 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
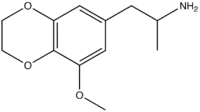
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-(8-Methoxy-2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-6-yl)propan-2-amine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H17NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 223.272 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
MEDA (3-methoxy-4,5-ethylenedioxyamphetamine) is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. MEDA was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, the minimum dosage is listed as 200 mg, and the duration unknown.[1] MEDA produces few to no effects. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of MEDA.
See also
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.