 A micro injection molded tiny part | |
| Process type | Injection molding process |
|---|---|
Micro injection molding is a molding process for the manufacture of plastics components for shot weights of 1 to 0.1 grams with tolerances in the range of 10 to 100 microns. This molding process permits the manufacture of complicated small geometries with maximum possible accuracy and precision.[1]
Basic concept
The basic concept of the micro injection molding process is quite similar to the regular injection molding process. In this process, a micro injection unit is integrated in the injection molding machine. When it comes to the production of micro components the machine and process technology mainly depend on the below points:
- Short dwell time
- Low shear stress on the polymer melt
- Homogeneous material preparation before molding
- Precision injection and ejection
- Accuracy of dimensions
Critical factors
Parting line issue
A parting line (PL) is the line of separation on the part where the two halves of the mold meet. The parting line matching for micro parts is a big issue. The interlocking features of mold cavity and core for precise mating are used to reduce such issues.
Degating issue
Another major critical factor of micro injection technology is that the smaller part size causes problems with degating (gate removal).
Sprue and runner size
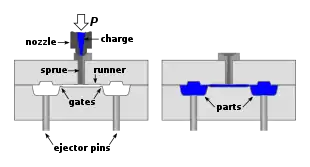
Runner and sprue diameters are another concern. The total volume of the feed system (sprue, runners and gates) can exceed the volume of the parts by a factor of 100 or more.
Materials and applications for micro injection molding
The most common polymers used in micro injection molding are reported in the table below:[2]
| Polymer family | Application |
|---|---|
| Polyoxymethylene (POM) | Micro gears and filters |
| Liquid-crystal polymer (LCP) | Connectors, ferrules and microelectronic
devices |
| Polyamide (PA or Nylon) | Micro gear wheels |
| Polysulfone (PSU) | Housing for microfluidic devices |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | Lens and sensors for optical applications
devices |
| Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) | Micro bearings & pistons |
| Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) | Optical fiber connector |
| Polyethylene (PE) | Child parts of micro actuators |
| Polylactic acid (PLA) | Biodegradable implants |
Machine used for micro injection molding
In the 1980s, micro injection molding techniques utilized traditional injection molding, but no dedicated machines were available until the mid-1990s. Currently, commercial micro molding systems are produced from Milacron, Arburg, and Sumitomo Demag as micro injection units for regular machines. At the same time, Wittmann Battenfeld, Babyplast and Desma are manufacturers of dedicated micro injection molding machines.[3]
Milacron developed two types of micro injection units:[2]
- A two-stage and all-electric injection unit accomplished by an extruder and injection plunger
- An all-electric injection unit with 14 mm screw to inject the polymer melt into the mold
Arburg developed a micro injection molding machine with an 8 mm injection to ensure high degree of dosing precision. This type of machine is combined with a second screw, which is responsible for melting and homogenous mixing of the material.[2]
Sumitomo Demag developed a customized micro molding injection unit suitable for micro parts weighing of 5 g to 0.1 g.[2]
Applications
Micro injection molding is widely applied for parts and devices in the medical, pharmaceutical, electronics, automotive, optical and other industries. In general, the medical micro injection molding market is the leading one, due to an increase in the usage of sophisticated micro components for endoscopic surgery, minimally invasive treatments, point-of-care testing and other advanced technology developments.[4] Applications in other fields include parts for electric motors, micron-tolerance door components, thing-wall containers, etc.

See also
References
- ↑ Sancho, Andreu; Arribas, Laura; Daniel, Teixidor (2017). "Micro-injection Moulding". Micro-Manufacturing Technologies and Their Applications. Springer Tracts in Mechanical Engineering (1st ed.). Springer, Cham. pp. 23–66. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-39651-4_2. ISBN 978-3-319-39651-4.
- 1 2 3 4 "The Micro Injection Moulding Process for Polymeric Components Manufacturing" (PDF). UL Prospector. Retrieved November 13, 2020.
- ↑ Piotter, V; Bauer, W; Benzler, T; Emde, A (2017). "Injection molding of components for microsystems". Microsystem Technologies (1st ed.). Springer. 7 (3): 99–102. doi:10.1007/s005420100094. S2CID 109715830.
- ↑ "Micro Injection Moulding Market: A phenomenal growth in the coming years". Micro Systems. Retrieved May 22, 2023.