
The 2000s drought in Australia, also known as the millennium drought[1] is said by some to be the worst drought recorded since European settlement.[2]
This drought affected most of southern Australia, including its largest cities and largest agricultural region (the Murray–Darling basin). It commenced with low rainfall conditions in late 1996 and through 1997, and worsened through particularly dry years in 2001 and 2002. By 2003 it was recognised as the worst drought on record.[2]
The year 2006 was the driest on record for many parts of the country and conditions remained hot and dry through to early 2010. The emergence of La Niña weather conditions in 2010 rapidly ended the drought, and led to floods in some locations, particularly in central and southern Queensland.
The drought placed extreme pressure on agricultural production and urban water supply in much of southern Australia. It has led to the construction of six major seawater desalination plants to provide water to Australia's major cities, and to changes in the management of water in the Murray–Darling basin, particularly the formation of the Murray–Darling Basin Authority.
Prelude to drought
Beginning in the second half of 1991, a very severe drought occurred throughout Queensland which intensified in 1994 and 1995 to become the worst on record.[3][4]
By October 1994, part of the upper Darling River system had collapsed and the Condamine River had reverted to a series of ponds. Across the state 40% of Queensland was drought declared.[5] From July to August 1995 the drought was further influenced by a strong El Niño weather pattern associated with high temperatures. According to Primary Industries Minister, Ed Casey, "the drought affected region stretched in a 200 km to 300 km wide strip from Stanthorpe to Charters Towers".[6] So few wheat and barley crops survived, about half the usual for that year, that grains had to be imported from other states.[7]
Geographic and seasonal characteristics, and compounding factors
The Bureau of Meteorology has characterised the Millennium Drought as primarily affecting:[8]
- Southern Australia (rainfall in northern Australia was above average during the same period).
- Cool season (April to October) rainfall, other than for Tasmania where rainfall was well below historical averages in both warm and cool seasons.
Although the period of the Millennium Drought was characterised by several El Niño weather patterns, which affect the entire southern Pacific region and typically bring hot and dry conditions to eastern Australia, it cannot be explained purely by natural variability. The Bureau of Meteorology concluded that climate change exacerbated the extent and severity of the drought.[8]
The effects of the drought on water availability was compounded by historically high temperatures over the same period. The Bureau of Meteorology's head of climate analysis, David Jones, released statistics showing that in 2007 South Australia, NSW, Victoria, the ACT and the Murray–Darling basin all set temperature records by a very large margin. 2007 was the eleventh year in a row that the Murray–Darling basin had experienced above average temperatures and was (at that time) Australia's sixth-warmest year on record. Jones warned that "There is absolutely no debate that Australia is warming... it may be time to stop describing south-eastern Australia as gripped by drought and instead accept the extreme dry as permanent."[9]
Timeline
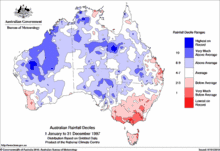
1996 to 2000: patchy rainfall in the south-east
Dry conditions began to emerge in south-eastern Australia during late 1996 and accentuated during the strong 1997 El Niño event.[10] Rainfall in 1998, 1999 and 2000 was closer to average, with isolated areas affected by rainfall well below average.
2001 to 2005: El Niño brings on strong drought conditions

According to the Bureau of Meteorology, much of eastern Australia experienced a dry 2001.[11] 2002 was one of Australia's driest and warmest years on record, with 'remarkably widespread' dry conditions, particularly in the eastern half of the country which was again affected by El Niño conditions. It was, at the time, Australia's fourth-driest year since 1900.[12]
The El Niño weather pattern broke down during 2003 but occasional strong rainfall in 2003 and 2004 failed to alleviate the cumulative effect of persistently low rainfall in south-eastern Australia, with some measurement stations having recorded below average rainfall for eight consecutive years.[13] Rainfall in early 2005 remained below average, and better rainfall in the second half of the year again failed to break continuing drought conditions in the south-east.[14]
2006 and 2007: extreme dry and hot conditions in the Murray–Darling basin
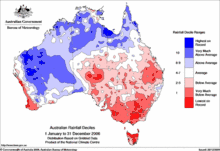
South-east Australia experienced its second-driest year on record in 2006, particularly affecting the major agricultural region of the Murray–Darling basin.[15] Despite slightly above normal summer/autumn rainfall, the late-winter to mid-spring rainfalls failed, resulting in the 2006 annual rainfall being 40 to 60% below normal over most of southern Australia. The average rainfall in the state of South Australia was the lowest since 1900 with only 108.8 millimetres (4.28 in) of rain recorded compared to the normal winter/spring average of 376.6 millimetres (14.83 in). Across Victoria and the Murray–Darling Basin the season was the second-driest since 1900. While New South Wales' rainfall was boosted by above normal falls along the north coast of the state, the state's average rainfall for the season was the third lowest since 1900. The situation was exacerbated by temperatures being the highest on record since the 1950s.[16][17]
In early 2007, senior weather forecasters predicted that the drought would ease along the east coast with a return to average rainfall from late February 2007. Forecasters believed that the El Niño effect that had been driving the drought since 2006 had ended.[18]
However, this did not turn out to be correct as 2007 saw record temperatures across the south of Australia, and only patchy rain. Promising early year rains transitioned into a very dry July–October period. Heavy rainfall in June and July, particularly in coastal regions of New South Wales and in Victoria's Gippsland region, together with tentative forecasts of a La Niña event, brought hope that the drought may have ended.[19] In August 2007, the Darling River flowed again after nearly a year of no flows;[20] however, the Murray-Darling Basin experienced their seventh consecutive year of below-average rain and inflows into the Basin during the winter of 2007 were still amongst the lowest on record, though marginally better than those of the winter of 2006 which had been the driest on record.
At the end of 2007 the Bureau of Meteorology estimated that south-eastern Australia had missed the equivalent of a full year's rain in the previous 11 years.[21]
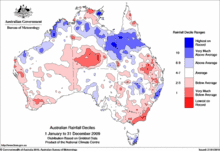
2008 and 2009: continuing hot and dry conditions
2008 and 2009 saw continuing hot and dry conditions in south-eastern Australia, with occasional heavy rainfall failing to break the continuing drought. The effects of the drought were exacerbated by Australia's (then) second-hottest year on record in 2009, with record-breaking heatwaves in January, February and the second half of the year.[22]
The drought in Sydney eased around April 2008 and Sydney's main water catchments reached 65 percent, 25 per cent fuller than they were at the same time the previous year.[23][24] However, Victoria remained drought affected, with Melbourne's water supplies dipping to around 30% by July 2008.[25] In Tasmania drought conditions worsened in 2008, with many areas reporting no significant rainfall for three years.[26]
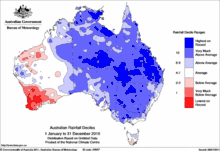
2010 and 2011: La Niña finally breaks the drought
Australia's weather pattern transitioned rapidly to a wet La Niña pattern during the autumn of 2010, resulting in record-breaking rains in the Murray-Darling basin and well above average rainfall across the south-east. For many locations this was the first year of above-average rainfall since 1996. The rainfall dramatically increased surface water storage and soil moisture, effectively ending the drought in the south-east.[27]
While 70% of New South Wales was in drought at the beginning of 2010, the entire state was officially out of drought by December. The entire state experienced its wettest spring on record. Several rivers, including rivers in the outback had flooded several times, and many dams were overflowing, including the Burrendong, Burrinjuck and Pindari Dams. Canberra's dams were above 90% capacity.
The 2010 Victorian storms in March did little to help Melbourne's storage levels, but steady winter rains, and the 2010 Victorian floods in September, rapidly increased storage levels. Melbourne also recorded its average annual rainfall in 2010 for the first time since 1996,[28] and its wettest spring since 1993.[29] By 2011, Victoria was drought free for the first time in almost 15 years and was instead gripped by very wet conditions and severe flooding.
Queensland experienced heavy storms in December 2010 and January 2011, resulting in widespread flooding.
Despite Western Australia experiencing its fifth-wettest spring on record, drought in the South West, Gascoyne and Pilbara regions of Western Australia's intensified in 2010, with the regions experiencing their driest year on record. Perth's dams registered their lowest inflows on record with the city itself recording its third-driest year on record, along with the hottest spring on record.[30]
In South Australia, only two regions in the Riverland remained in drought. Heavy rains elsewhere led to bumper harvests over much of the state, this in turn led to the largest mouse plague since 1993 across parts of South Australia, West Australia and Victoria. While some farmers tried to replant, in some areas many gave up as millions of mice covered their fields. Farmers often characterised the plague as being worse than the drought.[31]
Effects of the drought
Agriculture

Agricultural production was severely affected. Australia's cotton production had dropped, with the smallest area planted in 20 years, a 66% reduction compared to five years earlier which was considered a "normal" year. The crop had been half its usual size for three of the previous five years. Water use by the industry fell by 37% between 2000/01 and 2004/05, due mainly to the drought.[32] On the order of 20 cotton communities and 10,000 people directly employed by the cotton industry were impacted by the drought. The main areas affected were in New South Wales: Menindee where the area under production was reduced by 100%, Bourke had reduced the area under production by 99%, Walgett has reduced the area under production by 95%, the Macquarie River has reduced the area under production by 74% and the Gwydir River had reduced the area under production by 60%.
.jpg.webp)
In Queensland the worst-affected areas were Biloela which reduced the area under production by 100%, at Dirranbandi there was a 91% reduction, Central Highlands had reduced the area under production by 82% and Darling Downs had reduced the area under production by 78%. Bourke had adequate water for only one cotton crop from 2001 to 2006.[33] Stock feed was also becoming scarce and farmers were finding it difficult to feed cattle and sheep. Dairy producers were hit particularly hard by the drought with 2004 a particularly bleak year in the sector, as a drought-caused drop in production sent revenue in the industry down by 4.5%.[34]
Environment
In June 2008 it became known that an expert panel had warned of long term, maybe irreversible, severe ecological damage for the whole Murray-Darling basin if it did not receive sufficient water by October of that year.[35]
The very low flow to the Lower River Murray in South Australia (over Lock 1) resulted in the lowest water levels in over 90 years of records.[36] The lowest water levels during the extreme low flow period were reached in April 2009 and represented a 64% and 73% reduction in the volume of Lakes Alexandrina and Albert respectively. The low water levels and inflows meant there was no outflow from the lake system during the extreme low flow period. During this period the lake levels fell below mean sea level (approximately +0.2 m AHD) downstream of the barrages, reversing the usual positive hydraulic gradient from the lake to the sea. The seawater intrusion, lack of flushing, evapoconcentration and increased resuspension resulted in severe water quality impacts[36]
Exposure and oxidation of acid sulfate soils due to falling water levels from 2007 to 2009 in the Lower River Murray and Lower Lakes also resulted in acidification of soils, lake and ground water.[37][38][39] Large scale engineering interventions were undertaken to prevent further acidification, including construction of a bund and pumping of water to prevent exposure and acidification of Lake Albert.[40] Management of acidification in the Lower Lakes was also undertaken using aerial limestone dosing.[41][42]
Ironically, the easing of the drought led to a large blackwater (low dissolved oxygen) event across a large area of the River Murray during high flows in 2011. Organic carbon (dead plant material) that had been retained in the landscape during the drought was mobilised into the river system and the breakdown of this consumed dissolved oxygen.[43]
The environmental legacy of the drought persists in parts of the system. For example, as of 2014 Lake Albert salinity was still elevated four years after the drought, and acidity persists in soils and groundwater.[37][38]
Urban water
Australia had previously relied solely on water from dams for agriculture and consumption. The drought changed the way Australia treated its water resources. Because of the long-term effects of the drought now showing, many state governments attempted to "drought-proof" their states with more permanent solutions such as grey-water water-recycling, government rebates for home-owners to install water tanks, and tougher restrictions on industries.
The citizens of Toowoomba voted on, and rejected, a referendum on using recycled sewage water. As a result, no recycled sewage was added to Toowoomba's drinking supply.[44]
Most Australian mainland capital cities faced a major water crisis with less than 50% of water storages remaining.
Sydney
Plans for a desalination project in Sydney were temporarily halted in 2005 after public opposition and the discovery of new underground aquifers. By late 2006, however, with Sydney's water storages plunging to their lowest levels since the 1950s – around 33% of capacity – the authorities decided to reinstate the project. A$1.8 billion desalination plant was then constructed at Kurnell, in southern Sydney, opening in the summer of 2009–10.
The drought in Sydney eased around April 2008 and Sydney's main water catchments reached 65 percent, 25 per cent fuller than they were at the same time the previous year.[23][24]
Melbourne
Melbourne had rain up to 90% below the average for September and October 2006, compounding the problem of extremely low rainfall from the preceding winter months. Melbourne had also experienced high temperatures throughout October causing increased evaporation of water in dams and reservoirs, which resulted in their levels falling by around 0.1% a day. As a result of all these factors Melbourne was put on tight water restrictions and as of July 2009, water levels in its dams were at a mere 27% of capacity.[45]
Melbourne had had Stage 3a water restrictions from 1 April 2007, and narrowly avoided Stage 4 restrictions, with the minimum storage level of around 25.8%[46] remaining above the threshold of 25% for enacting Stage 4. This led to the construction of the North-South Pipeline which would divert water out of the Goulburn River and supply it to Melbourne to meet water demands. Many towns in Victoria were close to running out of water, with some of the few Victorian towns without water restrictions being in the East Gippsland water area, where reservoir levels were above 80%.
The Victorian Government also began building a $3.1 billion 150Gl (gigalitre) desalination plant, one of the world's largest. When completed in 2011, it would be capable of supplying up to a third of Melbourne's water needs.[47]
The 2010 Victorian storms in March did little to help Melbourne's storage levels, but steady winter rains, and the 2010 Victorian floods in September, rapidly increased storage levels. 2010 saw Australia officially record its wettest spring on record due to a moderate to strong La Nina developing over the region. Water restrictions were reduced to stage 3 on 2 April, and stage 2 on 1 September.[48]
Brisbane

Brisbane water levels reduced to under 20% of capacity, having had no substantial inflow for five years.[49]
Brisbane organised to be supplied via larger dams, a pipeline and possibly also recycling. The Gold Coast Desalination Plant was constructed at Bilinga, delivering water from 2009.[50]
The drought in Queensland had mostly eased with Brisbane recording very heavy rain in May 2009, and premier Anna Bligh announcing that South East Queensland was no longer experiencing drought.[51] Brisbane's dams were now at full capacity with the state in general experiencing its wettest spring on record. The end of the drought and heavy spring rains in Queensland culminated with devastating floods in December 2010 and January 2011.
Perth
In November 2006 Perth completed a seawater desalination plant that will supply the city with 17% of its needs.[52]
In 2010 Perth's dams registered their lowest inflows on record with the city itself recording its third-driest year on record, along with the hottest spring on record.[30]
Adelaide

In South Australia work on a small pilot desalination plant at Port Stanvac, costing $10 million and with a capacity of 100,000 litres per day, commenced in January 2008,[53] and was completed on 4 August 2008.[54] In 2007 the Federal Government pledged to contribute funds and construction began on a $1.1 billion desalination plant with a capacity of 50 gigalitres.
In June 2009 the South Australian Government announced that the plant's annual output was to be doubled from 50Gl to 100Gl, approximately 270 megalitres per day,[55] providing up to 50% of Adelaide's domestic water supply.[56]
Electricity supply
The drought had a material impact on Australia's National Electricity Market, particularly during autumn and winter 2007. It reduced output from major hydro-electric generators Snowy Hydro and Hydro Tasmania, and also constrained output from some coal-fired generators that use fresh water for cooling.
The Australian Energy Regulator found that these effects led to noticeably higher prices from around March 2007, but that these effects had largely eased by September.[57]
Policy responses
National Plan for Water Security
Then Prime Minister John Howard responded to extreme weather conditions to announce a major water policy reform agenda in January 2007, known as the National Plan for Water Security.[58]
This led to the passage of the Water Act (2007) by the Commonwealth Parliament, the formation of the Murray-Darling Basin Authority in 2008 and the publication of the Murray-Darling Basin Plan under the Gillard government in 2012.
Drought assistance
On 27 April 2012, Agriculture Minister Joe Ludwig stated that the two final areas in Australia receiving federal 'exceptional circumstances' drought support, Bundarra and Eurobodalla in New South Wales, would cease being eligible the following week.[59] The Federal Government had provided $4.5 billion in drought assistance since 2001.[60] The related move to end the exceptional circumstances interest rate subsidy program was criticised as premature by the NSW Farmers Association and National Farmers' Federation.[59] Research has shown the failure of crops and the financial problems this brings about can lead to increased stress and even suicides in some cases. To counter this rural Victoria invested in improving their mental health services during the drought period of 2001 to 2007. This played a major role in reducing the number of drought related suicides during this period.[61]
See also
References
- ↑ Agency, Digital Transformation. "Natural disasters in Australia – australia.gov.au". Archived from the original on 12 November 2017. Retrieved 25 September 2015.
- 1 2 "Rural News 03/09/2003: Worst drought on record". ABC. 3 September 2003. Retrieved 17 November 2006.
- ↑ Rankin, Robert. (1992) Secrets of the Scenic Rim. Rankin Publishers ISBN 0-9592418-3-3 (page 151)
- ↑ Collie, Gordon (26 August 1995). "Worst drought of century cripples farmers". The Courier-Mail. p. 14.
- ↑ Collie, Gordon. Dry tears of despair. The Courier-Mail. p. 29. 22 October 1994.
- ↑ Collie, Gordon. Water crisis threatens towns. The Courier Mail p. 3. 3 June 1995
- ↑ Coleman, Matthew (30 August 1995). "Crops worth $50m lost". The Courier-Mail.
- 1 2 Bureau of Meteorology (April 2015). "Recent rainfall, drought and southern Australia's long-term rainfall decline". Retrieved 29 March 2017.
- ↑ Richard Macey This drought may never break Sydney Morning Herald 4 January 2008
- ↑ Australian Bureau of Statistics (27 February 1998). "1998 Yearbook – Climate Variability and El Nino". www.abs.gov.au. Retrieved 26 January 2017.
- ↑ Bureau of Meteorology (3 January 2002). "Annual Australian Climate Summary 2001". www.bom.gov.au. Retrieved 26 January 2017.
- ↑ Bureau of Meteorology. "Annual Australian Climate Summary 2002". www.bom.gov.au. Retrieved 26 January 2017.
- ↑ Bureau of Meteorology. "Annual Australian Climate Summary 2004". www.bom.gov.au. Retrieved 26 January 2017.
- ↑ Bureau of Meteorology. "Annual Australian Climate Statement 2005". www.bom.gov.au. Retrieved 26 January 2017.
- ↑ Bureau of Meteorology. "Annual Climate Statement 2006". www.bom.gov.au. Retrieved 26 January 2017.
- ↑ "Statement on Drought for the 3, 6, and 10-month periods ending 31 October 2006 – Drought intensifies over eastern and southern Australia as spring rains fail". Drought Statements. National Climate Centre, Bureau of Meteorciology. 3 November 2006. Retrieved 13 November 2006.
- ↑ Australian Drought and Climate Change Archived 26 July 2018 at the Wayback Machine, retrieved on 7 June 2007.
- ↑ Barlow, Karen (22 February 2007). "El Nino declared over". Water. Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Archived from the original on 17 May 2012. Retrieved 23 October 2007.
The Bureau of Meteorology has declared that the El Nino which has made the drought so much worse for the past year or so has passed. A senior climatologist at the Bureau of Meteorology, Grant Beard, says it's time to be optimistic about drought-breaking rains, although the drought is far from over yet.
- ↑ "Is the drought over?". Sydney Radio ABC 702. Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 28 June 2007. Archived from the original on 25 December 2007. Retrieved 23 October 2007.
- ↑ Clarke, Sarah (28 August 2007). "Darling flow a mixed blessing". Water. Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 27 August 2019.
- ↑ Bureau of Meteorology. "Annual Australian Climate Statement 2007". www.bom.gov.au. Retrieved 26 January 2017.
- ↑ Bureau of Meteorology. "Annual Australian Climate Statement 2009". www.bom.gov.au. Retrieved 26 January 2017.
- 1 2 "More of NSW moves out of drought". The Sydney Morning Herald. 9 February 2008.
- 1 2 "It's going to rain for months: forecaster". The Sydney Morning Herald. 10 February 2008.
- ↑ "Storages over the years – Melbourne Water". Archived from the original on 7 September 2010. Retrieved 3 May 2012.
- ↑ "Bureau says Tassie drought worsening". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 10 October 2008. Retrieved 10 October 2008.
- ↑ Bureau of Meteorology. "Annual Australian Climate Statement 2010". www.bom.gov.au. Retrieved 26 January 2017.
- ↑ "Melbourne gets average rainfall for first time in 14 years". 25 November 2010.
- ↑ "Weather News – Melbourne's wettest spring in 17 years".
- 1 2 "WA rivers running dry".
- ↑ Kerry Staight Mouse plague 'worse than drought' ABC 5 July 2010
- ↑ ABS Water Account Australia 2004/05 figures quoted by Water and Cotton Fact Sheet of 13 February 2007 retrieved 5 March 2007 from Cotton Australia Archived 28 February 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Water and Cotton Fact Sheet of 13 February 2007 retrieved 5 March 2007 from Cotton Australia Archived 28 February 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "Dairy farmers face tough times". Archived from the original on 26 January 2012. Retrieved 3 May 2012.
- ↑ BBC News: Australian rivers face disaster
- 1 2 Mosley, LM; Zammit, B; Leyden, E; Heneker, TM; Hipsey, MR; Skinner, D; Aldridge, KT (2012). "The Impact of Extreme Low Flows on the Water Quality of the Lower Murray River and Lakes (South Australia)". Water Resources Management. 26: 3923–3946. doi:10.1007/s11269-012-0113-2. hdl:11343/282625.
- 1 2 Mosley LM, Palmer D, Leyden E, Fitzpatrick R, and Shand P (2014). Changes in acidity and metal geochemistry in soils, groundwater, drain and river water in the Lower Murray River after a severe drought. Science of the Total Environment 485–486: 281–291.
- 1 2 Mosley, LM; Zammit, B; Jolley, A; Barnett, L (2014). "Acidification of lake water due to drought". Journal of Hydrology. 511: 484–493. Bibcode:2014JHyd..511..484M. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.02.001.
- ↑ Mosley, LM; Palmer, D; Leyden, E; Fitzpatrick, R; Shand, P (2014). "Acidification of floodplains due to river level decline during drought". Journal of Contaminant Hydrology. 161: 10–23. Bibcode:2014JCHyd.161...10M. doi:10.1016/j.jconhyd.2014.03.003. PMID 24732706.
- ↑ Hipsey, M; Salmon, U; Mosley, LM (2014). "A three-dimensional hydro-geochemical model to assess lake acidification risk". Environmental Modelling and Software. 61: 433–457. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2014.02.007.
- ↑ Mosley, LM; Zammit, B; Jolley, A; Barnett, L; Fitzpatrick, R (2014). "Monitoring and assessment of surface water acidification following rewetting of oxidised acid sulfate soils". Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. 186: 1–18. doi:10.1007/s10661-013-3350-9. PMID 23900634.
- ↑ Mosley, LM; Shand, P; Self, P; Fitzpatrick, R (2014). "The geochemistry during management of lake acidification caused by the rewetting of sulfuric (pH<4) acid sulfate soils". Applied Geochemistry. 41: 49–56. Bibcode:2014ApGC...41...49M. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2013.11.010.
- ↑ Whitworth KL, Kerr JL, Mosley LM, Conallin J, Hardwick L, and Baldwin DS (2013). Options for managing hypoxic blackwater in river systems: case studies and framework, Environmental Management 114, 139–147.
- ↑ "Toowoomba says no to recycled water – National – smh.com.au". www.smh.com.au. Retrieved 21 December 2015.
- ↑ "Storage : Melbourne Water's Conserve Water". 3 January 2007. Archived from the original on 3 January 2007.
- ↑ "Weekly water update archive – Weekly water update – Melbourne Water". Archived from the original on 5 June 2012. Retrieved 3 May 2012.
- ↑ "Desalination project". Ourwater.vic.gov.au. 16 July 2012. Archived from the original on 19 February 2011. Retrieved 17 August 2012.
- ↑ State government eases Melbourne's water restrictions, The Age
- ↑ "Dam Levels".
- ↑ "Gold Coast Desalination Plant, Queensland - Water Technology". www.water-technology.net. Retrieved 10 April 2021.
- ↑ Drought over in SE Qld, ABC News, 20 May 2009
- ↑ "Perth Seawater Desalination Plant". Archived from the original on 5 May 2012. Retrieved 3 May 2012.
- ↑ Work begins on pilot desal plant Jeremy Roberts, The Australian, 21 January 2008. Retrieved 25 August 2011.
- ↑ Port Stanvac desalination pilot plant up and running AdelaideNow, 4 July 2008. Retrieved 25 August 2011.
- ↑ Acciona back to expand Adelaide desalination ABC News, 28 June 2009. Retrieved 25 August 2011.
- ↑ 100Gl desalination expansion in Public Works today Archived 11 June 2009 at the Wayback Machine Department of Premier & Cabinet, News release 9 June 2009. Retrieved 25 August 2011.
- ↑ Australian Energy Regulator (2008). State of the Energy Market: 2008. pp. 86–87.
- ↑ McCormick, Bill. "National Plan for Water Security". Parliament of Australia. Retrieved 29 March 2017.
- 1 2 Saffron Howden (27 April 2012). "It's official: Australia no longer in drought". Brisbanetimes.com.au. Retrieved 17 August 2012.
- ↑ "Minister declares end of drought". The Age. Melbourne.
- ↑ Guiney, R (Autumn 2017). "Farming suicides during the Victorian drought: 2001–2007". Australian Journal of Rural Health. 20: 11–5. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1584.2011.01244.x. PMID 22250871.