 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Corvasal, Corvaton, Molsidain, Molsidolat, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | By mouth (tablets), intravenous infusion |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 44–59% |
| Protein binding | 3–11% |
| Metabolism | Hydrolysis |
| Metabolites | Linsidomine |
| Elimination half-life | 1–2 hrs (linsidomine) |
| Excretion | >90% renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.042.902 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H14N4O4 |
| Molar mass | 242.235 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 140 to 141 °C (284 to 286 °F) |
| |
| |
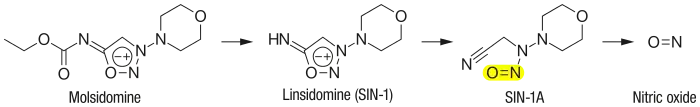
Molsidomine (trade names Corvasal, Corvaton and many others) is an orally active, long acting vasodilating drug used to treat angina pectoris. Molsidomine is metabolized in the liver to the active metabolite linsidomine. Linsidomine is an unstable compound that releases nitric oxide (NO) upon decay as the actual vasodilating compound.[1]
Medical uses
Molsidomine is used for the prevention and long-term treatment of stable and unstable angina pectoris, with or without left heart failure. It is also used to treat angina in the context of an acute myocardial infarction.[2][3]
Contraindications
The drug must not be used in patients with acute cardiac arrest or severe hypotension (low blood pressure), during lactation, and in combination with PDE5 inhibitors such as sildenafil.[2][3]
Side effects
The most common adverse effects are headache, which occurs in 10–25% of patients, and low blood pressure. Side effects occurring in fewer than 1% of patients include dizziness, nausea, reflex tachycardia (fast heartbeat), hypersensitivity reactions, as well as thrombocytopenia (low blood platelet count) in rare cases.[2][3]
Interactions
The blood pressure lowering effect of molsidomine can be amplified significantly by PDE5 inhibitors, potentially leading to fainting or myocardial infarction, and to a lesser extent by other antihypertensive drugs such as beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, or other nitrovasodilators. Ergolines can antagonise the effects of molsidomine.[2][3]
Pharmacology
Mechanism of action
Molsidomine belongs to the drug class of nitrovasodilators. It releases NO, which acts as a gaseous signaling molecule, relaxing the smooth muscles of blood vessels.[4][5]
Pharmacokinetics
The substance is quickly and almost completely (>90%) absorbed from the gut. Molsidomine is a prodrug that is hydrolysed to linsidomine (SIN-1) in the liver via first-pass effect, which subsequently releases NO. 44–59% of molsidomine reach the bloodstream in unchanged form, 3–11% of which are bound to plasma proteins. Both molsidomine and linsidomine reach their highest concentrations in the blood plasma after one to two hours. Linsidomine has a biological half-life of one to two hours. More than 90% are excreted via the kidney.[2][4]
Chemistry
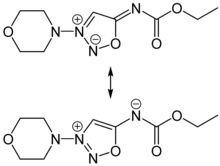
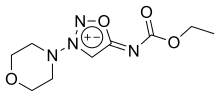
Molsidomine and linsidomine are sydnone imines, a class of mesoionic heterocyclic aromatic chemical compounds. Molsidomine melts at 140–141 °C (284–286 °F), is freely soluble in chloroform, soluble in aqueous hydrochloric acid, ethanol, ethyl acetate and methanol, sparingly soluble in water and acetone, and very slightly soluble in diethyl ether and petroleum ether. It is stable in aqueous solutions at pH 5–7, but not in alkaline solutions. Its absorption maximum is in the near ultraviolet, at 326 nm, in chloroform. The substance is sensitive to ultraviolet light at wavelengths shorter than 320 nm.[3]
Synthesis
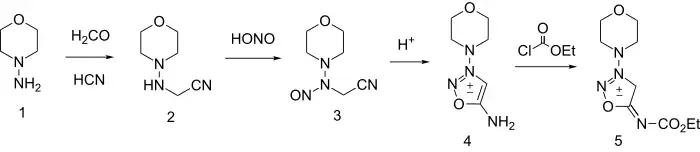
Its synthesis starts by reacting 1-aminomorpholine with formaldehyde and hydrogen cyanide to give 2. Nitrosation gives the N-nitroso analog (3) which cyclizes to the Linsidomine (4) on treatment with anhydrous acid. Formation of the ethyl urethane is then made possible by reacting linsidomine with ethyl chloroformate.
Also see a related structure called Ciclosidomine.
History
The substance was first synthesised at Takeda in 1970. Its antihypertensive and vasodilating properties were discovered the same year.[8]
References
- ↑ Rosenkranz B, Winkelmann BR, Parnham MJ (May 1996). "Clinical pharmacokinetics of molsidomine". Clinical Pharmacokinetics. 30 (5): 372–84. doi:10.2165/00003088-199630050-00004. PMID 8743336.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Austria-Codex (in German). Vienna: Österreichischer Apothekerverlag. 2018. Molsidolat 4 mg-Tabletten. ISBN 978-3-85200-196-8.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Dinnendahl V, Fricke U, eds. (2010). Arzneistoff-Profile (in German). Vol. 7 (24 ed.). Eschborn, Germany: Govi Pharmazeutischer Verlag. Molsidomin. ISBN 978-3-7741-9846-3.
- 1 2 3 Mutschler E, Schäfer-Korting M (2001). Arzneimittelwirkungen (in German) (8 ed.). Stuttgart: Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft. p. 558. ISBN 978-3-8047-1763-3.
- ↑ Stryer L (1995). Biochemistry (4th ed.). W.H. Freeman and Company. p. 732. ISBN 978-0-7167-2009-6.
- ↑ Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 19(1), 72-79, 1971-01-25.
- ↑ DE1695897 idem K Masuda & Y Imashiro, U.S. Patent 3,769,283 & US3812128 (1973 & 1974 to Takeda Pharmaceutical Co Ltd).
- ↑ Müller-Jahncke WB, Friedrich C, Meyer U (2005-01-01). Arzneimittelgeschichte (2nd ed.). Stuttgart: Wiss. Verl.-Ges. p. 163. ISBN 9783804721135.