 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Methylprop-2-enamide | |
| Other names
2-Methacrylamide; 2-Methyl-2-propenamide; 2-Methylacrylamide; 2-Methylpropenamide; α-Methyl acrylic amide; Methacrylic acid amide; Methacrylic amide; Methylacrylamide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.094 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H7NO | |
| Molar mass | 85.106 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White odorless crystals[1] |
| Density | 1.10-1.12 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | 106 to 109 °C (223 to 228 °F; 379 to 382 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 215 °C (419 °F; 488 K)[1] |
| 202 g/L (20 °C)[1] | |
| Hazards | |
| 510 °C (950 °F; 783 K)[1] | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
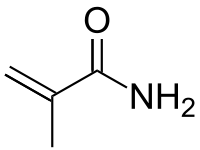
Methacrylamide is the organic compound with the formula CH2=C(CH3)C(O)NH2. A colorless or white solid, it is a monomer for the production of polymers and copolymers, some of which are used in hydrogels.[2] Methacrylamide is also a precursor of methyl methacrylate.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Record in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
- ↑ Kornev, Vladimir A.; Grebenik, Ekaterina A.; Solovieva, Anna B.; Dmitriev, Ruslan I.; Timashev, Peter S. (2018). "Hydrogel-assisted neuroregeneration approaches towards brain injury therapy: A state-of-the-art review". Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal. 16: 488–502. doi:10.1016/j.csbj.2018.10.011. PMC 6232648. PMID 30455858.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.