Miguel Peña Parish | |
|---|---|
.svg.png.webp) | |
| Coordinates: 10°08′56″N 68°00′08″W / 10.1489°N 68.0023°W | |
| Time zone | UTC−4 (VET) |
Miguel Peña is by far the largest civil parish in the municipality of Valencia, Carabobo, and one of the most populous in Venezuela. It is located in the Southern part of the city and it has most of Valencia's poorest slums. It has a surface of some 200 km² for a density of some 2500 inhabitants per km².[1]

General
The area was named after Miguel Peña (1781–1833),[2] a well-known politician from Valencia who was active in the formation of Venezuela in the early part of the 19th century.
The parish has undergone a dramatic population growth in the last 40 years from internal immigration, particularly poor farmers coming from the South and from Caracas and immigration from other Latin American countries. Most people have come attracted by job opportunities linked to Valencia's industrial development.
It is one of the most dangerous regions in Carabobo.[3]
Demographic growth
The following table shows part of the population growth of the last few years.
| Year | Population |
|---|---|
| 1990 | 233.829 |
| 1991 | 246.057 |
| 1992 | 258.300 |
| 1993 | 270.525 |
| 1994 | 282.818 |
| 1995 | 295.189 |
| 1996 | 307.665 |
| 1997 | 320.297 |
| 1998 | 333.152 |
| 1999 | 346.265 |
| 2000 | 359.582 |
| 2005 | 428.831 |
History
Around 1936 there was already a small settlement known as Cruz de Legua where now the Lomas de Funval urbanization is located. Still in the forties the area was used for farming. There were mainly large haciendas and some scattered houses where poor farmers lived.
Some urbanizations started to be built in the fifties and forties on the Northern part when Valencia started to become an industrial city. The main areas were Urbanización Mendoza, Urbanización El Palotal, Urbanización Ricardo Urriera and Urbanización Lomas de Funval. Some bridges were rebuilt giving access to Santa Rosa, El Boquete and Las Dos Bocas (currently the El Ahorcado bridge). There was almost no planning in the process.
The civil parish Miguel Peña was officially created by state law on 4 August 1971. Some avenues were built in the seventies, like the Aranzazu, the Sesquicentenaria, the Lisandro Alvarado and the Enrique Tejera avenues. Also a new road toward the South, to El Paíto, was made.
The chaotic urban expansion speeded up in the eighties and nineties, leading to a collapse of services and increased criminality. [5]
Administration and politics
Miguel Peña is a civil parish and as such has little administrative independence. It belongs to the Municipality of Valencia. The governing body is a junta parroquial with relatively little powers. There have been long discussions about making it an independent municipality, but this has not come to effect. ,[6][7]
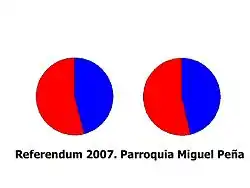
The area tends to vote for the Chávez system more than others in the region. In the referendum for the constitutional reform of 2 December 2007, 53.95% of the voters there supported the reform against 40.78 for the whole municipality of Valencia.[8]
Divisions
The region has grown without much planning. Some of the main areas are:
- The Fundación Mendoza (Mendoza Foundation): This urbanization was financed by the Mendoza entrepreneur and was destined mainly for his workers.
- El Palotal urbanization: This is an urbanization built by the Banco Obrero (Worker's Bank) for the working class. Houses were assigned during Rómulo Betancourt's government mostly to people who had opposed the Marcos Pérez Jiménez dictatorship.
- La Antena
- Las Flores
- La Unidad
- Ruiz Pineda
- Santa Inés
- Barrio (Slum) La Victoria
There are many other sectors that tend to be more precarious. Many of these areas lack services like electricity or proper water canalization.[9]
Some of the main avenues are:
- Avenida Las Ferias
- Avenida Lisandro Alvarado,
- Avenida Aranzazu
- Avenida la Romana
- Avenida Sesquicentenario
- Vía el Paito, which was built on the ancient Spanish road towards the town of Tocuyito and further to the Southwest.
Attractions
- Parque Recreacional del Sur

- Plaza de toros Monumental de Valencia, part of the Parque Recreacional del Sur
Culture and education
There is a smaller public library, Miguel Colombet, at Calle Sucre cruce con Branger.
There are two main secondary schools: Liceo Zuloaga and Liceo Ponce Bello. There are also dozens of basic schools.
Transportation
The area is mostly served by buses from different bus companies.
Metro stations
Valencia's underground line starts in this parish. The community has two underground stations:
- Estación La Monumental
- Estación Las Ferias.
Health
In spite of the size of the area, there is only one hospital and that is for pediatric purposes only, the Hospital Maternidad del Sur. Otherwise patients need to be treated in the Hospital de Carabobo or in smaller health centres.
Postal code
2001
References
- ↑ http://www.palimpalem.com/5/parroquiando/index.html?body2.html History of Miguel Peña (in Spanish)
- ↑ "La historia oculta de Valencia · Edición Aniversaria ·". www.notitarde.com. Archived from the original on 2006-11-16.
- ↑ http://www.eluniversal.com/2008/11/10/sucgc_art_en-carabobo-homicidi_1137374.shtml Crime in Carabobo, El Universal (Spanish)
- ↑ "Population of civil parishes in Carabobo". Archived from the original on 2011-07-23. Retrieved 2008-12-13.
- ↑ History of Miguel Peña
- ↑ News on new law for administrative divisions in Carabobo (Notitarde, Spanish)
- ↑ Oswaldo Feo Caballero discusses the politics of making Miguel Peña a municipality (Notitarde, Spanish)
- ↑ http://www.cne.gov.ve/divulgacion_referendo_reforma/index.php?cod_estado=07&cod_municipio=09&cod_parroquia=04 Results of constitutional referendum of 2 December 2007 in the Miguel Pena region
- ↑ "notitarde.com - valencia". historico.notitarde.com. Archived from the original on 2003-05-04.