Mobile literacy in South Africa refers to a range of informal education projects and initiatives that support literacy and digital fluency using mobile devices, especially mobile phones. It is also known by the abbreviation mLiteracy.[1]
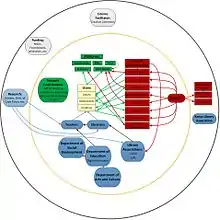
The mobile literacy ecosystem in South Africa was mapped in January 2015, using the UNESCO study "Reading in the Mobile Era: A Study of Mobile Reading in Developing Countries"[2] as a starting point.
Ecosystem of mLiteracy in South Africa
| Part of a series on the |
| Culture of South Africa |
|---|
 |
| People |
| Cuisine |
| Religion |
| Art |
| Sport |
The mobile literacy ecosystem in South Africa includes stakeholders who use mobile platforms to encourage access to text, stories and reading materials. This includes content providers, platforms, mobile networks, funding agencies, training facilities (including schools and libraries), authors and users. Most of the projects use open licences, specifically Creative Commons licences. The target groups of most projects have been children, teenagers and young adults.
Content providers
- African Storybook. Founded in 2013, the African Storybook has published illustrated children's stories in English and over 40 African languages.[3]
- Book Dash. Founded in 2014, Book Dash creates free print and mobile-ready African storybooks for young children, published under a Creative Commons licence.
- FunDza publishes stories for teenagers and young adults in all eleven official languages of South Africa. Readers can comment and write their own stories.
- Nal'ibali. Primarily aimed at adults, Nal'ibali publishes stories in all official South African languages which parents can read to their children.
- Penreach hosts the Asifundze Programme in Mpumalanga, focused on improving literacy and numeracy among young children between the ages of 5 and 9.
- Worldreader was founded in 2010 by Coleen McElwee and David Risher, the former Senior Vice President for Amazon's US Retail. It publishes ebooks for developing countries at discounted prices.
- Yoza Cellphone Stories was launched in 2009 as a Shuttleworth Foundation project led by Steve Vosloo, digital policy specialist for UNICEF’s Office of Global Insight and Policy. No longer active, its stories are housed on the FunDza website.
- Puku Foundation is a reading promotion, indigenous language advocacy and book curation organisation. One of Puku’s primary vehicles is a digital encyclopedia that houses and reviews children’s literature.
Contribution and licence activators
- Creative Commons South Africa provides a pool of copyright licenses in order to simplify sharing creative works and enabling universal access to knowledge. Some of the above-mentioned projects work under a CC license.
- WikiAfrica is an initiative which aims at encouraging the transfer and development of African content onto Wikipedia. They are training people, groups and organisations to contribute or donate African knowledge to Wikipedia and improve the current lack of presence of voices from Africa.
- Wikipedia Zero is an initiative that grants access to Wikipedia without any airtime costs. In South Africa there is a limited version of Wikipedia Zero available to users of the MTN network.
Library-based projects
- The Johannesburg City Library has launched some initiatives supporting eLearning and promoting techno-literacy.
- The Library and Information Association of South Africa (LIASA), launched in 1997, aims at building capacity for libraries, expanding access to content and providing a platform for libraries and librarians.
- The Ulwazi Programme, established in 2008 by the eThekwini Municipality’s Libraries and Heritage Department, Ulwazi was the first project by a library in South African to collect and share knowledge about local culture and history. The project encouraged local communities to participate in sharing local knowledge online and increase internet use in Africa.
Research into mobile literacy
- Researching Mobile Media at the University of Cape Town
A number of research initiatives on mobile literacy have been done by researchers at the University of Cape Town. Studies on digital literacy and the link between mobile literacy and multilingualism[4] are among them. Projects have highlighted the critical significance of public access locations like libraries and cybercafes in promoting mobile literacy.[5] This expands on research conducted at the University of Cape Town's Centre for ICT4D, which investigates how technological improvements might promote media sharing on mobile devices[6] and characterizes the nature of mobile-first digital literacy practices.[7]
International affiliated organisations
- Electronic Information for Libraries (EIFL) in Africa, conducts programmes in Ethiopia, Ghana, Kenya and South Africa that focus on training in Information and Communication for librarians.
- Goethe-Institut Johannesburg: The Goethe-Institut is the Federal Republic of Germany’s cultural institute, active worldwide. It promotes the study of German abroad and encourages international cultural exchange. Since the implementation of a new digital strategy in the year 2014, a strong focus lies on initiating an international dialogue about the implications, challenges and possibilities of digital developments in education, culture and society.
- Kenya National Library Service: Kisumu & Kibera project. National Library Service of Kenya (KNLS) develops, promotes, establishes and equips libraries in Kenya. Their mission is to enable access to information and knowledge to promote literacy in Kenya.
- German Library Association: compared to South Africa, mobile phones do not play a very significant role in Germany, but they are becoming more important in Germany as well. The GLA has launched the "Reading is strength" project which aims at improving digital and new media competence.
- Mobiliteracy Uganda: supported by the United States Agency for International Development promotes literacy by sending messages containing reading lessons to an adult's phone they can share with their children. Alternatively, additional audio files are used in order to enable illiterate parents to participate in the project.
- Sen Mobile: launched in Senegal, Sen Mobile provides Mobile Development, SMS Service, Quality Assurance and Quality & Training. Their main focus is mobile learning, health and entertainment.
Developments and challenges
Since the implementation of the first projects in the year 2009,[8] the mLiteracy landscape in South Africa has undergone some promising developments:
- The number of feature and smart phones is rising significantly.[9]
- More and more mLiteracy projects for formal and informal learning have been established (see above)
- The importance of training educators and parents in the field of the educational potential of mobile phones is growing.[10]
- Access to literature and literacy projects via mobile phone serves the form of communication young people are accustomed to.
- The number of relevant content (for example e-books) is growing. (partly provided by the above projects).
On the other hand, there are still a number of major challenges:
- The lack of Africa-relevant content and content in African languages remains a major problem.[11]
- The costs of airtime to access information via mobile phones can in many cases be a threshold, the majority of users (96%) access the internet on their mobile phone via prepaid, which is more expensive than network contracts.[12]
- Most of the projects that make content available for free rely on funding from NGOs and are therefore often not sustainable.[13]
- Parents, educators and librarians are not aware enough about the opportunities the access to information via mobile phone offers.
- Gender equality is also a problem when it come to access to mobile phones. The UNESCO study "Reading in the mobile era" shows that there are by far more male mobile readers than female. But once women gain access, they tend to read six times longer than men. The study also showed, that 2/3 of the women read stories, which they access via their phones, to their children. Making mobile devices accessible for women, will also increase childhood literacy.[14]
See also
References
- ↑ Pegrum, Mark (2014). "Teaching Literacy/Ies with Mobile Devices". Mobile Learning. London: Palgrave Macmillan. doi:10.1057/9781137309815_6. ISBN 978-1-137-30981-5.
- ↑ "Reading in the mobile era: a study of mobile reading in developing countries". Archived from the original on 2015-02-10.
- ↑ The African Storybook. "The African Storybook". The African Storybook. Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original on 2013-12-17. Retrieved 2015-02-08.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) Walton, Marion: Mobile Literacy & South African Teens: Leisure reading, writing, and MXit chatting for teens in Langa and Guguletu (December 2009) (Retrieved 2.8.2015) - ↑ Walton, M., & Donner, J. Public access, private mobile: The interplay of shared access and the mobile Internet for teenagers in Cape Town. Global Impact Study Research Report Series., 1–69. (2012). (Retrieved 2.8.2015)
- ↑ Walton, Marion; Hassreiter, Silke; Marsden, Gary; Allen, Sena (May 18, 2012). "Degrees of Sharing: Proximate Media Sharing and Messaging by Young People in Khayelitsha". University of Cape Town – via pubs.cs.uct.ac.za.
- ↑ Donner, Jonathan; Gitau, Shikoh; Marsden, Gary (April 8, 2011). "Exploring Mobile-only Internet Use: Results of a Training Study in Urban South Africa". International Journal of Communication. 5: 24 – via ijoc.org.
- ↑ "...the pilot phase of the project a mobile novel (m-novel) was written and published in September 2009 on a mobisite and on MXit". (Retrieved 8.2.2015)
- ↑ "Nearly two-thirds (65%) of households in 23 countries in sub-Saharan Africa had at least one mobile phone in 2013, with median growth of 27% since 2008 and median annual growth of 5%." (Retrieved 8.2.2015)
- ↑ "UNESCO Policy Guidelines" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 January 2016. Retrieved 9 February 2015.
- ↑ "Where is Africa on the Internet?". Archived from the original on 2015-02-15. Retrieved 2015-02-08. "There are more Wikipedia articles written about Antarctica than all but one of the 54 countries in Africa." (Retrieved 8.2.2015)
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original on 2016-03-25. Retrieved 2015-02-08.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) Research ICT Africa Policy Brief No 2: Internet going mobile - Internet access and usage in 11 African countries (Sept. 2012) (retrieved 8.2.2015) - ↑ "Steve Vosloo". Retrieved 9 February 2015.
- ↑ "Reading in the mobile era".
Literature
- Reading in the mobile era (UNESCO, 2014) (Retrieved 8.2.2015)
- UNESCO policy guidelines for mobile learning (2013) (Retrieved 8.2.2015)
- The Future of Mobile Learning: implications for policy makers and planners (UNESCO, 2013) (Retrieved 8.2.2015)
- Turning on Mobile Learning in Africa and the Middle East: illustrative initiatives and policy implications (UNESCO 2012) (Retrieved 8.2.2015)
- Walton, Marion: Mobile Literacy & South African Teens: Leisure reading, writing, and MXit chatting for teens in Langa and Guguletu (December 2009) (Retrieved 2.8.2015)
- Mobile for Reading: A landscape research review (June, 2014) (Retrieved 8.2.2015)
- Walton, M., & Donner, J. Public access, private mobile: The interplay of shared access and the mobile Internet for teenagers in Cape Town. Global Impact Study Research Report Series., 1–69. (2012). (Retrieved 2.8.2015)