 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Fluorophosphonic acid[1] | |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.202.790 |
| EC Number |
|
| 100863 | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
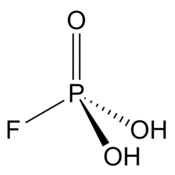
| H2PO3F | |
| Molar mass | 99.985 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid[1] |
| Odor | Practically odorless[1] |
| Density | 1.818 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | −78 °C (−108 °F; 195 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | Decomposes |
| yes | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards |
Causes skin burns and eye damage. |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Danger | |
| H301, H311, H314, H330 | |
| P260, P264, P270, P271, P280, P284, P301+P310, P301+P330+P331, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P312, P320, P321, P322, P330, P361, P363, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Fluorophosphoric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula H2PO3F. It is a colorless viscous liquid that solidifies to a rigid glass upon cooling at −78 °C (−108 °F).[2][1]
Preparation
Fluorophosphoric acid is produced commercially by treating phosphorus pentoxide with hydrogen fluoride. A less pure product can also be prepared by hydrolysis of phosphorus oxyfluoride, a reaction that first produces difluorophosphoric acid:[2]
- POF3 + H2O → HPO2F2 + HF
The next steps give monofluorophosphoric acid:
- HPO2F2 + H2O → H2PO3F + HF
Reactions
Fluorophosphoric acid is a dibasic acid, with pKa1 of 5.5 and pKa2 of around 8.5.[1] The conjugate bases are the monofluorophosphates, which are hydrolytically robust. When fluorophosphoric acid is diluted with water, it hydrolyzes, producing phosphoric acid. Fluorophosphoric acid is not flammable.[1]
Uses
Fluorophosphoric acid is used to make protective coatings on metal surfaces, as a metal cleaner and as an electrolytic or chemical polishing agent. The sodium salt of this acid, sodium monofluorophosphate, is the most used dentifrice additive for the reduction of tooth decay.[1]
Safety
Fluorophosphoric acid is corrosive to living tissue. It can cause severe skin burns and permanent eye damage. Ingestion can cause severe burns and permanent damage to gastrointestinal system. Inhalation of this acid may cause severe burns to respiratory system and chemical pneumonia. Inhalation, ingestion or contact with skin with this acid may cause severe injury or death. Symptoms from contact or inhalation may be delayed.[1]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Fluorophosphoric-acid
- 1 2 Charles B. Lindahl; Tariq Mahmood (2000). "Fluorine Compounds, Inorganic, Phosphorus". Kirk‐Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. doi:10.1002/0471238961.1608151912091404.a01. ISBN 978-0-471-48494-3.