The Maritimes Basin is a Mid-Devonian to Early Permian sedimentary basin that underlies parts of the northeastern United States and Atlantic Canada.[1] It is a composite basin, meaning that it consists of many sub-basins, such as the Windsor-Kennetcook Basin of Nova Scotia. Some of these basins host important natural resources, including coal, petroleum, and minerals such as sylvite, halite, and barite. The Maritimes Basin was deposited and tectonically-modified during the final assembly of Pangea.
List of sub-basins in Nova Scotia
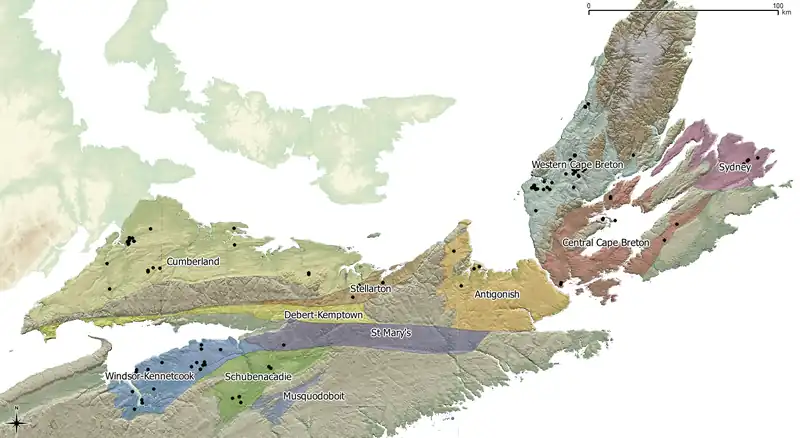
The Maritimes Basin consists of eleven sub-basins in Nova Scotia:
- Windsor-Kennetcook Basin
- Debert-Kemptown Basin
- Shubenacadie Basin
- Musquodoboit Basin
- Cumberland Basin
- Stellarton Basin
- St. Mary's Basin
- Antigonish Basin
- Western Cape Breton Basin
- Central Cape Breton Basin
- Sydney Basin
The region has a complex basin history in terms of syndepositional deformation and superimposition of numerous episodes of fault reactivation in the basin. As such, each basin has distinctive stratigraphy, especially within the lowermost Carboniferous section.
The eleven sub-basins are located in this clickable map:[2]
References
- ↑ Gibling, M.R.; Culshaw, N.; Rygel, M.C.; Pascucci, V. (2008), "Chapter 6: The Maritimes Basin of Atlantic Canada: Basin creation and destruction in the collisional zone of Pangea", in Miall, A.D. (ed.), Sedimentary Basins of the World, vol. 5, pp. 211–244, doi:10.1016/S1874-5997(08)00006-3
- ↑ Bianco, E. (2013). Seismic Interpretation of the Windsor-Kennetcook Basin. Geological survey of Canada Open File 7452. doi:10.4095/292763. Available online.