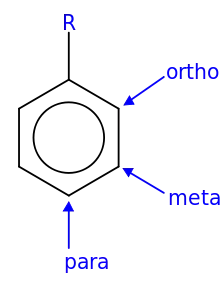
Positions on an aromatic ring relative to the R group
In chemistry, meta is a prefix, used for systematic names in IUPAC nomenclature. It has several meanings.[1]
- In organic chemistry, meta indicates the positions of substituents in aromatic cyclic compounds. The substituents have the 1,3-positions, for example in resorcinol.
- Meta may also denote the dehydrated form of an acid, salt or organic derivative in a series. For example:
- 2 bisulfite (HSO−3) → 1 metabisulfite (S2O2−5) + H2O
- 3 orthophosphoric acid (H3PO4) → 1 trimetaphosphoric acid (H3P3O9) + 3 H2O
- Meta-antimonic acid, the dehydrated form of antimonic acid (H3SbO4), is HSbO3.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ "Definition of meta-". www.dictionary.com. 2016-02-10. Retrieved 2019-10-03.
- ↑ Kern, Sergius (1875-02-19). Crookes, William (ed.). "New Method of Quantitative Analysis of Ordinary Alloys". Chemical News and Journal of Industrial Science. London: Chemical news office. XXXI (795): 76.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.