| Metamicrocotyla | |
|---|---|
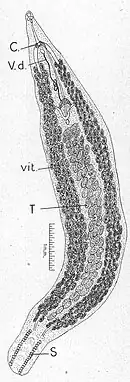 | |
| Metamicrocotyla cephalus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Platyhelminthes |
| Class: | Monogenea |
| Order: | Mazocraeidea |
| Family: | Microcotylidae |
| Subfamily: | Metamicrocotylinae |
| Genus: | Metamicrocotyla Yamaguti, 1953 |
Metamicrocotyla is a genus which belongs to the family Microcotylidae and class Monogenea. It was created by Yamaguti in 1953 to include Metamicrocotyla bora and Metamicrocotyla filiformis from the gills off the flathead grey mullet Mugil cephalus (Mugilidae).[1] As all Monogenea, species of Metamicrocotyla are ectoparasites that affect their host by attaching themselves as larvae on the gills of the fish and grow into adult stage. This larval stage is called oncomiracidium, and is characterized as free swimming and ciliated. Members of Metamicrocotyla are characterized by a symmetrical haptor, a variable number of postovarian testes and with no cirrus nor vagina. their genital atrium is provided with paired groups of spines or hooks.[1]
Species
According to the World Register of Marine Species,[2] this genus includes 10 species:
- Metamicrocotyla bora Yamaguti, 1953 [1]
- Metamicrocotyla cephalus (Azim, 1939) Hargis, 1954 [3]
- Metamicrocotyla chamelensis Bravo-Hollis, 1983
- Metamicrocotyla filiformis Yamaguti, 1953
- Metamicrocotyla gracilis Lee, 1984
- Metamicrocotyla inoblita Buhrnheim, 1970
- Metamicrocotyla macracantha (Alexander, 1954) Koratha, 1955
- Metamicrocotyla manaarensis Unnithan, 1971
- Metamicrocotyla mugilis Yamaguti, 1968
- Metamicrocotyla pacifica Bravo-Hollis, 1982
References
- 1 2 3 Yamaguti, S. (1953). Parasitic worms mainly from Celebes. Part 2. Monogenetic trematodes of fishes. Acta Medicinae Okayama, 8(3). PDF

- ↑ WoRMS (2019). Metamicrocotyla Yamaguti, 1953. Accessed at: http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=119380 on 2019-11-26
- ↑ Azim, Abdel (1939). "Note sur Microcotyle cephalus n. sp., ectoparasite des arcs branchiaux de Mugil cephalus". Annales de Parasitologie Humaine et Comparée. 17 (1): 17–20. doi:10.1051/parasite/1939-1940171017.
