In anesthesia, the Mallampati score or Mallampati classification, named after the Indian anaesthesiologist Seshagiri Mallampati, is used to predict the ease of endotracheal intubation.[1] The test comprises a visual assessment of the distance from the tongue base to the roof of the mouth, and therefore the amount of space in which there is to work. It is an indirect way of assessing how difficult an intubation will be; this is more definitively scored using the Cormack–Lehane classification system, which describes what is actually seen using direct laryngoscopy during the intubation process itself. A high Mallampati score (class 3 or 4) is associated with more difficult intubation as well as a higher incidence of sleep apnea.[2]
Technique
The score is assessed by asking the patient, in a sitting posture, to open their mouth and to protrude the tongue as much as possible.[1] The anatomy of the oral cavity is visualized; specifically, the assessor notes whether the base of the uvula, faucial pillars (the arches in front of and behind the tonsils) and soft palate are visible. Scoring is generally done without phonation. Depending on whether the tongue is maximally protruded and/or the patient asked to phonate, the scoring may vary.
Modified Mallampati Scoring:[3]
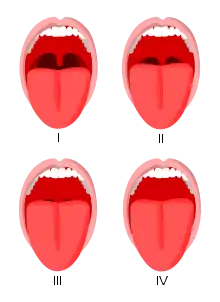
- Class I: Soft palate, uvula, fauces, pillars visible.
- Class II: Soft palate, major part of uvula, fauces visible.
- Class III: Soft palate, base of uvula visible.
- Class IV: Only hard palate visible.
Original Mallampati Scoring:[1]
- Class 1: Faucial pillars, soft palate and uvula could be visualized.
- Class 2: Faucial pillars and soft palate could be visualized, but uvula was masked by the base of the tongue.
- Class 3: Only soft palate visualized.
Further research may be needed to determine the most effective consistent and predictive approach on which to standardize Mallampati Scoring.
Clinical significance
While Mallampati classes I and II are associated with relatively easy intubation, classes III and IV are associated with increased difficulty.
A systematic review of 42 studies, with 34,513 participants, found that the modified Mallampati score is a good predictor of difficult direct laryngoscopy and intubation, but poor at predicting difficult bag mask ventilation.[4][5] Therefore, the study concluded that while useful in combination with other tests to predict the difficulty of an airway, it is not sufficiently accurate alone.
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Mallampati, SR; Gatt, SP; Gugino, LD; Desai, SP; Waraksa, B; Freiberger, D; Liu, PL (Jul 1985). "A clinical sign to predict difficult tracheal intubation: a prospective study". Canadian Anaesthetists' Society Journal. 32 (4): 429–34. doi:10.1007/BF03011357. PMID 4027773.
- ↑ Nuckton TJ, Glidden DV, Browner WS, Claman DM (Jul 1, 2006). "Physical examination: Mallampati score as an independent predictor of obstructive sleep apnea". Sleep. 29 (7): 903–8. doi:10.1093/sleep/29.7.903. PMID 16895257.
- ↑ Samsoon, GL; Young, JR (May 1987). "Difficult tracheal intubation: a retrospective study". Anaesthesia. 42 (5): 487–90. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2044.1987.tb04039.x. PMID 3592174.
- ↑ Lee, A; Fan, LT; Gin, T; Karmakar, MK; Ngan Kee, WD (Jun 2006). "A systematic review (meta-analysis) of the accuracy of the Mallampati tests to predict the difficult airway". Anesthesia and Analgesia. 102 (6): 1867–78. doi:10.1213/01.ane.0000217211.12232.55. PMID 16717341. S2CID 23652343.
- ↑ Roth, Dominik; Pace, Nathan L.; Lee, Anna; Hovhannisyan, Karen; Warenits, Alexandra-Maria; Arrich, Jasmin; Herkner, Harald (2018-05-15). "Airway physical examination tests for detection of difficult airway management in apparently normal adult patients". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 5 (5): CD008874. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008874.pub2. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 6404686. PMID 29761867.
External links
- Mallampati score - fpnotebook.com