 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
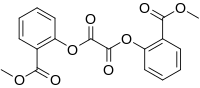
| Preferred IUPAC name
Bis[2-(methoxycarbonyl)phenyl] oxalate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H14O8 | |
| Molar mass | 358.302 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
MCPO is a chemical compound that can be used to produce chemiluminescence.[1] MCPO is mainly used for its chemiluminescent properties and is most commonly used in demonstrations of chemiluminescence as a safer alternative to TCPO. It is used as an alternative to TCPO due to its safer reaction product of methyl salicylate rather than the product of TCP, 2,4,6-trichlorophenol, a known carcinogen.
Synthesis
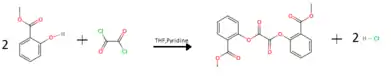
MCPO is synthesized by reacting methyl salicylate with oxalyl chloride in a solution of THF and pyridine:[1]
Pyridine reacts with HCl produced forming the THF insoluble pyridine hydrochloride salt. Water is then added to the solution to dissolve the precipitated pyridine HCl and decrease the solubility of the MCPO in solution, causing it to precipitate. The MCPO precipitate is then filtered and washed with water to remove contaminants.
See also
References
- 1 2 Cambrea, Lee R; Davis, Matthew C; Groshens, Thomas J; Meylemans, Heather A (2013). "A Soluble, Halogen-Free Oxalate from Methyl Salicylate for Chemiluminescence Demonstrations". Journal of Chemical Education. 90 (9): 1253. Bibcode:2013JChEd..90.1253C. doi:10.1021/ed300565u.