| |||
| Identifiers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.362 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID |
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| CH6Si | |||
| Molar mass | 46.14 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colorless gas[1] | ||
| Density | 0.628 g cm−3 | ||
| Melting point | −157 °C (−251 °F; 116 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −57 °C (−71 °F; 216 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
   | |||
| Danger | |||
| H220, H280, H312, H315, H319, H332, H335, H336 | |||
| P210, P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P312, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P322, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P363, P377, P381, P403, P403+P233, P405, P410+P403, P501 | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
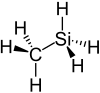
Methylsilane is the organosilicon compound with the formula CH3SiH3. It is a colorless gas that ignites in air. It can be prepared by reduction of methyltrichlorosilane with lithium aluminium hydride.[2] It has been investigated as a precursor to silicon carbide.[3]
Methylsilane has been the subject of extensive theoretical analysis.[4]
References
- ↑ MSDS from Matheson Tri-Gas
- ↑ Tannenbaum, Stanley; Kaye, Samuel; Lewenz, George F. (1953). "Synthesis and Properties of Some Alkylsilanes". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 75 (15): 3753–3757. doi:10.1021/ja01111a043.
- ↑ Hurwitz, F. I.; Kacik, T. A.; Bu, Xin-Ya; Masnovi, J.; Heimann, P. J.; Beyene, K. (1995). "Pyrolytic conversion of methyl- and vinylsilane polymers to Si-C ceramics". Journal of Materials Science. 30 (12): 3130–3136. doi:10.1007/BF01209227. S2CID 97973689.
- ↑ Nguyen, Kiet A.; Gordon, Mark S.; Raghavachari, Krishnan (1994). "Mechanisms and Energetics of the Reaction of Si+ with CH3-SiH3". The Journal of Physical Chemistry. 98 (27): 6704. doi:10.1021/j100078a010.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.