In industrial organization, the minimum efficient scale (MES) or efficient scale of production is the lowest point where the plant (or firm) can produce such that its long run average costs are minimized. It is also the point at which the firm can achieve necessary economies of scale for it to compete effectively within the market.[1]
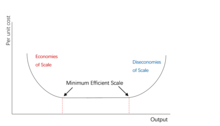
Measurement of the MES
Economies of scale refers to the cost advantage arise from increasing amount of production. Mathematically, it is a situation in which the firm can double its output for less than doubling the cost, which brings cost advantages. Usually, economies of scale can be represented in connection with a cost-production elasticity, Ec.[2]
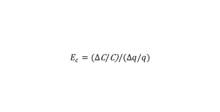
The cost-production elasticity equation can be rewritten to express the relationship between marginal cost and average cost.
The minimum efficient scale can be computed by equating average cost (AC) with marginal cost (MC): The rationale behind this is that if a firm were to produce a small number of units, its average cost per unit would be high because the bulk of the costs would come from fixed costs. But if the firm produces more units, the average cost incurred per unit will be lower as the fixed costs are spread over a larger number of units; the marginal cost is below the average cost, pulling the latter down. The efficient scale of production is then reached when the average cost is at its minimum and therefore the same as the marginal cost.
Relationship to market structure
The concept of minimum efficient scale is useful in determining the likely market structure of a market. For instance, if the minimum efficient scale is small relative to the overall size of the market (demand for the good), there will be a large number of firms. The firms in this market will be likely to behave in a perfectly competitive manner due to the large number of competitors.[3] However, if the minimum efficient scale can only be achieved at a significantly high levels of output relative to the overall size of the market, the number of firms will be small, the market is likely to be a oligopoly or monopoly market.
MES in L-shaped cost curve

Modern cost theory and recent empirical studies[4][5] suggest that, instead of a U-shaped curve due to the presence of diseconomies of scale, the long run average cost curve is more likely to be L-shaped. In the L-shaped cost curve, the long run cost would keep fixed with a significantly increased scale of output once the firm reaches the minimum efficient scale (MES).
However, the average cost in an L-shaped curve may further decrease even though most economies of scale have been exploited when firms achieve the MES because of technical and production economies. For instance, the firm may obtain further economies of scale from skill improvement by training the employees, decentralization in management. Secondly, repair cost and scrap rate will decrease when the firm reaches a certain size. Thirdly, improvement in the firm's vertical integration, producing by a firm itself some of the materials and equipment it needs at a lower cost for its production process instead of buying them from other firms.
See also
References
- ↑ Besanko, David; Dranove, David; Shanley, Mark (2015). Economics of strategy (7th ed.). Hoboken: Wiley. ISBN 9781119042310.
- ↑ Pindyck, Robert; Rubinfeld, Daniel (2017). Microeconomics, Global Edition (9th ed.). Harlow, United Kingdom: Pearson. ISBN 978-1292213378.
- ↑ Carlton D. and Perloff M.: "Modern Industrial Organization" Fourth Edition, 2005
- ↑ Johnston, J. (1952-02-01). "Statistical Cost Functions in Electricity Supply". Oxford Economic Papers. 4: 68-105. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.oep.a042200.
- ↑ Dean, Joel (1937-03-01). "Statistical Cost Curves". Journal of the American Statistical Association. 32 (197): 83-89. doi:10.1080/01621459.1937.10502751.