Middletown Historic District | |
 From left to right on each row: Jacob Brookover House, Andrews House, Jacob Danner House, former Wayside Theatre, former Larrick's Tavern, Bailey House and former Middletown State Bank, Grace United Methodist Church, former Middletown School, St. Thomas Chapel | |
| Location | Bounded by Main Street, Church Street, Senseney Avenue, First Street, Sixth Street, Middletown, Virginia, United States |
|---|---|
| Area | 100 acres (40 ha) |
| Built | 1750–1950 |
| Architectural style | Greek Revival, Gothic Revival, et al. |
| NRHP reference No. | 03000566[1] |
| VLR No. | 034-5001 |
| Significant dates | |
| Added to NRHP | June 23, 2003 |
| Designated VLR | March 19, 2003[1] |
The Middletown Historic District is a national historic district located in Middletown, Virginia. It originally encompassed 234 contributing properties, the majority of which are residential buildings and their associated outbuildings. The boundaries of the historic district are approximately Church Street, Senseney Avenue, and First through Sixth Streets, except for a portion of Main Street that ends just south of Reliance Road (Route 627).
The non-residential historic structures include four specialty shops, a former theater, four churches, the Town Hall, two former schools, three warehouses and an inn. Notable buildings include the former Middletown Mission Church (c. 1818), Grace United Methodist Church (1897), the former Mt. Zion Church (1880), the former Middletown School (1909), the Town Hall (1880), the Wayside Inn (1797), Larrick's Tavern (1750), the former Wayside Theatre (1946), and Lafolette House (1800). Located in the district and separately listed on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) and Virginia Landmarks Register (VLR) is St. Thomas Chapel (1837).
The area that is present-day Middletown began developing in the mid-18th century due to the Great Wagon Road that brought settlers and commerce to the Shenandoah Valley. When the Virginia General Assembly formally established Middletown in 1796, there were already many residential and commercial buildings in the area. The town continued to develop thanks to the Valley Turnpike, present-day Main Street/U.S. Route 11, which connected the town to nearby Newtown (Stephens City) and Strasburg.
During the 19th century Middletown experienced continued residential and commercial growth until the Civil War. Many skirmishes took place in the area during Jackson's Valley campaign. The 1864 Battle of Cedar Creek, which began just south of the town limits before moving north through the town, resulted in many damaged properties. Commerce increased after a railroad track built in 1870 helped the town recover from the war's effects. Many of the town's historic houses were constructed in the late-19th century.
In the 20th century Route 11 was widened, utilities were installed, and the county's first high school opened in Middletown. Additional houses, warehouses, and commercial buildings, including a bank and movie theater, were constructed. A fire station built in the 1960s replaced historic houses, a trend that continued during the next few decades.
Due to the efforts of a local heritage group and with support from residents, a large portion of the town was listed as a historic district by the VLR and NRHP in 2003. Despite the historic designation, there have been several contributing properties demolished. Town officials are hoping to avoid further demolition by encouraging residents to maintain their property and by preventing the construction of buildings that do not fit in with the character of the historic district.
Geography
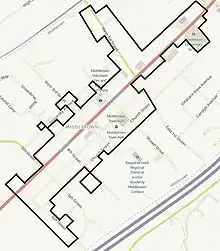
Middletown is located in southern Frederick County, Virginia, one of several counties in the Shenandoah Valley. The nearest towns are Stephens City, five miles (8 km) north, and Strasburg, five miles south. The town is bordered by Laurel Ridge Community College to the north, Interstate 81 to the east, and the Cedar Creek and Belle Grove National Historical Park to the south.[2]
The historic district encompasses approximately 100 acres (40.4 ha), including the town's original 60 acres (24.3 ha), and additional properties on Main Street, north of First Street (Route 627), stretching almost to Reliance Road. The historic district is centered around Main Street, the portion of U.S. Route 11 located in the town, which runs southwest to northeast. The other streets in the historic district running southwest to northeast are Church Street, which is south of Main Street, and Senseney Avenue, located north of Main Street. The streets running northwest to southeast are First through Sixth Streets. There are also alleys running parallel to the streets which are included in the historic district's boundaries.[2]
History
17th and 18th centuries
Present-day Middletown was part of the Fairfax Grant, a 17th-century land grant by King Charles II, encompassing a portion of colonial Virginia. The Van Meter brothers, who had acquired a 40,000-acre (16,187 ha) portion of this grant, later conveyed the land to German immigrant Jost Hite in 1731. During the next few decades, a 2,168-acre (877 ha) portion of this grant was conveyed to various men, ending with Dr. Peter Senseney, who acquired it in several transactions beginning in 1776. He moved to nearby Winchester and left the land for his children to maintain. Clockmaker Jacob Danner was tasked with surveying the area, then known as Senseney Town, and plotting 126 half-acre (0.2 ha) lots to establish a town. Middletown, possibly named because it was halfway between Newtown (later renamed Stephens City) and Strasburg, was established on May 4, 1796, by the Virginia General Assembly. It was chartered by the Frederick County government in 1796, becoming the third town established in the county.[2][3][4]
The town was centered around the Great Wagon Road, later renamed Valley Turnpike followed by U.S. Route 11. The portion passing through Middletown, present-day Main Street, was designed to be wider than standard streets to accommodate commercial traffic. Commercial buildings, including the Wayside Inn (7783 Main Street; originally known as Larrick's Hotel and Wilkinson's Tavern) and Larrick's Tavern (7793 Main Street), were built in the 18th century.[2][4] Houses built on Main Street during this time include the Jacob Danner House (7846 Main Street), Cirrani House (7896 Main Street), and Hoffman House (7827 Main Street). The Weaver-Jenkins House (7805 Church Street) and George Wright House (7845 Church Street) also date to the 18th century.[2]
19th century

Less than half of the lots were sold by 1804 when Senseney died. Many of these lots were conveyed to his widow and children. Danner continued assisting the town's development, serving as the community leader until his death in 1850. During his stewardship local churches were founded, businesses continued to open, two schools operated, all while the population slowly increased. A Methodist church for white residents was built at present-day 7893 Senseney Avenue in 1818 and later given to the town's African American residents, who renamed it the Colored People's Church. The latter congregation later moved to nearby 7913 Senseney Avenue which was named Mt. Zion Methodist Church.[2]
Most of the residences built in the early-19th century were log houses, including the Jacob Brookover House (7868 Main Street) and the houses at 7930 and 7952 Main Street. Many of these log houses were later covered with weatherboard, stucco, or brick, the latter beginning in the 1830s.[2] The turnpike was paved in 1834, bringing additional commerce through Middletown and further increasing the population.[2][4] St. Thomas Episcopal Church, which included members of the Hite family, was founded in 1834. The congregation built the Gothic Revival St. Thomas Chapel (7854 Church Street) in 1837.[2][5] The white Methodist congregation built a brick church in 1852 on the corner of Main and present-day Third Streets, which has since been demolished.[2]
During the Civil War, the Shenandoah Valley was the site of many battles. Soldiers traveled up and down the turnpike between Winchester and points south, with several bloody battles taking place in and around Middletown. Buildings in the town were often hit with artillery.[2][3][4] Confederate soldiers used St. Thomas Chapel as a hospital until Union soldiers arrived and kicked them out. They later used the church as a stable and burned most of the interior.[5] The last major battle to take place in the area, just south of the town limits, was the Battle of Cedar Creek. Fighting took place around the Belle Grove Plantation and Monte Vista before moving north through the town.[2][3][4] Middletown slowly recovered after the war, with commerce increasing after a railroad track was built around 1870 between Winchester and Strasburg.[2]
The town was incorporated in 1878. A town council was established and J. W. Rhodes served as the first mayor.[6] These new local officials redrew the town's plats, changed the address number system, and renamed streets, except for Main Street. Many of the surviving buildings in the historic district were built in the late-19th century, representing various architectural styles. Folk Victorian, Greek Revival, Colonial Revival, Queen Anne, and Italiante houses were built, along with additional vernacular buildings, which had been present since the town's beginnings.[2] A log cabin school that stood on Church Street from around 1800 was demolished in 1880 and replaced with the first Middletown Public School (7875 Church Street). During the last decade of the 19th century the Methodist church was replaced with an imposing Romanesque Revival building (7882 Main Street) and the town's first bank and only historic brick commercial building, Middletown State Bank (7843 Main Street), opened.[2][4][6]
20th century

Electricity and phone service arrived in Middletown in the early 20th century, and when Route 11 was widened, none of the properties fronting Main Street were demolished because buildings had been constructed further away from the road in anticipation of future development.[2][4] The town's first auto repair shop, Stubley's Garage (no address listed; between 7957 and 7969 Main Street) was built around this time.[2][6] A new Middletown School (7690 Main Street, formerly 7688) was built in 1909, becoming the county's first high school and one of the first agricultural high schools in Virginia. The schoolmaster lived in an American Foursquare house (7700 Main Street) that is located next door. African American children attended the segregated Senseney-Middletown Colored Elementary School (7883 Senseney Avenue). The former school on Church Street was deeded to the town. One of the requirements in the deed was that the Independent Order of Odd Fellows (IOOF) would be allowed to met on the second floor.[2]
Residential buildings constructed in the 1920s include an American Craftsman house (7895 Main Street), a bungalow (7935 Church Street), and the vernacular 2435 First Street, which later served as a nursing home. A warehouse (2325 First Street) that was later home to Route 11 Potato Chips was built around the same time. Among the buildings constructed in the 1930s and 1940s were a dance hall and eleven bungalows for employees of the American Viscose Corporation in nearby Front Royal. The dance hall and some of the bungalows were later demolished.[2]
There were several significant fires in Middletown in the early-20th century. Following a devastating fire that took place on Main Street in 1941, residents and town officials saw the need for a volunteer fire company. This did not occur until two years later due to events taking place during World War II. In 1946 the Bordon-Lee Theater (7853 Main Street), which played films, was built on the site of the former Shenandoah Normal School, which had been recently destroyed in a fire. Fifteen years later the property began housing a live theater company and was later renamed the Wayside Theatre.[2][6]
A water tower was built on Church Street in 1950 followed by the installation of natural gas mains in the late 1950s. A central sewer system and connections to Winchester's water supply lines were added in the 1960s. In 1962 the fire station was built with an expansion added 30 years later. The station replaced two historic houses, which were two of many that were demolished in the 20th century and replaced with commercial properties. The IOOF deeded its interest of the former school on Church Street to the town in 1965. The building now houses the Town Hall. The Middletown Police Department is located in a commercial building constructed in 1989.[2][6] A fire destroyed a large portion of the Wayside Inn in the 1980s, but it was later restored. The town's water tower was demolished in the 1990s.[6]

21st century
In 2002 a survey asked residents if they wanted to create a historic district to recognize and preserve the town's remaining historic structures. Ninety percent of residents voted in favor of creating the historic district. The preservation effort was spearheaded by the Middletown Heritage Society, formed in 1999.[2][7] Following thorough research of the town's structures and history, the Middletown Historic District was added to the Virginia Landmarks Register on March 19, 2003, and the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) on June 23, 2003.[1][7]
Despite the historic district designation, there have been 12 historic buildings and numerous outbuildings demolished since 2003. Despite some opposition, a Dollar General store replaced the Rinker House (7695 Main Street), also known as the Cooper House, and its four contributing properties: a meat house, chicken coop, garage, and tool shed.[2][8] The Evans House (7708 Main Street) was also demolished and replaced with two residential buildings.[2][9] The Wayside Theatre closed in 2013, ending 50 years of live performances.[10]
In the 2020s a proposed historic overlay district that would encompass 176 parcels in the town was met with opposition from some residents, who feared it would lead to property maintenance guidelines and reviews of any architectural changes to buildings.[11] Town officials aim to establish an ordinance to preserve the historic district's remaining contributing buildings. Avoiding further demolition of historic buildings and demolition by neglect are top priorities, in addition to encouraging proper upkeep of buildings and streetscapes, and preventing commercial or industrial buildings that do not fit in with the character of the historic district.[12]
Contributing properties
At the time the historic district was added to the NRHP and VLR there were 234 contributing properties, including houses, commercial buildings, churches, warehouses, and former schools, and 64 non-contributing properties. A large number of outbuildings are among the contributing properties, including barns, icehouses, chicken coops, and outhouses. Most of these are no longer used for their original purposes. Many of the houses feature large yards. Non-contributing properties include several houses, the fire station, one strip mall, two multi-family buildings, and four commercial buildings, including the police station. Most of these were built in the late-20th and early-21st centuries, or have been significantly altered.[2]
Non-residential

A large number of the historic district's contributing properties are located along Main Street. The most notable of these is the Wayside Inn (7783 Main Street), the oldest portion of which dates back to 1797 and features Colonial Revival details. The adjoining properties include Larrick's Tavern (7793 Main Street), built in the 1750s with Folk Victorian additions in the 19th century, and the vernacular former Wayside Inn office (7751 Main Street), built around 1870. Other imposing structures located along Main Street include the Romanesque Revival Grace United Methodist Church (7882 Main Street), built in 1897, the Colonial Revival former Middletown School (7690 Main Street), built in 1909, and the vernacular former Wayside Theatre (7853 Main Street), built in 1946 as the Bordon-Lee Theater.[2]
The only contributing property in the historic district individually listed on the NRHP is St. Thomas Chapel (7854 Church Street), a small Gothic Revival church built in 1837. The only other non-residential building on Church Street is the vernacular Town Hall (7875 Church Street), built in 1880 as a school and modified in the 1960s. Historic buildings on Senseney Avenue include the vernacular former Middletown Missionary Church (7893 Senseney Avenue; previously a Methodist church), built in 1818, the vernacular former Mt. Zion Methodist Church (7913 Senseney Avenue), built sometime between 1880 and 1900, and the vernacular former Senseney-Middletown Colored Elementary School (7883 Senseney Avenue), built in 1880. Other non-residential contributing buildings, all vernacular, include the former Middletown State Bank (7843 Main Street), former Miller Store (7805 Main Street), former Route 11 Potato Chips warehouse (2325 First Street), former Larrick's Store (2465 First Street), and a warehouse (2493 First Street).[2]
Residential
Main Street

The majority of contributing properties in the historic district are residential and many include contributing outbuildings. One of the oldest buildings on Main Street is the Jacob Danner House (7846 Main Street), also known as the Wiley-Crouse House, which was built as a log cabin in the late 18th century and later renovated with vernacular and Folk Victorian details. The oldest portion of the vernacular and Greek Revival Cirrani House (7896 Main Street) was built in 1779. The vernacular Hoffman House (7827 Main Street) was built around 1797. During the Civil War, a cannonball passed through one of the house's walls. The log cabin Jacob Brookover House (7868 Main Street) and the stucco-covered log cabin Munzing-Cave House (7969 Main Street) were built around 1800. The vernacular Jacob Rodes House (7828 Main Street), featuring Greek Revival details, was also built around 1800. A Folk Victorian style house at 7927 Main Street was built in the 1820s.[2]
Residences on Main Street built in the late-19th and early 20th centuries include the Folk Victorian James L. Willey House (8034 Main Street) and Will Willey House (8026 Main Street), American Foursquare former schoolmaster's house (7700 Main Street) and Campbell House (8049 Main Street), the Queen Anne 7772 Main Street, the vernacular Hite-Edmonson House (7841 Main Street) and former Gladys Lantzer Nursing Home (7913 Main Street), and 7701–7703 Main Street, one of the town's two historic duplexes. Several vernacular bungalows built in the 1930s and 1940s are located between First Street and Reliance Road.[2]
Church Street and Senseney Avenue
There are 25 historic houses on Church Street. A log cabin (7805 Church Street), historically known as the Weaver-Jenkins House or Caroline Jenkins Cabin, was built around 1790 and is the oldest building on the street. Other houses on Church Street that were originally log cabins include the Gordon-Sperry House (7948 Church Street), built sometime between 1820 and 1840, and the McDonald House (7945 Church Street), built in the mid-19th century. The vernacular George Wright House (7845 Church Street) was built in the 1790s. Early-19th century houses on Church Street that are made of brick or wood frame include the vernacular 7822 Church Street and Carper House (7813 Church Street). Houses built in the late-19th century include the vernacular 7825 Church Street, the Folk Victorian 7894 Church Street and Alfred Wiley House (7957 Church Street), and the Queen Anne Dr. G. W. Larrick House (7919 Church Street). The vernacular Andrews House (7967 Church Street), built in the 1890s, originally served as the parsonage for the nearby Methodist church.[2]

Ten historic houses are located on Senseney Avenue. The vernacular 7816 Senseney Avenue and 7826 Senseney Avenue are the oldest houses, both with log sections dating to around 1800. Another early-19th century house is the vernacular 7942 Senseney Avenue. The remaining houses are vernacular and were built between 1880 and 1920, except for the American Craftsman 7857 Senseney Avenue.[2]
First through Sixth Streets
There are 11 historic houses on First Street, the oldest being the vernacular Lafolette House (2458 First Street). The oldest portion is a log structure built around 1800. Other houses include the Folk Victorian Ridings House (2349 First Street) and 2371 First Street, the American Craftsman 2385 First Street, and three Colonial Revival houses: 2416 First Street, 2432 First Street, and 2434 First Street. The remaining houses are vernacular. There are two contributing houses on Fourth Street, 2190 Fourth Street and 2191 Fourth Street. Both are vernacular and were built in the late-19th century. There is one contributing house on Fifth Street. The vernacular house, 2310 Fifth Street, was built around 1852 and originally faced Main Street. It was moved to its current location around 1940. There are three contributing houses on Sixth Street. The Wright House (2239 Sixth Street), also known as Maplewood, was built in 1856 and is the town's only example of Italianate architecture. The other houses are the vernacular 2149 Sixth Street, built around 1900, and the Folk Victorian 2150 Sixth Street, built in the late-19th century.[2]
List of contributing buildings
| Rating[2] | Image | Address[2] | Year[2] | Style[2] | Comments[2] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contributing |  |
7800 Church Street 39°1′43.41″N 78°16′35.36″W / 39.0287250°N 78.2764889°W |
1900–1930 | American Craftsman | ||
| Contributing |  |
7805 Church Street 39°1′43.08″N 78°16′35.91″W / 39.0286333°N 78.2766417°W |
1804 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Caroline Jenkins Cabin or the Weaver-Jenkins House. It is believed to have been built in 1804 by the original owner, Ezer Ellis. | |
| Contributing |  |
7813 Church Street 39°1′42.5″N 78°16′36.46″W / 39.028472°N 78.2767944°W |
1820–1830 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Carper House. | |
| Contributing |  |
7822 Church Street 39°1′42.21″N 78°16′35.94″W / 39.0283917°N 78.2766500°W |
1830/1855 | Vernacular | Built in two sections, one around 1830 and the second around 1855. | |
| Contributing |  |
7825 Church Street 39°1′42.63″N 78°16′35.77″W / 39.0285083°N 78.2766028°W |
1880–1910 | Vernacular | ||
| Contributing |  |
7845 Church Street 39°1′40.81″N 78°16′38.9″W / 39.0280028°N 78.277472°W |
1790s | Vernacular | Historically known as the George Wright House. Built in the 1790s with an addition between 1820 and 1840. | |
| Individually listed |  |
7854 Church Street 39°1′40.02″N 78°16′40.31″W / 39.0277833°N 78.2778639°W |
1837 | Gothic Revival | St. Thomas Chapel, Middletown's Episcopal church for almost 100 years. Used as a hospital and stable during the Civil War. Listed on the National Register of Historic Places and Virginia Landmarks Register in 1973. | |
| Contributing |  |
7874 Church Street 39°1′42.5″N 78°16′36.46″W / 39.028472°N 78.2767944°W |
1870–1890 | Vernacular | ||
| Contributing |  |
7875 Church Street 39°1′38.64″N 78°16′41.57″W / 39.0274000°N 78.2782139°W |
1880 | Vernacular | Served as a school from 1880 to 1908. Deeded by the International Order of Odd Fellows to the town government in 1965. Renovated and serves as the Middletown Town Hall. | |
| Contributing |  |
7883 Church Street 39°1′37.78″N 78°16′42.86″W / 39.0271611°N 78.2785722°W |
1890–1910 | Folk Victorian | ||
| Contributing |  |
7884 Church Street 39°1′38.08″N 78°16′42.37″W / 39.0272444°N 78.2784361°W |
1880–1910 | Vernacular | ||
| Contributing |  |
7893 Church Street 39°1′36.39″N 78°16′44.62″W / 39.0267750°N 78.2790611°W |
1870–1900 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Margaret J. Rogers House. | |
| Contributing |  |
7894 Church Street 39°1′36.09″N 78°16′42.87″W / 39.0266917°N 78.2785750°W |
1870–1890 | Folk Victorian | ||
| Contributing |  |
7907 Church Street 39°1′35.86″N 78°16′45.39″W / 39.0266278°N 78.2792750°W |
1870–1900 | Vernacular | ||
| Contributing |  |
7916 Church Street 39°1′36.27″N 78°16′44.97″W / 39.0267417°N 78.2791583°W |
1870–1900 | Vernacular | Historically known as the R. C. Stickley House. Built as the parsonage for nearby St. Thomas Chapel. | |
| Contributing |  |
7919 Church Street 39°1′35.03″N 78°16′46.32″W / 39.0263972°N 78.2795333°W |
1882 | Queen Anne | Historically known as the Dr. G. W. Larrick House. Built in 1882, with later additions and modifications in 1900, 1968, and 1978. Some of the house's Gothic-style windows were originally in the now-demolished Methodist church built in 1853. | |
| Contributing |  |
7935 Church Street 39°1′33.4″N 78°16′48.57″W / 39.025944°N 78.2801583°W |
1920–1940 | Vernacular | ||
| Contributing |  |
7945 Church Street 39°1′32.99″N 78°16′48.98″W / 39.0258306°N 78.2802722°W |
Mid-19th century | Vernacular | Historically known as the McDonald House. Built in the mid-19th century with additions between 1910 and 1930. | |
| Contributing |  |
7948 Church Street 39°1′32.61″N 78°16′48.63″W / 39.0257250°N 78.2801750°W |
1820–1840 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Gordon-Sperry House. Built between 1820 and 1840 as a log cabin with later modifications in 1870. | |
| Contributing |  |
7957 Church Street 39°1′32.07″N 78°16′50.36″W / 39.0255750°N 78.2806556°W |
1895 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Alfred Wiley House. | |
| Contributing |  |
7967 Church Street 39°1′31.97″N 78°16′50.55″W / 39.0255472°N 78.2807083°W |
1890–1900 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Andrews House. Built between 1890 and 1900, with later additions in the 1970s, and originally served as the parsonage for the nearby Methodist church. | |
| Contributing |  |
7995 Church Street 39°1′29.44″N 78°16′53.65″W / 39.0248444°N 78.2815694°W |
1890–1910 | Vernacular | ||
| Contributing |  |
8007 Church Street 39°1′28.87″N 78°16′54.45″W / 39.0246861°N 78.2817917°W |
1880–1910 | Vernacular | ||
| Demolished | 8019 Church Street 39°1′28″N 78°16′55.9″W / 39.02444°N 78.282194°W |
1880–1910 | Vernacular | |||
| Contributing |  |
8022 Church Street 39°1′27.22″N 78°16′56.48″W / 39.0242278°N 78.2823556°W |
1890–1920 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Lock [Lauck] House or Dicks House. | |
| Contributing |  |
8030 Church Street 39°1′26.6″N 78°16′57.61″W / 39.024056°N 78.2826694°W |
1846 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Cooley House or the Achilles G. Willey House. | |
| Contributing |  |
8043 Church Street 39°1′26.68″N 78°16′57.31″W / 39.0240778°N 78.2825861°W |
1870–1910 | Queen Anne | Historically known as the Emma Andrews House. | |
| Contributing |  |
2325 First Street 39°1′48.3″N 78°16′38.9″W / 39.030083°N 78.277472°W |
1930s | Vernacular | Warehouse that later served as the first Route 11 Potato Chips factory. | |
| Contributing |  |
2349 First Street 39°1′51.47″N 78°16′42.01″W / 39.0309639°N 78.2783361°W |
1870–1890 | Folk Victorian | Historically known as the Ridings House. | |
| Contributing |  |
2371 First Street 39°1′52.46″N 78°16′42.39″W / 39.0312389°N 78.2784417°W |
1880–1910 | Folk Victorian | Built between 1880 and 1910 with modifications between 1910–1930 and 1940–1960. | |
| Contributing |  |
2376 First Street 39°1′52.16″N 78°16′41.93″W / 39.0311556°N 78.2783139°W |
1880–1910 | Vernacular | ||
| Contributing |  |
2385 First Street 39°1′53.08″N 78°16′43.05″W / 39.0314111°N 78.2786250°W |
1930s | American Craftsman | ||
| Demolished | 2408 First Street 39°1′53.3″N 78°16′43″W / 39.031472°N 78.27861°W |
1915–1930 | Vernacular | |||
| Contributing |  |
2416 First Street 39°1′53.75″N 78°16′43.82″W / 39.0315972°N 78.2788389°W |
1900–1920 | Colonial Revival | ||
| Contributing |  |
2432-2434 First Street 39°1′55.43″N 78°16′44.75″W / 39.0320639°N 78.2790972°W |
1910–1930 | Colonial Revival | One of two duplexes that are contributing properties to the historic district. | |
| Contributing |  |
2435 First Street 39°1′56.35″N 78°16′45.63″W / 39.0323194°N 78.2793417°W |
1920–1940 | Vernacular | ||
| Contributing |  |
2457 First Street 39°1′57.87″N 78°16′46.98″W / 39.0327417°N 78.2797167°W |
1890–1920 | Vernacular | ||
| Contributing |  |
2458 First Street 39°1′56.72″N 78°16′45.77″W / 39.0324222°N 78.2793806°W |
1800 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Lafolette House. | |
| Contributing |  |
2465 First Street 39°1′58.84″N 78°16′47.83″W / 39.0330111°N 78.2799528°W |
1880–1910 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Klines Store, Carpers Store, or Larricks Store. | |
| Contributing |  |
2470 First Street 39°1′56.77″N 78°16′45.8″W / 39.0324361°N 78.279389°W |
1890–1920 | Vernacular | ||
| Demolished | 2493 First Street 39°2′00.5″N 78°16′48″W / 39.033472°N 78.28000°W |
1900–1930 | Vernacular | |||
| Contributing |  |
2190 Fourth Street 39°1′31.67″N 78°16′48.46″W / 39.0254639°N 78.2801278°W |
1870–1900 | Vernacular | Built between 1870 and 1900 with modifications in the 1970s. | |
| Contributing |  |
2191 Fourth Street 39°1′30.51″N 78°16′46.27″W / 39.0251417°N 78.2795194°W |
1890–1910 | Vernacular | ||
| Contributing |  |
2310 Fifth Street 39°1′32.63″N 78°17′00.55″W / 39.0257306°N 78.2834861°W |
1852 | Vernacular | Built around 1852 with modifications between 1920 and 1950. The house originally faced Main Street but was moved around 1940. | |
| Contributing |  |
2149 Sixth Street 39°1′21.39″N 78°16′52.34″W / 39.0226083°N 78.2812056°W |
1890–1910 | Vernacular | Built as a tenant house of nearby Maplewood. | |
| Contributing |  |
2150 Sixth Street 39°1′22.08″N 78°16′53.21″W / 39.0228000°N 78.2814472°W |
1870–1900 | Folk Victorian | ||
| Contributing |  |
2239 Sixth Street 38°54′03.89″N 77°01′06.08″W / 38.9010806°N 77.0183556°W |
1856 | Italianate | Historically known as Maplewood or the Wright House. Middletown's only example of Italianate architecture. | |
| Contributing |  |
7816 Senseney Avenue 39°1′50.19″N 78°16′43.74″W / 39.0306083°N 78.2788167°W |
1800–1820 | Vernacular | ||
| Contributing |  |
7826 Senseney Avenue 39°1′49.51″N 78°16′44.73″W / 39.0304194°N 78.2790917°W |
1800–1830 | Vernacular | Built between 1800 and 1830 with a second portion added between 1870 and 1910. | |
| Contributing |  |
7836 Senseney Avenue 39°1′49.15″N 78°16′45.17″W / 39.0303194°N 78.2792139°W |
1910–1940 | Vernacular | ||
| Contributing |  |
7844 Senseney Avenue 39°1′47.87″N 78°16′46.76″W / 39.0299639°N 78.2796556°W |
1892 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Ralph Carper House. | |
| Contributing |  |
7848 Senseney Avenue 39°1′47.68″N 78°16′47.09″W / 39.0299111°N 78.2797472°W |
1890–1920 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Lewis A. Gossard House. | |
| Contributing |  |
7857 Senseney Avenue 39°1′47.42″N 78°16′47.72″W / 39.0298389°N 78.2799222°W |
1900–1930 | American Craftsman | ||
| Contributing |  |
7883 Senseney Avenue 39°1′44.14″N 78°16′51.65″W / 39.0289278°N 78.2810139°W |
1880 | Vernacular | Served as the Senseney-Middletown Colored Elementary School from 1939 to 1960 and was later converted into a residence. | |
| Contributing |  |
7890 Senseney Avenue 39°1′43.7″N 78°16′52.36″W / 39.028806°N 78.2812111°W |
1890–1920 | Vernacular | ||
| Contributing |  |
7893 Senseney Avenue 39°1′43.41″N 78°16′52.55″W / 39.0287250°N 78.2812639°W |
1818 | Vernacular | The former Middletown Missionary Church. | |
| Contributing |  |
7913 Senseney Avenue 39°1′42.79″N 78°16′53.57″W / 39.0285528°N 78.2815472°W |
1880 | Vernacular | The former Mt. Zion Methodist Church that was converted into a residence in 1992. | |
| Contributing |  |
7942 Senseney Avenue 39°1′40.21″N 78°16′56.7″W / 39.0278361°N 78.282417°W |
1810–1850 | Vernacular | ||
| Contributing |  |
7948 Senseney Avenue 39°1′40″N 78°16′57″W / 39.02778°N 78.28250°W |
1880–1910 | Vernacular | ||
| Contributing |  |
7965 Senseney Avenue 39°1′38.23″N 78°16′59.15″W / 39.0272861°N 78.2830972°W |
1880–1910 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Mitchell House. | |
| Contributing |  |
7616 Main Street 39°1′59.04″N 78°16′22.62″W / 39.0330667°N 78.2729500°W |
1941 | Bungalow | One of eleven bungalows built for American Viscose Corporation employees. | |
| Contributing |  |
7624 Main Street 39°1′58.38″N 78°16′23.25″W / 39.0328833°N 78.2731250°W |
1941 | Bungalow | One of eleven bungalows built for American Viscose Corporation employees. | |
| Demolished | 7625 Main Street 39°1′59.9″N 78°16′23.2″W / 39.033306°N 78.273111°W |
1935–1950 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Dellinger House. | ||
| Demolished | 7632 Main Street 39°1′58.2″N 78°16′22.8″W / 39.032833°N 78.273000°W |
1941 | Bungalow | One of eleven bungalows built for American Viscose Corporation employees. | ||
| Demolished | 7640 Main Street 39°1′57.6″N 78°16′23.1″W / 39.032667°N 78.273083°W |
1941 | Bungalow | One of eleven bungalows built for American Viscose Corporation employees. | ||
| Demolished | 7648 Main Street 39°1′57.3″N 78°16′23.6″W / 39.032583°N 78.273222°W |
1941 | Bungalow | One of eleven bungalows built for American Viscose Corporation employees. | ||
| Demolished | 7656 Main Street 39°1′56.6″N 78°16′23.3″W / 39.032389°N 78.273139°W |
1941 | Bungalow | One of eleven bungalows built for American Viscose Corporation employees. | ||
| Demolished | 7664 Main Street 39°1′56.5″N 78°16′24.4″W / 39.032361°N 78.273444°W |
1941 | Bungalow | One of eleven bungalows built for American Viscose Corporation employees. | ||
| Contributing |  |
7665 Main Street 39°1′58.34″N 78°16′23.33″W / 39.0328722°N 78.2731472°W |
1910–1930 | American Craftsman | ||
| Contributing |  |
7690 Main Street 39°1′52.91″N 78°16′24.29″W / 39.0313639°N 78.2734139°W |
1909 | Colonial Revival | Middletown School from 1909 to 1984. Now serves as a private residence. | |
| Demolished | 7695 Main Street 39°1′56.6″N 78°16′27.6″W / 39.032389°N 78.274333°W |
1890–1920 | Colonial Revival | Historically known as the Rinker House or Cooper House. | ||
| Contributing |  |
7700 Main Street 39°1′54.19″N 78°16′28.85″W / 39.0317194°N 78.2746806°W |
1891 | American Foursquare | Previously served as the Schoolmaster's House for the neighboring Middletown School. | |
| Contributing |  |
7701-7703 Main Street 39°1′54.33″N 78°16′28.66″W / 39.0317583°N 78.2746278°W |
1880–1910 | Vernacular | Perved served as a feed store and a restaurant. One of two duplexes that are contributing properties to the historic district. | |
| Contributing |  |
7705 Main Street 39°1′53.87″N 78°16′29.37″W / 39.0316306°N 78.2748250°W |
1930–1950 | Bungalow | One of eleven bungalows built for American Viscose Corporation employees. | |
| Demolished |  |
7708 Main Street 39°1′52.86″N 78°16′29.1″W / 39.0313500°N 78.274750°W |
1890–1910 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Evans House. | |
| Contributing |  |
7709 Main Street 39°1′53.91″N 78°16′29.35″W / 39.0316417°N 78.2748194°W |
1930 | Bungalow | One of eleven bungalows built for American Viscose Corporation employees. | |
| Contributing |  |
7713 Main Street Middletown 39°1′53.57″N 78°16′29.9″W / 39.0315472°N 78.274972°W |
1930 | Bungalow | One of eleven bungalows built for American Viscose Corporation employees. | |
| Contributing |  |
7723 Main Street 39°1′52.42″N 78°01′31.1″W / 39.0312278°N 78.025306°W |
1940 | Vernacular | ||
| Contributing |  |
7729 Main Street 39°1′51.98″N 78°16′31.76″W / 39.0311056°N 78.2754889°W |
1940 | Bungalow | One of eleven bungalows built for American Viscose Corporation employees. | |
| Contributing |  |
7745 Main Street 39°1′51.47″N 78°16′32.56″W / 39.0309639°N 78.2757111°W |
Mid-19th century | Folk Victorian | Built in the mid-19th century with modifications in the early 20th century. | |
| Contributing |  |
7751 Main Street 39°1′50.3″N 78°16′34.4″W / 39.030639°N 78.276222°W |
1870–1910 | Vernacular | Previously served as office space for the Wayside Inn. | |
| Contributing |  |
7752 Main Street 39°1′50.55″N 78°16′33.91″W / 39.0307083°N 78.2760861°W |
1880–1910 | Vernacular | ||
| Contributing |  |
7760 Main Street 39°1′49.88″N 78°16′34.95″W / 39.0305222°N 78.2763750°W |
1870–1900 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Everly House. | |
| Contributing |  |
7772 Main Street 39°1′48.29″N 78°16′34.86″W / 39.0300806°N 78.2763500°W |
1880–1910 | Queen Anne | ||
| Contributing |  |
7780 Main Street 39°1′48.01″N 78°16′37.04″W / 39.0300028°N 78.2769556°W |
1931 | Colonial Revival | ||
| Contributing |  |
7783 Main Street 39°1′48.82″N 78°16′36.6″W / 39.0302278°N 78.276833°W |
1797 | Vernacular | Wayside Inn. Oldest portion of the building dates to 1797. Later additions and renovations in the 19th and 20th centuries. | |
| Contributing |  |
7793 Main Street 39°1′48.95″N 78°16′39.03″W / 39.0302639°N 78.2775083°W |
1750–1760 | Vernacular | The former Larrick's Tavern. Oldest portion of the building dates to 1750–1760 with later modifications between 1780–1810 and 1870–1900. | |
| Contributing |  |
7805 Main Street 39°1′45.94″N 78°16′39.18″W / 39.0294278°N 78.2775500°W |
1890 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Catlett-Owings-Long House or the Miller Store. | |
| Contributing |  |
7820 Main Street 39°1′50.3″N 78°16′40.2″W / 39.030639°N 78.277833°W |
1911–1915 | Vernacular | ||
| Contributing |  |
7827 Main Street 39°1′45.51″N 78°16′40.52″W / 39.0293083°N 78.2779222°W |
1797 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Hoffman House. Believed to be built in 1797 by its first owner, Isaac Klotz, with later modifications between 1820 and 1840. | |
| Contributing |  |
7828 Main Street 39°1′44.37″N 78°16′41.41″W / 39.0289917°N 78.2781694°W |
1800 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Jacob Rodes House. Built around 1800 with later modifications between 1830–1850 and the early 20th century. | |
| Contributing |  |
7837 Main Street 39°1′45.08″N 78°16′41.54″W / 39.0291889°N 78.2782056°W |
1890 | Colonial Revival | Historically known as the Yates House or the Sherwood House. | |
| Contributing |  |
7840 Main Street 39°1′44.29″N 78°16′42.67″W / 39.0289694°N 78.2785194°W |
1891 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Danner House or the Bugarski House. Built in 1891 with modifications in the 20th century. | |
| Contributing |  |
7841 Main Street 39°1′44.83″N 78°16′42.42″W / 39.0291194°N 78.2784500°W |
1880–1910 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Hite-Edmonson House or the Bailey House. | |
| Contributing |  |
7843 Main Street 39°1′45.46″N 78°16′43.73″W / 39.0292944°N 78.2788139°W |
1890 | Vernacular | Middletown State Bank until 1967, when it merged with F&M (Farmers and Merchants) National Bank, later closing in 1985. | |
| Contributing |  |
7846 Main Street 39°1′43.68″N 78°16′42.34″W / 39.0288000°N 78.2784278°W |
1780–1800 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Jacob Danner House or the Wiley-Crouse House. | |
| Contributing |  |
7849 Main Street 39°1′43.83″N 78°16′43.52″W / 39.0288417°N 78.2787556°W |
1880–1910 | Vernacular | The building is composed of two structures that were combined: the former Rhodes Store and House, which later served as the post office, and the Goode House. | |
| Contributing |  |
7853 Main Street 39°1′42.89″N 78°16′44.23″W / 39.0285806°N 78.2789528°W |
1946 | Vernacular | The former Wayside Theatre. Built as a movie theater called the Bordon-Lee Theater or Middletown Movie Theater. | |
| Contributing |  |
7864 Main Street 39°1′42.24″N 78°16′44.92″W / 39.0284000°N 78.2791444°W |
1870–1900 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Edmonson House or the Mercer House. | |
| Contributing |  |
7868 Main Street 39°1′42.38″N 78°16′45.52″W / 39.0284389°N 78.2793111°W |
1800 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Jacob Brookover House or the Snyder House. Built around 1800 with additions and modifications between 1820–1840 and in 1970. | |
| Contributing |  |
7875 Main Street 39°1′42.01″N 78°16′45.58″W / 39.0283361°N 78.2793278°W |
1870 | Vernacular | ||
| Contributing |  |
7876 Main Street 39°1′42.01″N 78°16′46.07″W / 39.0283361°N 78.2794639°W |
1880–1910 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Ludwig House or the Furr House. | |
| Demolished | 7881 Main Street 39°1′41.8″N 78°16′46.8″W / 39.028278°N 78.279667°W |
1900–1920 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Mowery House. | ||
| Contributing |  |
7882 Main Street 39°1′40.88″N 78°16′47.23″W / 39.0280222°N 78.2797861°W |
1897 | Romanesque Revival | Grace United Methodist Church | |
| Contributing |  |
7889 Main Street 39°1′40.43″N 78°16′47.67″W / 39.0278972°N 78.2799083°W |
1890–1910 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Dellinger-Shull House or the Woods-Berent House. | |
| Contributing |  |
7895 Main Street 39°1′40.21″N 78°16′47.97″W / 39.0278361°N 78.2799917°W |
1920 | American Craftsman | Historically known as the Dellinger-Ambrose House or the Hartley House. | |
| Contributing |  |
7896 Main Street 39°1′39.07″N 78°16′46.42″W / 39.0275194°N 78.2795611°W |
1779 | Greek Revival | Historically known as the Cirrani House. Built in 1779 with additions between 1820 and 1850. | |
| Contributing |  |
7907 Main Street 39°1′39.32″N 78°16′49.18″W / 39.0275889°N 78.2803278°W |
1870–1900 | Vernacular | ||
| Contributing |  |
7913 Main Street 39°1′40″N 78°16′50.92″W / 39.02778°N 78.2808111°W |
1910 | Vernacular | Formerly known as the Gladys Lantzer Nursing Home. | |
| Contributing |  |
7924 Main Street 39°1′38.37″N 78°16′50.33″W / 39.0273250°N 78.2806472°W |
1790–1810 | Vernacular | Built between 1790 and 1810 with modifications in the mid and late-19th century. | |
| Contributing |  |
7927 Main Street 39°1′39.35″N 78°16′51.78″W / 39.0275972°N 78.2810500°W |
1820–1830 | Folk Victorian | Built between 1820 and 1830 with modifications between 1880 and 1910. | |
| Contributing |  |
7930 Main Street 39°1′38.01″N 78°16′50.69″W / 39.0272250°N 78.2807472°W |
1810–1830 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Huddle House. | |
| Contributing |  |
7939 Main Street 39°1′37.37″N 78°16′51.62″W / 39.0270472°N 78.2810056°W |
1830–1850 | Vernacular | Built between 1830 and 1850 with modifications between 1910 and 1930. | |
| Contributing |  |
7948 Main Street 39°1′36.1″N 78°16′52.94″W / 39.026694°N 78.2813722°W |
1890–1920 | Vernacular | ||
| Contributing |  |
7952 Main Street 39°1′36.09″N 78°16′53.02″W / 39.0266917°N 78.2813944°W |
1810–1830 | Vernacular | Built between 1810 and 1830 with modifications between 1890–1910 and 1960–1980. | |
| Contributing |  |
7957 Main Street 39°1′36.24″N 78°16′53.54″W / 39.0267333°N 78.2815389°W |
1810–1840 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Evans-Hodson House. Built between 1810 and 1840 with modifications between 1880 and 1920. | |
| Contributing |  |
No address listed 39°1′35.9″N 78°16′54.26″W / 39.026639°N 78.2817389°W |
1910–1930 | Vernacular | Historically known as Stubley's Garage. | |
| Contributing |  |
7960 Main Street 39°1′35.43″N 78°16′54.09″W / 39.0265083°N 78.2816917°W |
1900–1930 | Colonial Revival | ||
| Contributing |  |
7969 Main Street 39°1′35.72″N 78°16′54.94″W / 39.0265889°N 78.2819278°W |
1800 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Munzing-Cave House. Built around 1800 with modifications between 1820 and 1840. | |
| Contributing |  |
7979 Main Street 39°1′34.72″N 78°16′56.1″W / 39.0263111°N 78.282250°W |
1800–1810 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Jacob Willey House. Built between 1800 and 1810 with modifications between 1830–1850 and 1870–1900. | |
| Contributing |  |
7985 Main Street 39°1′34.41″N 78°16′56.7″W / 39.0262250°N 78.282417°W |
Mid-19th century | Vernacular | ||
| Contributing |  |
7994 Main Street 39°1′32.92″N 78°16′57.03″W / 39.0258111°N 78.2825083°W |
1890–1920 | Vernacular | ||
| Contributing |  |
8004 Main Street 39°1′31.91″N 78°16′58.82″W / 39.0255306°N 78.2830056°W |
1800–1810 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Jacob Willey House. Built between 1800 and 1810 with additions and modifications between 1830–1850 and 1870–1900. | |
| Contributing |  |
8026 Main Street 39°1′29.93″N 78°16′59.27″W / 39.0249806°N 78.2831306°W |
1870–1900 | Folk Victorian | Historically known as the Will Willey House or the Coverstone-Robertson House. | |
| Contributing |  |
8034 Main Street 39°1′29.25″N 78°17′00.16″W / 39.0247917°N 78.2833778°W |
1880–1910 | Folk Victorian | Historically known as the James L. Willey House. | |
| Contributing |  |
8043 Main Street 39°1′30.23″N 78°17′2.28″W / 39.0250639°N 78.2839667°W |
1830–1850 | Vernacular | Historically known as the Isaac Rhodes House or the Dalby House. | |
| Contributing |  |
8046 Main Street 39°1′29.58″N 78°17′1.89″W / 39.0248833°N 78.2838583°W |
1910–1930 | Colonial Revival/American Craftsman | ||
| Contributing |  |
8049 Main Street 39°1′28.89″N 78°17′6.38″W / 39.0246917°N 78.2851056°W |
1900–1920 | American Foursquare | Historically known as the Campbell House. | |
Notes
- 1.^ 7625, 7632, 7640, 7648, 7656, 7664, 7695, 7708 and 7881 Main Street; 8019 Church Street; 2408 and 2493 First Street
References
- 1 2 3 "Virginia Landmarks Register". Virginia Department of Historic Resources. Archived from the original on January 31, 2023. Retrieved May 9, 2023.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 Tess Klimm; Helen Lee Fletcher & Guy M. Jones (November 2002). "National Register of Historic Places Inventory/Nomination: Middletown Historic District" (PDF). Virginia Department of Historic Resources. Archived (PDF) from the original on April 28, 2023. Retrieved May 7, 2023.
- 1 2 3 "History". Town of Middletown. Archived from the original on February 6, 2023. Retrieved May 9, 2023.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Harbaugh IV, Charles; Pennington, Jeff (2015). Middletown. Arcadia Publishing Incorporated. pp. 7–10. ISBN 9781439649268.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - 1 2 Virginia Historic Landmarks Commission (January 1973). "National Register of Historic Places Inventory-Nomination Form" (PDF). Virginia Department of Historic Resources. Archived (PDF) from the original on April 28, 2023. Retrieved May 9, 2023.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Kalbian, Maral S. "Rural Landmarks Survey Report Frederick County, Virginia: Phases I-III 1988–1992" (PDF). Virginia Department of Historic Resources. pp. 227–235. Archived (PDF) from the original on September 11, 2022. Retrieved May 9, 2023.
- 1 2 "Middletown Heritage Society Collection". Handley Regional Library System. Archived from the original on September 23, 2020. Retrieved May 9, 2023.
- ↑ Williams, J.R. (April 10, 2011). "Middletown Approves Dollar General Plan". The Northern Virginia Daily. Retrieved May 9, 2023.
- ↑ "Frederick County Tax Map". Frederick County Real Estate Division. Archived from the original on December 6, 2022. Retrieved May 9, 2023.
- ↑ Keelor, Josette (June 4, 2021). "Wayside Theatre gets another act: Actor creates website to tell theater's history". The Northern Virginia Daily. Retrieved May 9, 2023.
- ↑ Janney, Josh (July 9, 2021). "Middletown Revisits Historic Overlay District". The Northern Virginia Daily. Archived from the original on October 21, 2021. Retrieved May 9, 2023.
- ↑ "Comprehensive Plan 2038" (PDF). Town of Middletown. Retrieved May 9, 2023.
External links
 Media related to Middletown Historic District at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Middletown Historic District at Wikimedia Commons