compass-M3 | 29 April 2012 20:50 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3B | C11 | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot A07 | Operational | BeiDou-2 |
| 13 | Compass-M4 | C12 | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot A08 | Operational | BeiDou-2 | |||
| 14 | Compass-M5 | 18 September 2012 19:10 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3B | N/A | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot B03 | Retired October 21, 2014 |
BeiDou-2, transmission ended on 21 October 2014[11] |
| 15 | Compass-M6 | C14 | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot B04 | Operational | BeiDou-2 | |||
| 16 | Compass-G6 | 25 October 2012 15:33 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3C | C02 | GEO 80° E | Operational | BeiDou-2, last satellite of the second generation[12] |
| 17 | Beidou-3 I1-S | 30 March 2015 13:52 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3C/YZ-1 | C31 | 55° inclination IGSO 95° E | Experiment | BeiDou-3, third generation validation satellite[13] |
| 18 | Beidou-3 M1-S | 25 July 2015 12:29 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3B/YZ-1 | C57 | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot A01 | Experiment | BeiDou-3, third generation validation satellite |
| 19 | Beidou-3 M2-S | C58 | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot A06 | Experiment | BeiDou-3, third generation validation satellite | |||
| 20 | Beidou-3 I2-S | 29 September 2015 23:13 |
Xichang, LC-3 | Long March 3B | C56 | 55° inclination IGSO 95° E | Experiment | BeiDou-3, third generation validation satellite |
| 21 | Beidou-3 M3-S | 1 February 2016 07:29 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3C/YZ-1 | N/A | MEO ~21,500 km | Retired | BeiDou-3, third generation validation satellite |
| 22 | Compass-IGSO6 | 29 March 2016 20:11 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3A | C13 | 55° inclination IGSO 95° E | Operational | BeiDou-2, for reliability redundancy improving, formerly PNR C15[11] |
| 23 | Compass-G7 | 12 June 2016 15:30 |
Xichang, LC-3 | Long March 3C | C03 | GEO 110.5° E | Operational | BeiDou-2, for reliability redundancy improving |
| 24 | BeiDou-3 M1 | 5 November 2017 11:45 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3B/YZ-1 | C19 | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot B07 | Operational | BeiDou-3, third generation navigation satellite. PRN C19 used until 12 June 2018.[11] |
| 25 | BeiDou-3 M2 | C20 | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot B08 | Operational | BeiDou-3 | |||
| 26 | BeiDou-3 M7 | 11 January 2018 23:18 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3B/YZ-1 | C27 | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot A04 | Operational | BeiDou-3, PRN C28 used until 12 June 2018. |
| 27 | BeiDou-3 M8 | C28 | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot A05 | Operational | BeiDou-3 | |||
| 28 | BeiDou-3 M3 | 12 February 2018 05:03 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3B/YZ-1 | C21 | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot B05 | Operational | BeiDou-3 |
| 29 | BeiDou-3 M4 | C22 | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot B06 | Operational | BeiDou-3 | |||
| 30 | BeiDou-3 M9 | 29 March 2018 17:56 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3B/YZ-1 | C29 | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot A02 | Operational | BeiDou-3 |
| 31 | BeiDou-3 M10 | C30 | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot A03 | Operational | BeiDou-3 | |||
| 32 | Compass-IGSO7 | 9 July 2018 20:58 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3A | C16 | 55° inclination IGSO 95° E[14] | Operational | BeiDou-2, for reliability redundancy improving |
| 33 | BeiDou-3 M5 | 29 July 2018 01:48 |
Xichang, LC-3 | Long March 3B/YZ-1 | C23 | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot C07 | Operational | BeiDou-3 |
| 34 | BeiDou-3 M6 | C24 | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot C01 | Operational | BeiDou-3 | |||
| 35 | BeiDou-3 M11 | 24 August 2018 23:52 |
Xichang, LC-3 | Long March 3B/YZ-1 | C25 | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot C08 | Operational | BeiDou-3 |
| 36 | BeiDou-3 M12 | C26 | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot C02 | Operational | BeiDou-3 | |||
| 37 | BeiDou-3 M13 | 19 September 2018 14:07 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3B/YZ-1 | C32 | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot B01 | Operational | BeiDou-3, with COSPAS-SARSAT MEOSAR payloads. |
| 38 | BeiDou-3 M14 | C33 | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot B03 | Operational | BeiDou-3, with COSPAS-SARSAT MEOSAR payloads. | |||
| 39 | BeiDou-3 M15 | 15 October 2018 04:23 |
Xichang, LC-3 | Long March 3B/YZ-1 | C34 | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot A07 | Operational | BeiDou-3 |
| 40 | BeiDou-3 M16 | C35 | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot A01 | Operational | BeiDou-3 | |||
| 41 | BeiDou-3 G1 | 1 November 2018 15:57 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3B/E | C59 | GEO 144.2° E | Operational | BeiDou-3 |
| 42 | BeiDou-3 M17 | 18 November 2018 18:07 |
Xichang, LC-3 | Long March 3B/YZ-1 | C36 | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot C04 | Operational | BeiDou-3 |
| 43 | BeiDou-3 M18 | C37 | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot C06 | Operational | BeiDou-3 | |||
| 44 | BeiDou-3 I1 | 20 April 2019 14:41 |
Xichang, LC-3 | Long March 3B/E | C38 | 55° inclination IGSO | Operational | BeiDou-3 |
| 45 | Compass-G8 | 17 May 2019 15:48 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3C | C01 | GEO | Operational | BeiDou-2, for reliability redundancy improving |
| 46 | BeiDou-3 I2 | 24 June 2019 18:09 |
Xichang, LC-3 | Long March 3B/E | C39 | 55° inclination IGSO | Operational | BeiDou-3 |
| 47 | BeiDou-3 M23 | 22 September 2019 21:10 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3B/YZ-1 | C45 | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot C03 | Operational | BeiDou-3, with COSPAS-SARSAT MEOSAR payloads. |
| 48 | BeiDou-3 M24 | C46 | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot C05 | Operational | BeiDou-3, with COSPAS-SARSAT MEOSAR payloads. | |||
| 49 | BeiDou-3 I3 | 4 November 2019 17:43 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3B/E | C40 | 55° inclination IGSO | Operational | BeiDou-3 |
| 50 | BeiDou-3 M21 | 23 November 2019 00:55 |
Xichang, LC-3 | Long March 3B/YZ-1 | C43 | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot A06 | Operational | BeiDou-3, with COSPAS-SARSAT MEOSAR payloads. |
| 51 | BeiDou-3 M22 | C44 | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot A08 | Operational | BeiDou-3, with COSPAS-SARSAT MEOSAR payloads. | |||
| 52 | BeiDou-3 M19 | 16 December 2019 07:22 |
Xichang, LC-3 | Long March 3B/YZ-1 | C41 | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot B02 | Operational | BeiDou-3 |
| 53 | BeiDou-3 M20 | C42 | MEO ~21,500 km, Slot B04 | Operational | BeiDou-3 | |||
| 54 | BeiDou-3 G2 | 9 March 2020 11:55 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3B/E | C60 | GEO | Operational | BeiDou-3 |
| 55 | BeiDou-3 G3 | 23 June 2020 01:43 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3B/E | C61 | GEO | In-orbit testing | BeiDou-3 |
| 56 | BeiDou-3 G4 | 17 May 2023 02:49 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3B/E | C62 | GEO | In-orbit testing | BeiDou-3 |
| 57 | BeiDou-3 M25 | 26 December 2023 03:26 |
Xichang, LC-2 | Long March 3B/E/YZ-1 | MEO | In-orbit testing | BeiDou-3, for reliability redundancy improving | |
| 58 | BeiDou-3 M26 | MEO | In-orbit testing | BeiDou-3, for reliability redundancy improving |
Medium Earth Orbit Satellites Orbital slots
| Slot | Plane | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | |
| 01 | 3-M16 | 3-M13 | 3-M6 |
| 02 | 3-M9 | 3-M19 | 3-M12 |
| 03 | 3-M10 | 3-M14 | 3-M23 |
| 04 | 3-M7 | 3-M20 | 3-M17 |
| 05 | 3-M8 | 3-M3 | 3-M24 |
| 06 | 3-M21 | 3-M4 | 3-M18 |
| 07 | 3-M15 | 3-M1 | 3-M5 |
| 08 | 3-M22 | 3-M2 | 3-M11 |
| Number in italic are under commissioning. Numbers in parentheses refer to non-operational satellites. | |||



See also
References
- 1 2 Update on the BeiDou Satellite Navigation System Archived 23 October 2018 at the Wayback Machine. 12th ICG Meeting. Jia-Qing Ma, China Satellite Navigation Office.
- ↑ "China's Shijian-21 towed dead satellite to a high graveyard orbit". Spacenews. 27 January 2022. Retrieved 25 May 2022.
- ↑ "China's Shijian-21 towed dead satellite to a high graveyard orbit". Spacenews. 27 January 2022. Retrieved 25 May 2022.
- ↑ Goebel, Greg (1 September 2008). "International Navigation Satellite Systems". vectorsite.net. Archived from the original on 1 October 2015. Retrieved 6 April 2007.
- ↑ "China Launches Another Compass GEO Navigation Satellite". Inside GNSS. 2 June 2010. Archived from the original on 11 June 2010. Retrieved 4 June 2010.
- ↑ Spaceflight Now - Launch Log
- ↑ "北斗卫星导航系统卫星状态". Archived from the original on 24 October 2014. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
- 1 2 "Constellation Status". Test and Assessment Research Center of China Satellite Navigation Office. Retrieved 30 January 2022.
- 1 2 "The Almanac: GPS World". GPS World. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- ↑ "China's Shijian-21 towed dead satellite to a high graveyard orbit". 27 January 2022.
- 1 2 3 "IGS MGEX BeiDou". mgex.igs.org. Archived from the original on 14 December 2017. Retrieved 17 December 2019.
- ↑ "中国北斗,与美国GPS比肩而立". 人民日报海外版. 2 March 2013. Retrieved 16 June 2017.
- ↑ "中国北斗导航卫星再次进入密集发射期". 中国新闻社. 31 March 2015. Retrieved 16 June 2017.
- ↑ "系统基本信息". www.csno-tarc.cn. Archived from the original on 17 September 2018. Retrieved 27 February 2018.
External links
- BeiDou Constellation Status (Test and Assessment Research Center of China Satellite Navigation Office)
- CelesTrak: Beidou (Orbital elements from NORAD); see search for retired satellites