 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
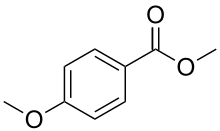
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methyl 4-methoxybenzoate | |
| Other names
p-Anisic acid methyl ester; 4-(Methoxycarbonyl)anisole; 4-Methoxybenzoic acid methyl ester; Methyl p-anisate; Methyl p-methoxybenzoate; p-Methoxybenzoic acid methyl ester | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.104 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H10O3 | |
| Molar mass | 166.176 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 48 to 51 °C (118 to 124 °F; 321 to 324 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 244 to 245 °C (471 to 473 °F; 517 to 518 K)[1] |
| -98.6·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Methyl anisate is the methyl ester of p-anisic acid. It is found in star anise.
It is an organic compound commonly used within the food industry. It is also commonly employed as a fragrance for certain perfumes. This compound can be synthesized directly through the mixture of methanol and methoxybenzoic acid. Its type of odor is characteristic to that of feijoa tree fruits, a flowery odour.
References
- 1 2 Methyl anisate, chemexper.com
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.