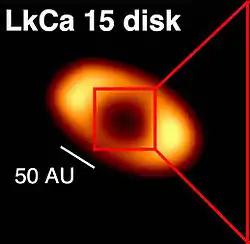
 LkCa 15 protoplanetary disk | |
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Taurus |
| Right ascension | 04h 39m 17.796s[1] |
| Declination | +22° 21′ 03.48″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | +11.91[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | K5V[2] |
| Variable type | T Tauri[1] |
| Astrometry | |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 10.572[3] mas/yr Dec.: -17.527[3] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 6.3619 ± 0.0264 mas[3] |
| Distance | 513 ± 2 ly (157.2 ± 0.7 pc) |
| Details | |
| Mass | 0.97 ± 0.03[2] M☉ |
| Radius | 1.2[4] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 1.22[5] L☉ |
| Temperature | 4730[4] K |
| Age | 2[2] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
LkCa 15 is a T Tauri star in the Taurus Molecular Cloud. These types of stars are relatively young pre-main-sequence stars that show irregular variations in brightness.[7] It has a mass that is about 97% of the Sun,[2] an effective temperature of 4370 K,[5] and is slightly cooler than the Sun. Its apparent magnitude is 11.91,[2] meaning it is not visible to the naked eye.
Planetary system
LkCa 15 is surrounded by a protoplanetary disk, typical of many T Tauri stars.[7] The disk around the star is about 55 times more massive than Jupiter,[8] and consists of three major belts (components).[4] Small changes in the observed brightness of the disk may be due to a planetary companion; the star was believed to have a protoplanetary object or exoplanet orbiting it, known as LkCa 15 b[9][10] This name stems from an older survey.[11] Later, the existence of up to three planets was suspected. The planets' existence was refuted in 2019 as higher resolution imaging became available.[4]
| Companion (in order from star) |
Mass | Semimajor axis (AU) |
Orbital period (days) |
Eccentricity | Inclination | Radius |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protoplanetary disk component 1 | 0.12–3[4] AU | 50[4]° | — | |||
| b (unconfirmed) | 6±1 MJ | 15.7±2.1 | 40000 | — | — | — |
| Protoplanetary disk component 2 | 20–40[4] AU | 51.5[4]° | — | |||
| Protoplanetary disk component 3 | 55–160[4] AU | 50[4]° | — | |||
LkCa 15 b is a candidate protoplanetary object in orbit around LkCa 15, a star in the Taurus-Auriga Star Forming Region. Its potential discovery was effected by direct imaging techniques using the Keck II telescope in 2011 by Adam Kraus and Michael Ireland.[9] A 2015 study of observations from the Magellan Telescopes and the Large Binocular Telescope argued that the planet is forming through accretion.[10] It would be the first observed exoplanet seen in the process of active accretion.[12] The planet’s existence was refuted in 2019 as higher resolution imaging became available.[4]
References
- 1 2 3 4 "EM* LkCa 15". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Notes on LKCA 15 b". Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia. 1995. Retrieved 26 December 2016.
- 1 2 3 Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (2021). "Gaia Early Data Release 3: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 649: A1. arXiv:2012.01533. Bibcode:2021A&A...649A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202039657. S2CID 227254300. (Erratum: doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202039657e). Gaia EDR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Currie, Thayne; et al. (2019), "No Clear, Direct Evidence for Multiple Protoplanets Orbiting Lk Ca 15: Lk Ca 15 BCD are Likely Inner Disk Signals", The Astrophysical Journal, 877 (1): L3, arXiv:1905.04322, Bibcode:2019ApJ...877L...3C, doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ab1b42, S2CID 152282903
- 1 2 Thalmann, C.; Mulders, G. D.; Hodapp, K.; Janson, M.; Grady, C. A.; Min, M.; De Juan Ovelar, M.; Carson, J.; Brandt, T.; Bonnefoy, M.; McElwain, M. W.; Leisenring, J.; Dominik, C.; Henning, T.; Tamura, M. (2014). "The architecture of the Lk Ca 15 transitional disk revealed by high-contrast imaging". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 566: A51. arXiv:1402.1766. Bibcode:2014A&A...566A..51T. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201322915. S2CID 34485844.
- ↑ Alencar, S. H. P.; Bouvier, J.; Donati, J.-F.; Alecian, E.; Folsom, C. P.; Grankin, K.; Hussain, G. A. J.; Hill, C.; Cody, A.-M.; Carmona, A.; Dougados, C.; Gregory, S. G.; Herczeg, G.; Ménard, F.; Moutou, C.; Malo, L.; Takami, M.; collaboration, MaTYSSE (December 2018). "Inner disk structure of the classical T Tauri star LkCa 15". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 620: A195. arXiv:1811.04806. Bibcode:2018A&A...620A.195A. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201834263.
- 1 2 "Encyclopedia of Science: T Tauri star". Archived from the original on 27 January 2021. Retrieved 17 January 2017.
- ↑ Andrews, Sean M.; Williams, Jonathan P. (2005). "Circumstellar Dust Disks in Taurus-Auriga: The Submillimeter Perspective". The Astrophysical Journal. 631 (2): 1134–1160. arXiv:astro-ph/0506187. Bibcode:2005ApJ...631.1134A. doi:10.1086/432712. S2CID 17583379.
- 1 2 Kraus, Adam L.; Ireland, Michael J. (2012). "LkCa 15: A Young Exoplanet Caught at Formation?". The Astrophysical Journal. 745 (1): 5. arXiv:1110.3808. Bibcode:2012ApJ...745....5K. doi:10.1088/0004-637x/745/1/5. S2CID 73598684.
- 1 2 Sallum, S.; Follette, K. B.; Eisner, J. A.; Close, L. M.; Hinz, P.; Kratter, K.; Males, J.; Skemer, A.; MacIntosh, B.; Tuthill, P.; Bailey, V.; Defrère, D.; Morzinski, K.; Rodigas, T.; Spalding, E.; Vaz, A.; Weinberger, A. J. (2015). "Accreting protoplanets in the Lk Ca 15 transition disk". Nature. 527 (7578): 342–4. arXiv:1511.07456. Bibcode:2015Natur.527..342S. doi:10.1038/nature15761. PMID 26581290. S2CID 916170.
- ↑ Herbig, G. H.; Vrba, F. J.; Rydgren, A. E. (1986). "A spectroscopic survey of the Taurus-Auriga dark clouds for pre-main-sequence stars having CA II H, K emission". The Astronomical Journal. 91: 575. Bibcode:1986AJ.....91..575H. doi:10.1086/114039.
- ↑ Irene Klotz (18 November 2015). "Astronomers see planet still growing in its stellar womb". News Daily. Reuters. Archived from the original on 19 November 2015. Retrieved 20 November 2015.