| Mediterranean grenadier | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Gadiformes |
| Family: | Macrouridae |
| Genus: | Coryphaenoides |
| Species: | C. mediterraneus |
| Binomial name | |
| Coryphaenoides mediterraneus (Giglioli, 1893) | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
| |
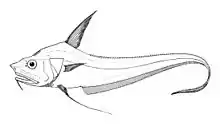
The Mediterranean grenadier (Coryphaenoides mediterraneus) is a species of deep-sea fish in the family Macrouridae.[3][4][5]
Description
The Mediterranean grenadier has a measurement of up to 73 cm (29 in).[6] The head is scaled except for its gular and branchiostegal membranes; it has a blunt snout.[7][8] Its brain shows increased volume in the octavolateral area (premotor organization of body movements) and gustatory area (taste); this is unsurprising as it lives in near-total darkness and is dependent on chemosensory inputs to find prey.[9]
Habitat
The Mediterranean grenadier lives in the North Atlantic Ocean, Mediterranean Sea and Gulf of Mexico; it is bathydemersal, living at depths of 1,000–4,262 m (3,281–13,983 ft).[6][10][11]
Behaviour
The Mediterranean grenadier feeds on small benthic invertebrates.[6] They exhibit a cycle of daily activity, because the solar cycle influences the movement of pelagic prey who move vertically during the day.[12] They are parasitised by many species of cestode worms.[13]
References
- ↑ Nedreaas, K.; Lorance, P.; Cook, R.; Fernandes, P.; Florin, A.-B.; Nielsen, J.; Iwamoto, T. (2015). "Coryphaenoides mediterraneus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T198595A60791796. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T198595A60791796.en. Retrieved 25 June 2023.
- ↑ "WoRMS - World Register of Marine Species - Coryphaenoides mediterraneus (Giglioli, 1893)". www.marinespecies.org.
- ↑ Ramos, Ana; Ramil, Fran; Sanz, José Luis (September 25, 2017). Deep-Sea Ecosystems Off Mauritania: Research of Marine Biodiversity and Habitats in the Northwest African Margin. Springer. ISBN 9789402410235 – via Google Books.
- ↑ Emde, Gerhard von der; Mogdans, Joachim; Kapoor, B. G. (December 6, 2012). The Senses of Fish: Adaptations for the Reception of Natural Stimuli. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 9789400710603 – via Google Books.
- ↑ Goffredo, Stefano; Dubinsky, Zvy (September 9, 2013). The Mediterranean Sea: Its history and present challenges. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 9789400767041 – via Google Books.
- 1 2 3 "Coryphaenoides mediterraneus, Mediterranean grenadier". fishbase.mnhn.fr.
- ↑ "Mediterranean grenadier - Coryphaenoides mediterraneus - (Giglioli, 1893)". eunis.eea.europa.eu.
- ↑ McEachran, John (October 28, 2010). Fishes of the Gulf of Mexico, Vol. 1: Myxiniformes to Gasterosteiformes. University of Texas Press. ISBN 9780292793231 – via Google Books.
- ↑ Reutter, Klaus (January 8, 2005). Fish Chemosenses. CRC Press. ISBN 9781482294392 – via Google Books.
- ↑ McIntyre, Alasdair (November 18, 2010). Life in the World's Oceans: Diversity, Distribution, and Abundance. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9781444396201 – via Google Books.
- ↑ "Coryphaenoides mediterraneus (Giglioli, 1893)". www.gbif.org.
- ↑ Bruslé, Jacques; Quignard, Jean-Pierre (March 31, 2020). Fish Behavior 1: Eco-ethology. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9781119721895 – via Google Books.
- ↑ Pandian, T. J. (January 28, 2020). Reproduction and Development in Platyhelminthes. CRC Press. ISBN 9781000054880 – via Google Books.
