 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
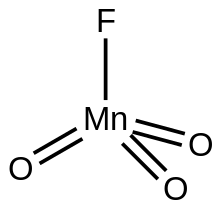
| FMnO3 | |
| Molar mass | 121.933 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | green liquid |
| Density | 6.042 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −45 °C (−49 °F; 228 K) |
| Boiling point | decomposition above its melting point |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Manganese trioxide fluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula MnO3F. A green diamagnetic liquid, the compound has no applications, but it is of some academic interest as a rare example of a metal trioxide fluoride.
The compound was detected in the 1880s but was only purified and crystallized much more recently.[1] It can be prepared by fluorosulfuric acid and potassium permanganate:
- KMnO4 + 2HF → MnO3F + KF + H2O
MnO3F crystallizes as a monomer, as confirmed by X-ray crystallography. The molecules are tetrahedral with Mn-O and Mn-F distances of 1.59 and 1.72 Å, respectively.
In contrast with MnO3F, TcO3F and ReO3F have more complex structures as solids. The Re compound crystallizes as chains or rings consisting of fluoride-bridge octahedra. TcO3F crystallizes as dimers with fluoride bridges.[2] The rhenium compound also forms stable adducts with Lewis bases,[3] whereas the MnO3F is unstable in the presence of Lewis bases.
References
- ↑ Schmidbaur, Hubert; Schwarz, W. H. Eugen (2021). "Permanganyl Fluoride: A Brief History of the Molecule MnO3F and of Those Who Cared for It". Chemistry – A European Journal. 27 (23): 6848–6859. doi:10.1002/chem.202004759. PMC 8247864. PMID 33219726.
- ↑ Supeł, Joanna; Abram, Ulrich; Hagenbach, Adelheid; Seppelt, Konrad (2007). "Technetium Fluoride Trioxide, TcO3F, Preparation and Properties". Inorganic Chemistry. 46 (14): 5591–5595. doi:10.1021/ic070333y. PMID 17547395.
- ↑ Supeł, Joanna; Marx, Rupert; Seppelt, Konrad (2005). "Preparation and Structure of Rhenium Fluoride Trioxide ReO3F, and the Polymorphism of Rhenium Trifluoride Dioxide, ReO2F3". Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie. 631 (15): 2979–2986. doi:10.1002/zaac.200500239.