| Moscow Metro | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 | |||
     .jpg.webp)        | |||
| Overview | |||
| Native name | Московский метрополитен | ||
| Owner | Government of Moscow | ||
| Area served | Moscow | ||
| Locale | Federal city of Moscow and cities of Kotelniki, Krasnogorsk, Lyubertsy, Reutov in Moscow Oblast, Russia | ||
| Transit type | Rapid transit | ||
| Number of lines | 19 (including the Moscow Monorail and the Moscow Central Circle)[1] | ||
| Number of stations | 263[1] 300 (including 6 stations of the Moscow Monorail and 31 stations of the Moscow Central Circle) | ||
| Daily ridership | (average) 7.5 million (highest, 26 Dec 2014) 9.715 million [1] | ||
| Annual ridership | 2.5 billion (2018)[1] | ||
| Chief executive | Viktor Kozlovsky | ||
| Website | mosmetro | ||
| Operation | |||
| Began operation | 15 May 1935 | ||
| Operator(s) | Moskovsky Metropoliten | ||
| Headway | Peak hours: 1.3 - 1.7 mins Off-peak: 2.5 - 10 minutes | ||
| Technical | |||
| System length | 449.1 km (279.1 mi)[1] 507.8 km (315.5 mi) including Moscow Monorail and Moscow Central Circle | ||
| Track gauge | 1,520 mm (4 ft 11+27⁄32 in) | ||
| Electrification | 825 Volt DC third rail, 3 kV DC overhead line | ||
| Average speed | 39.54 km/h (24.57 mph)[1] | ||
| Top speed | 80 km/h (50 mph)[1] | ||
| |||
The Moscow Metro[lower-alpha 1] is a metro system serving the Russian capital of Moscow as well as the neighbouring cities of Krasnogorsk, Reutov, Lyubertsy and Kotelniki in Moscow Oblast. Opened in 1935 with one 11-kilometre (6.8 mi) line and 13 stations, it was the first underground railway system in the Soviet Union.
As of 2023, the Moscow Metro, excluding the Moscow Central Circle, the Moscow Central Diameters and the Moscow Monorail, had 263 stations (300 with Moscow Central Circle and the Monorail) and its route length was 449.1 km (279.1 mi) (without Moscow Central Circle and the Monorail),[1] making it the 10th-longest in the world and the longest outside China. It is the third metro system in the world (after Madrid and Beijing), which has two ring lines.[2] The system is mostly underground, with the deepest section 84 metres (276 ft) underground at the Park Pobedy station, one of the world's deepest underground stations. It is the busiest metro system in Europe, the busiest in the world outside Asia, and is considered a tourist attraction in itself.[3]
The Moscow Metro is a world leader in the frequency of train traffic—intervals during peak hours do not exceed 90 seconds.[4]
Name
The full legal name of the metro has been "Moscow Order of Lenin and Order of the Red Banner of Labor V.I. Lenin Metro" (Московский ордена Ленина и ордена Трудового Красного Знамени метрополитен имени В.И. Ленина) since 1955. This is usually shortened to V.I. Lenin Metro (Метрополитен им. В.И. Ленина). This shorter official name appears on many stations. Although there were proposals to remove Lenin from the official name, it still stands. During the 1990s and 2000s, Lenin's name was excluded from the signage on newly built and reconstructed stations. In 2016, the authorities promised to return the official name of the metro to all the stations' signage.[5]
The first official name of the metro was L. M. Kaganovich Metro (Метрополитен им. Л.М. Кагановича) after Lazar Kaganovich.[6] (see History section). However, when the Metro was awarded the Order of Lenin, it was officially renamed "Moscow Order of Lenin L. M. Kaganovich Metro" (Московский ордена Ленина Метрополитен им. Л. М. Кагановича) in 1947. And when the metro was renamed in 1955, Kaganovich was "given a consolation prize" by renaming the Okhotny Ryad station to "Imeni Kaganovicha". Yet in a matter of only two years, the original Okhotny Ryad name of the station was reinstated.[7]
Operations
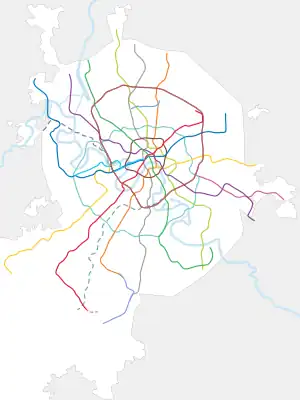
The Moscow Metro, a state-owned enterprise,[8] is 449 km (279 mi) long and consists of 15 lines and 263 stations[9] organized in a spoke-hub distribution paradigm, with the majority of rail lines running radially from the centre of Moscow to the outlying areas. The Koltsevaya Line (line 5) forms a 20-kilometre (12 mi) long circle which enables passenger travel between these diameters, and the new Moscow Central Circle (line 14) and even newer Bolshaya Koltsevaya line (line 11) form a 54-kilometre (34 mi) and 57-kilometre (35 mi) long circles respectively that serve a similar purpose on middle periphery.[10] Most stations and lines are underground, but some lines have at-grade and elevated sections; the Filyovskaya Line, Butovskaya Line and the Central Circle Line are the three lines that are at grade or mostly at grade.
The Moscow Metro uses 1,520 mm (4 ft 11+27⁄32 in) Russian gauge, like other Russian railways, and an underrunning third rail with a supply of 825 Volts DC, except lines 13 and 14, the former being a monorail, and the latter being directly connected to the mainlines with 3000V DC overhead lines, as is typical. The average distance between stations is 1.7 kilometres (1.1 mi); the shortest (502 metres (1,647 ft) long) section is between Vystavochnaya and Mezhdunarodnaya, and the longest (6.62 kilometres (4.11 mi) long) is between Krylatskoye and Strogino. Long distances between stations have the positive effect of a high cruising speed of 41.7 kilometres per hour (25.9 mph).
The Moscow Metro opens at 05:25 and closes at 01:00.[11] The exact opening time varies at different stations according to the arrival of the first train, but all stations simultaneously close their entrances at 01:00 for maintenance, and so do transfer corridors. The minimum interval between trains is 90 seconds during the morning and evening rush hours.[1]
As of 2017, the system had an average daily ridership of 6.99 million passengers. Peak daily ridership of 9.71 million was recorded on 26 December 2014.[1]
Free Wi-Fi has been available on all lines of the Moscow Metro since 2 December 2014.[12]
Stations
Of the metro's 250 stations, 88 are deep underground, 123 are shallow, 12 are surface-level and 5 are elevated.
The deep stations comprise 55 triple-vaulted pylon stations, 19 triple-vaulted column stations, and one single-vault station. The shallow stations comprise 79 spanned column stations (a large portion of them following the "centipede" design), 33 single-vaulted stations (Kharkov technology), and four single-spanned stations. In addition, there are 12 ground-level stations, four elevated stations, and one station (Vorobyovy Gory) on a bridge. Two stations have three tracks, and one has double halls. Seven of the stations have side platforms (only one of which is subterranean). In addition, there were two temporary stations within rail yards.
The stations being constructed under Stalin's regime, in the style of socialist classicism, were meant as underground "palaces of the people". Stations such as Komsomolskaya, Kiyevskaya or Mayakovskaya and others built after 1935 in the second phase of the evolution of the network are tourist landmarks: their photogenic architecture, large chandeliers and detailed decoration are unusual for an urban transport system of the twentieth century.
The stations opened in the 21st century are influenced by an international and more neutral style with improved technical quality.[13]
 Ploshchad Revolyutsii (1938)
Ploshchad Revolyutsii (1938) Baumanskaya (1944)
Baumanskaya (1944) Novoslobodskaya (1952)
Novoslobodskaya (1952)
 Leninsky Prospekt (1962)
Leninsky Prospekt (1962).jpg.webp) Kakhovskaya (1969) (after 2021 reconstruction)
Kakhovskaya (1969) (after 2021 reconstruction) Tretyakovskaya (early station, 1971)
Tretyakovskaya (early station, 1971) Shabolovskaya (1980)
Shabolovskaya (1980) Tretyakovskaya (additional adjacent station, 1986)
Tretyakovskaya (additional adjacent station, 1986) Konkovo (1987)
Konkovo (1987) Tyoply Stan (1987)
Tyoply Stan (1987) Rimskaya (1995)
Rimskaya (1995) Park Pobedy (2003)
Park Pobedy (2003) Slavyansky Bulvar (2008)
Slavyansky Bulvar (2008) Novokosino (2012)
Novokosino (2012) Kosino (2019)
Kosino (2019)
Rolling stock
Since the beginning, platforms have been at least 155 metres (509 ft) long to accommodate eight-car trains. The only exceptions are on the Filyovskaya Line: Vystavochnaya, Mezhdunarodnaya, Studencheskaya, Kutuzovskaya, Fili, Bagrationovskaya, Filyovsky Park and Pionerskaya, which only allows six-car trains (note that this list includes all ground-level stations on the line, except Kuntsevskaya, which allows normal length trains).
Trains on the Zamoskvoretskaya, Kaluzhsko-Rizhskaya, Tagansko-Krasnopresnenskaya, Kalininskaya, Solntsevskaya, Bolshaya Koltsevaya, Serpukhovsko-Timiryazevskaya, Lyublinsko-Dmitrovskaya and Nekrasovskaya lines have eight cars, on the Sokolnicheskaya line seven or eight cars, on the original Koltsevaya line seven cars, and on the Filyovskaya line six cars. The Arbatsko-Pokrovskaya line also once ran seven-car 81-717 size trains, but now use five-car trains of another type. Butovskaya line uses three-car trains of another type.
Dimensions have varied subtly, but for the most cars fit into the ranges of 19–20 metres (62 ft 4 in – 65 ft 7 in) long and 2.65–2.7 metres (8 ft 8+3⁄8 in – 8 ft 10+1⁄4 in) wide with 4 doors per side. The 81-740/741 Rusich deviates greatly from this, with a 3-car Rusich being roughly 4 normal cars and a 5-car Rusich being 7 normal cars.
| Car | Delivered | In service |
|---|---|---|
| А/Б ("A/B") | 1934–1939 | 1935–1975 |
| B ("V", earlier C) | 1927–1930 | 1946–1968 |
| Г ("G") | 1939–1940, 1946–1956 | 1940–1983 |
| Д ("D") | 1955–1963 | 1955–1995 |
| E/Ем/Еж ("E/Em/Ezh") | 1959–1979 | 1962–2020 |
| 81-717/81-714 | 1976–2011 | 1977 ff. |
| И ("I", 81-715/716) | 1974, 1980–1981, 1985 | — |
| 81-720/721 "Yauza" | 1991–2004 | 1998–2019 |
| 81-740/741 "Rusich" | 2002–2013 | 2003 ff. |
| 81-760/761 "Oka" | 2010–2016 | 2012 ff. |
| 81-765/766/767 "Moskva" | 2016–2020 | 2017 ff. |
| 81-775/776/777 "Moskva 2020" | 2020 ff. | 2020 ff. |
Trains no longer in operation
The V-type trains were formerly from Berlin U-Bahn C-class trains from 1945 to 1969, until its complete demise in 1970. They were transported from the Berlin U-Bahn during the Soviet occupation. A-type and B-type trains were custom-made since the opening.
.jpg.webp) A-type
A-type B-type
B-type V-4-type (former Berlin Class C-1)
V-4-type (former Berlin Class C-1).jpg.webp) V2-type (former Berlin Class C-2)
V2-type (former Berlin Class C-2) G-type
G-type D-type
D-type E-type
E-type I-1-type (81-715.1/716.1)
I-1-type (81-715.1/716.1) I-2-type (81-715.2/716.2)
I-2-type (81-715.2/716.2)
Trains in operation
Currently, the Metro only operates 81-style trains.
Rolling stock on several lines was replaced with articulated 81-740/741 Rusich trains, which were originally designed for light rail subway lines. The Butovskaya Line was designed by different standards, and has shorter (96-metre (315 ft) long) platforms. It employs articulated 81-740/741 trains, which consist of three cars (although the line can also use traditional four-car trains).
On the Moscow Monorail, Intamin P30 trains are used, consisting of six short cars. On the Moscow Central Circle, which is a route on the conventional railway line, ES2G Lastochka trains are used, consisting of five cars.

 81-717.5A/81-714.5A-type ("retro train")
81-717.5A/81-714.5A-type ("retro train").jpg.webp) 81-717.6-714.6-type
81-717.6-714.6-type

![81-765/766/767-type ("Moscow") [ru]](../I/81-765-766-767_on_Barrikadnaya_metro_station.jpg.webp) 81-765/766/767-type ("Moscow")
81-765/766/767-type ("Moscow")_(cropped).jpg.webp) 81-775/776/777-type ("Moscow-2020")
81-775/776/777-type ("Moscow-2020") Intamin P30 train (operates on the Monorail line)
Intamin P30 train (operates on the Monorail line) ES2G Lastochka train (operates on the Moscow Central Circle line)
ES2G Lastochka train (operates on the Moscow Central Circle line)
Network
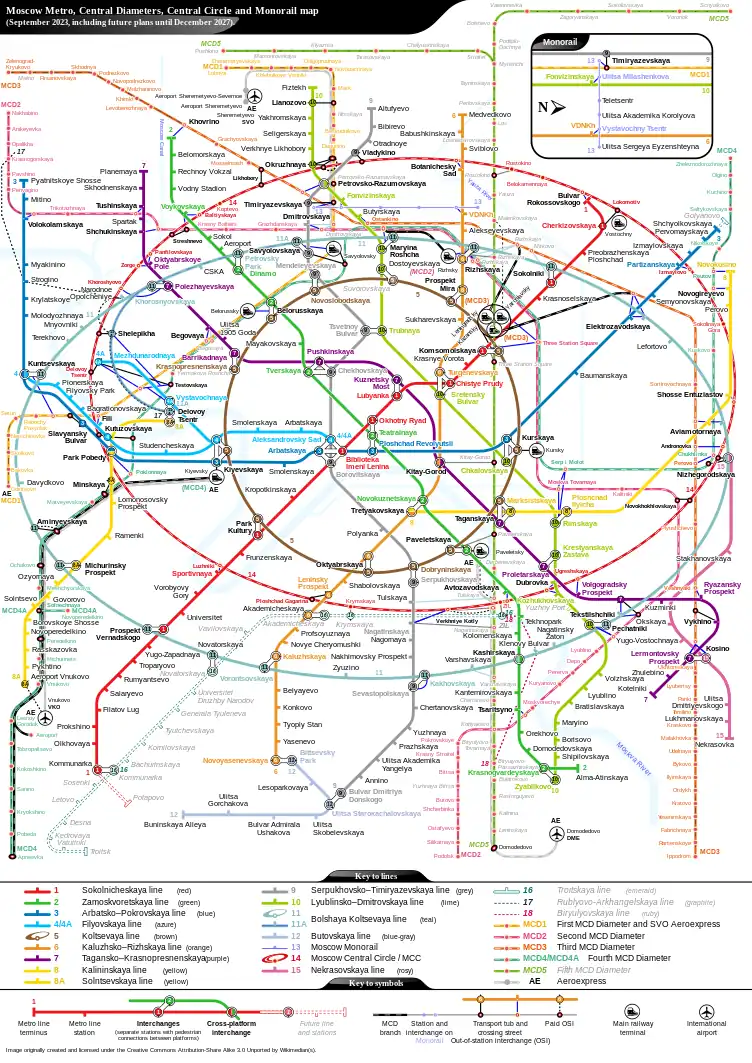
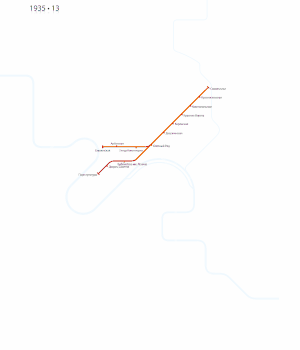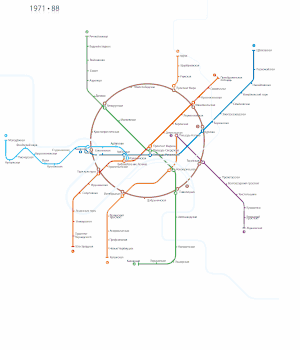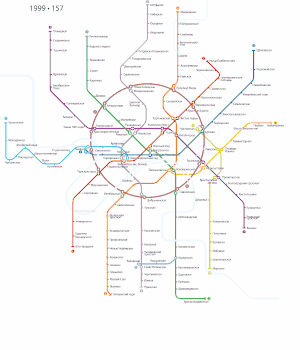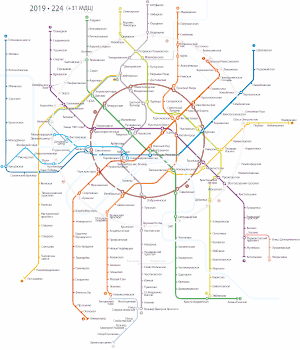
Lines
Each line is identified by a name, an alphanumeric index (usually consisting of just a number, and sometimes a letter suffix), and a colour.[14] The colour assigned to each line for display on maps and signs is its colloquial identifier, except for the nondescript greens and blues assigned to the Bolshaya Koltsevaya, the Zamoskvoretskaya, the Lyublinsko-Dmitrovskaya, and Butovskaya lines (lines, 11, 2, 10, and 12, respectively). The upcoming station is announced by a male voice on inbound trains to the city center (on the Circle line, the clockwise trains), and by a female voice on outbound trains (anti-clockwise trains on the Circle line).[14]
The metro has a connection to the Moscow Monorail, a 4.7-kilometre (2.9 mi), six-station monorail line between Timiryazevskaya and VDNKh which opened in January 2008. Prior to the official opening, the monorail had operated in "excursion mode" since 2004.
| Icon | Line Name | First opened | Latest extension |
Length (km) |
Stations | Avg. dist. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| English | Russian | ||||||
| Sokolnicheskaya | Сокольническая | 1935 | 2019 | 41.5 | 26 | 1.6 | |
| Zamoskvoretskaya | Замоскворецкая | 1938 | 2018 | 42.8 | 24 | 1.86 | |
| Arbatsko-Pokrovskaya | Арбатско-Покровская | 1938 | 2012 | 45.1 | 22 | 2.15 | |
| Filyovskaya | Филёвская | 1958 (1935)[Note 1] | 2006 | 14.9 | 13 | 1.24 | |
| Koltsevaya (Circle) | Кольцевая | 1950 | 1954 | 19.3 | 12 | 1.61 | |
| Kaluzhsko-Rizhskaya | Калужско-Рижская | 1958 | 1990 | 37.8 | 24 | 1.63 | |
| Tagansko-Krasnopresnenskaya | Таганско-Краснопресненская | 1966 | 2015 | 42.2 | 23 | 1.92 | |
| Kalininskaya[Note 2] | Калининская | 1979 | 2012 | 16.3 | 8 | 2.36 | |
| Solntsevskaya[Note 2] | Солнцевская | 2014 | 2023 | 28,3 | 14 | 2.02 | |
| Serpukhovsko-Timiryazevskaya | Серпуховско-Тимирязевская | 1983 | 2002 | 41.5 | 25 | 1.72 | |
| Lyublinsko-Dmitrovskaya | Люблинско-Дмитровская | 1995 | 2023 | 44.3 | 26 | 1.77 | |
| Bolshaya Koltsevaya (Big Circle) | Большая кольцевая | 2018 | 2023 | 61.7 | 31 | 1.99 | |
| Butovskaya | Бутовская | 2003 | 2014 | 10.0 | 7 | 1.67 | |
| Moscow Central Circle[Note 3] | Московское центральное кольцо | 2016 | 2016 | 54.0 | 31 | 1.74 | |
| Nekrasovskaya | Некрасовская | 2019 | 2020 | 14.0 | 8 | 1,75 | |
| Total | 514.5 | 294 | 1.75 | ||||
| Light rail | |||||||
| Monorail[Note 4] | Монорельс | 2004 | 2004 | 4.7 | 6 | 0.94 | |
| Other urban rail lines [Note 5] | |||||||
| Line D1 (Moscow Central Diameters) | Белорусско-Савёловский диаметр | 2019 | 2020 | 52 | 24 | 2.26 | |
| Line D2 (Moscow Central Diameters) | Курско-Рижский диаметр | 2019 | 2023 | 80 | 35 | 2.29 | |
| Line D3 (Moscow Central Diameters) | Leningradskoe - Kazanskiy диаметр | 2023 | 2023 | 82 | 42 | 2.26 | |
| Line D4 (Moscow Central Diameters) | Kaluzhsko-Nizhegorodsky диаметр | 2023 | 2023 | 86 | 38 | 2.26 | |
| Total | 832.3 | 439 | 1.98 | ||||
| |||||||
Also, from 11 August 1969 to 26 October 2019, the Moscow Metro included Kakhovskaya line 3.3 km long with 3 stations, which closed for a long reconstruction. On 7 December 2021, Kakhovskaya is reopened after reconstruction as part of the Bolshaya Koltsevaya line. The renewed Varshavskaya and Kashirskaya stations reopened as part of the Bolshaya Koltsevaya line, which became fully functional on 1 March 2023. Its new stations included Pechatniki, Nagatinsky Zaton and Klenovy Bulvar.[15]
Renamed lines
- Sokolnicheskaya line was previously named Kirovsko-Fruzenskaya
- Zamoskvoretskaya line was previously named Gorkovsko-Zamoskvoretskaya.
- Filyovskaya line was previously named Arbatsko-Filyovskaya.
- Tagansko-Krasnopresnenskaya line was previously named Zhdanovsko-Krasnopresnenskaya
History




The first plans for a metro system in Moscow date back to the Russian Empire but were postponed by World War I, the October Revolution and the Russian Civil War. In 1923, the Moscow City Council formed the Underground Railway Design Office at the Moscow Board of Urban Railways. It carried out preliminary studies, and by 1928 had developed a project for the first route from Sokolniki to the city centre. At the same time, an offer was made to the German company Siemens Bauunion to submit its own project for the same route. In June 1931, the decision to begin construction of the Moscow Metro was made by the Central Committee of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union. In January 1932 the plan for the first lines was approved, and on 21 March 1933 the Soviet government approved a plan for 10 lines with a total route length of 80 km (50 mi).
The first lines were built using the Moscow general plan designed by Lazar Kaganovich, along with his project managers (notably Ivan M. Kuznetsov and, later, Isaac Y. Segal) in the 1930s–1950s, and the Metro was named after him until 1955 (Metropoliten im. L.M. Kaganovicha).[6] The Moscow Metro construction engineers consulted with their counterparts from the London Underground, the world's oldest metro system, in 1936: British architect Charles Holden and administrator Frank Pick had been working on the station developments of the Piccadilly Line extension, and Soviet delegates to London were impressed by Holden's thoroughly modern redeployment of classical elements and use of high-quality materials for the circular ticket hall of Piccadilly Circus, and so engaged Pick and Holden as advisors to Moscow's metro system.[16] Partly because of this connection, the design of Gants Hill tube station, which was completed in 1947, is reminiscent of a Moscow Metro station. Indeed, Holden's homage to Moscow has been described as a gesture of gratitude for the USSR's helpful role in The Second World War.[17][18]
Soviet workers did the labour and the art work, but the main engineering designs, routes, and construction plans were handled by specialists recruited from London Underground. The British called for tunnelling instead of the "cut-and-cover" technique, the use of escalators instead of lifts, the routes and the design of the rolling stock.[19] The paranoia of the NKVD was evident when the secret police arrested numerous British engineers for espionage because they gained an in-depth knowledge of the city's physical layout. Engineers for the Metropolitan-Vickers Electrical Company (Metrovick) were given a show trial and deported in 1933, ending the role of British business in the USSR.[20]
First four stages of construction
| External videos | |
|---|---|


The first line was opened to the public on 15 May 1935 at 07:00 am.[21] It was 11 kilometres (6.8 mi) long and included 13 stations. The day was celebrated as a technological and ideological victory for socialism (and, by extension, Stalinism). An estimated 285,000 people rode the Metro at its debut, and its design was greeted with pride; street celebrations included parades, plays and concerts. The Bolshoi Theatre presented a choral performance by 2,200 Metro workers; 55,000 colored posters (lauding the Metro as the busiest and fastest in the world) and 25,000 copies of "Songs of the Joyous Metro Conquerors" were distributed.[22] The Moscow Metro averaged 47 km/h (29 mph) and had a top speed of 80 km/h (50 mph).[23] In comparison, New York City Subway trains averaged a slower 25 miles per hour (40 km/h) and had a top speed of 45 miles per hour (72 km/h).[22] While the celebration was an expression of popular joy it was also an effective propaganda display, legitimizing the Metro and declaring it a success.
The initial line connected Sokolniki to Okhotny Ryad then branching to Park Kultury and Smolenskaya.[24] The latter branch was extended westwards to a new station (Kiyevskaya) in March 1937, the first Metro line crossing the Moskva River over the Smolensky Metro Bridge.
The second stage was completed before the war. In March 1938, the Arbatskaya branch was split and extended to the Kurskaya station (now the dark-blue Arbatsko-Pokrovskaya Line). In September 1938, the Gorkovskaya Line opened between Sokol and Teatralnaya. Here the architecture was based on that of the most popular stations in existence (Krasniye Vorota, Okhotnyi Ryad and Kropotkinskaya); while following the popular art-deco style, it was merged with socialist themes. The first deep-level column station Mayakovskaya was built at the same time.
Building work on the third stage was delayed (but not interrupted) during World War II, and two Metro sections were put into service; Teatralnaya–Avtozavodskaya (three stations, crossing the Moskva River through a deep tunnel) and Kurskaya–Partizanskaya (four stations) were inaugurated in 1943 and 1944 respectively. War motifs replaced socialist visions in the architectural design of these stations. During the Siege of Moscow in the fall and winter of 1941, Metro stations were used as air-raid shelters; the Council of Ministers moved its offices to the Mayakovskaya platforms, where Stalin made public speeches on several occasions. The Chistiye Prudy station was also walled off, and the headquarters of the Air Defence established there.
After the war ended in 1945, construction began on the fourth stage of the Metro, which included the Koltsevaya Line, a deep part of the Arbatsko-Pokrovskaya line from Ploshchad Revolyutsii to Kievskaya and a surface extension to Pervomaiskaya during the early 1950s. The decoration and design characteristic of the Moscow Metro is considered to have reached its zenith in these stations. The Koltsevaya Line was first planned as a line running under the Garden Ring, a wide avenue encircling the borders of Moscow's city centre. The first part of the line – from Park Kultury to Kurskaya (1950) – follows this avenue. Plans were later changed and the northern part of the ring line runs 1–1.5 kilometres (0.62–0.93 mi) outside the Sadovoye Koltso, thus providing service for seven (out of nine) rail terminals. The next part of the Koltsevaya Line opened in 1952 (Kurskaya–Belorusskaya), and in 1954 the ring line was completed.
Stalinist ideals in Metro's history

When the Metro opened in 1935, it immediately became the centrepiece of the transportation system (as opposed to horse-carried barrows still widely used in 1930s Moscow). It also became the prototype, the vision for future Soviet large-scale technologies. The artwork of the 13 original stations became nationally and internationally famous. For example, the Sverdlov Square subway station featured porcelain bas-reliefs depicting the daily life of the Soviet peoples, and the bas-reliefs at the Dynamo Stadium sports complex glorified sports and physical prowess on the powerful new "Homo Sovieticus" (Soviet man).[25] The metro was touted as the symbol of the new social order – a sort of Communist cathedral of engineering modernity.[26]
The Metro was also iconic for showcasing Socialist Realism in public art. The method was influenced by Nikolay Chernyshevsky, Lenin's favorite 19th-century nihilist, who stated that "art is no useful unless it serves politics".[22] This maxim sums up the reasons why the stations combined aesthetics, technology and ideology: any plan which did not incorporate all three areas cohesively was rejected.
- Kaganovich was in charge; he designed the subway so that citizens would absorb the values and ethos of Stalinist civilization as they rode. Without this cohesion, the Metro would not reflect Socialist Realism. If the Metro did not utilize Socialist Realism, it would fail to illustrate Stalinist values and transform Soviet citizens into socialists. Anything less than Socialist Realism's grand artistic complexity would fail to inspire a long-lasting, nationalistic attachment to Stalin's new society.[27]
- Socialist Realism was in fact a method, not exactly a style.[28]
Bright future and literal brightness in the Metro of Moscow

The Moscow Metro was one of the USSR's most ambitious architectural projects. The metro's artists and architects worked to design a structure that embodied svet (literally "light", figuratively "radiance" or "brilliance") and svetloe budushchee (a well-lit/radiant/bright future).[28] With their reflective marble walls, high ceilings and grand chandeliers, many Moscow Metro stations have been likened to an "artificial underground sun".[29]
This palatial underground environment[29] reminded Metro users their taxes were spent on materializing bright future; also, the design was useful for demonstrating the extra structural strength of the underground works (as in Metro doubling as bunkers, bomb shelters).
The chief lighting engineer was Abram Damsky, a graduate of the Higher State Art-Technical Institute in Moscow. By 1930 he was a chief designer in Moscow's Elektrosvet Factory, and during World War II was sent to the Metrostroi (Metro Construction) Factory as head of the lighting shop.[30] Damsky recognized the importance of efficiency, as well as the potential for light as an expressive form. His team experimented with different materials (most often cast bronze, aluminum, sheet brass, steel, and milk glass) and methods to optimize the technology.[30] Damsky's discourse on "Lamps and Architecture 1930–1950" describes in detail the epic chandeliers installed in the Taganskaya Station and the Kaluzhskaia station (Oktyabrskaya nowadays, not to be confused with contemporary "Kaluzhskaya" station on line 6).
The Kaluzhskaya Station was designed by the architect [Leonid] Poliakov. Poliakov's decision to base his design on a reinterpretation of Russian classical architecture clearly influenced the concept of the lamps, some of which I planned in collaboration with the architect himself. The shape of the lamps was a torch – the torch of victory, as Polyakov put it... The artistic quality and stylistic unity of all the lamps throughout the station's interior made them perhaps the most successful element of the architectural composition. All were made of cast aluminum decorated in a black and gold anodized coating, a technique which the Metrostroi factory had only just mastered.
The Taganskaia Metro Station on the Ring Line was designed in...quite another style by the architects K.S. Ryzhkov and A. Medvedev... Their subject matter dealt with images of war and victory...The overall effect was one of ceremony ... In the platform halls the blue ceramic bodies of the chandeliers played a more modest role, but still emphasised the overall expressiveness of the lamp.[30]
— Abram Damsky, Lamps and Architecture 1930–1950
The work of Abram Damsky further publicized these ideas hoping people would associate the party with the idea of bright future.
Industrialization
.jpg.webp)
Stalin's first five-year plan (1928–1932) facilitated rapid industrialization to build a socialist motherland. The plan was ambitious, seeking to reorient an agrarian society towards industrialism. It was Stalin's fanatical energy, large-scale planning, and resource distribution that kept up the pace of industrialization. The first five-year plan was instrumental in the completion of the Moscow Metro; without industrialization, the Soviet Union would not have had the raw materials necessary for the project. For example, steel was a main component of many subway stations. Before industrialization, it would have been impossible for the Soviet Union to produce enough steel to incorporate it into the metro's design; in addition, a steel shortage would have limited the size of the subway system and its technological advancement.
The Moscow Metro furthered the construction of a socialist Soviet Union because the project accorded with Stalin's second five-year plan. The Second Plan focused on urbanization and the development of social services. The Moscow Metro was necessary to cope with the influx of peasants who migrated to the city during the 1930s; Moscow's population had grown from 2.16 million in 1928 to 3.6 million in 1933. The Metro also bolstered Moscow's shaky infrastructure and its communal services, which hitherto were nearly nonexistent.[22]
Mobilization

The Communist Party had the power to mobilize; because the party was a single source of control, it could focus its resources. The most notable example of mobilization in the Soviet Union occurred during World War II. The country also mobilized in order to complete the Moscow Metro with unprecedented speed. One of the main motivation factors of the mobilization was to overtake the West and prove that a socialist metro could surpass capitalist designs. It was especially important to the Soviet Union that socialism succeed industrially, technologically, and artistically in the 1930s, since capitalism was at a low ebb during the Great Depression.
The person in charge of Metro mobilization was Lazar Kaganovich. A prominent Party member, he assumed control of the project as chief overseer. Kaganovich was nicknamed the "Iron Commissar"; he shared Stalin's fanatical energy, dramatic oratory flare, and ability to keep workers building quickly with threats and punishment.[22] He was determined to realise the Moscow Metro, regardless of cost. Without Kaganovich's managerial ability, the Moscow Metro might have met the same fate as the Palace of the Soviets: failure.

This was a comprehensive mobilization; the project drew resources and workers from the entire Soviet Union. In his article, archeologist Mike O'Mahoney describes the scope of the Metro mobilization:
A specialist workforce had been drawn from many different regions, including miners from the Ukrainian and Siberian coalfields and construction workers from the iron and steel mills of Magnitogorsk, the Dniepr hydroelectric power station, and the Turkestan-Siberian railway... materials used in the construction of the metro included iron from Siberian Kuznetsk, timber from northern Russia, cement from the Volga region and the norther Caucasus, bitumen from Baku, and marble and granite from quarries in Karelia, the Crimea, the Caucasus, the Urals, and the Soviet Far East[31]
— Mike O'Mahoney, Archeological Fantasies: Constructing History on the Moscow Metro
Skilled engineers were scarce, and unskilled workers were instrumental to the realization of the metro. The Metrostroi (the organization responsible for the Metro's construction) conducted massive recruitment campaigns. It printed 15,000 copies of Udarnik metrostroia (Metrostroi Shock Worker, its daily newspaper) and 700 other newsletters (some in different languages) to attract unskilled laborers. Kaganovich was closely involved in the recruitment campaign, targeting the Komsomol generation because of its strength and youth.
Later Soviet stations
"Fifth stage" set of stations

.jpg.webp)
The beginning of the Cold War led to the construction of a deep section of the Arbatsko-Pokrovskaya Line. The stations on this line were planned as shelters in the event of nuclear war. After finishing the line in 1953 the upper tracks between Ploshchad Revolyutsii and Kiyevskaya were closed, and later reopened in 1958 as a part of the Filyovskaya Line. The stations, too, were supplied with tight gates and life-sustenance systems to function as proper nuclear shelters.
In the further development of the Metro the term "stages" was not used any more, although sometimes the stations opened in 1957–1959 are referred to as the "fifth stage".
Nikita Khrushchev's era of cost cutting

_(5404633837).jpg.webp)

During the late 1950s and throughout the 1960s, the architectural extravagance of new Metro stations was decisively rejected on the orders of Nikita Khrushchev. He had a preference for a utilitarian "minimalism"-like approach to design, similar to Brutalism style. The idea behind the rejection was similar to one used to create Khrushchyovkas: cheap yet easily mass-produced buildings. Stations of his era, as well as most 1970s stations, were simple in design and style, with walls covered with identical square ceramic tiles. Even decorations at the Metro stations almost finished at the time of the ban (such as VDNKh and Alexeyevskaya) got their final decors simplified: VDNKh's arcs/portals, for example, got plain green paint to contrast with well-detailed decorations and pannos around them.
A typical layout of the cheap shallow-dug metro station (which quickly became known as Sorokonozhka – "centipede", from early designs with 40 concrete columns in two rows) was developed for all new stations, and the stations were built to look almost identical, differing from each other only in colours of the marble and ceramic tiles. Most stations were built with simpler, cheap technology; this resulted in utilitarian design being flawed in some ways. Some stations such as adjacent Rechnoi Vokzal and Vodny Stadion or sequiential Leninsky Prospect, Akadmicheskaya, Profsoyuznaya and Novye Cheryomushki would have a similar look due to the extensive use of same-sized white or off-white ceramic tiles with hard-to-feel differences.
Walls with cheap ceramic tiles were susceptible to train-related vibration: some tiles would eventually fall off and break. It was not always possible to replace the missing tiles with the ones of the exact color and tone, which eventually led to variegated parts of the walls.
Metro stations of late USSR
The contrasting style gap between the powerfully decorated stations of Moscow's center and the spartan-looking stations of the 1960s was eventually filled. In the mid-1970s the architectural extravagance was partially restored. However, the newer design of shallow "centipede" stations (now with 26 columns, more widely spaced) continued to dominate. For example, Kaluzhskaya "centipede" station from 1974 (adjacent to Novye Cheryomushki station) features non-flat tiles (with 3D effect utilized), and Medvedkovo from 1978 features complex decorations.
1971 station Kitay-Gorod ("Ploshchad Nogina" at the time) features cross-platform interchange (Line 6 and line 7). Although built without "centipede" design or cheap ceramic tiles, the station utilizes near-grayscale selection of colors. It is to note the "southbound" and "northbound" halls of the station have identical look.
Babushkinskaya station from 1978 is a no-column station (similar to Biblioteka Imeni Lenina from 1935). 1983 Chertanovskaya station has resemblance to Kropotkinskaya (from 1935). Some stations, such as the deep-dug Shabolovskaya (1980), have the near-tunnel walls decorated with metal sheets, not tiles. Tyoply Stan features a theme related to the name and the location of the station ("Tyoply Stan" used to literally mean warm area): its walls are covered in brick-colored ribbed panes, which look like radiators).
Downtown area got such stations as Borovitskaya (1986), with uncovered red bricks and gray, concrete-like colors accompanying a single gold-plated decorative pane known as "Tree of peoples' of USSR" or additional station hall for Tretyakovskaya to house cross-platform interchange system between line 6 and line 8. To this day, Tretyakovskaya metro station consists of two contrasting halls: brutalism-like 1971 hall and custom design hall reminiscent of Tretyakovskaya Galereya from 1986.
Post-USSR stations of the modern Russian Federation
Metro stations of the 1990s and 2000s vary in style, but some of the stations seem to have their own themes:


- Ulitsa Akademika Yangelya station used to feature thick orange neon lamp-like sodium lights instead of regular white lights.
- Park Pobedy, the deepest station of the Moscow Metro, was built in 2003; it features extensive use of dark orange polished granite.
- Slavyansky Bulvar station utilizes a plant-inspired theme (similar to "bionic style").
- The sleek variant of aforementioned bionic style is somewhat represented in various Line 10 stations.
- Sretensky Bulvar station of line 10 is decorated with paintings of nearby memorials and locations.
- Strogino station has a theme of huge eye-shaped boundaries for lights; with "eyes" occupying the station's ceiling.
- Troparyovo (2014) features trees made of polished metal. The trees hold the station's diamond-shaped lights. The station, however, is noticeably dim-lit.
- Delovoy Tsentr (2016, MCC, overground station) has green tint.
- Lomonosovsky Prospekt (Line 8A) is decorated with various equations.
- Olkhovaya (2019) uses other plant-inspired themes (ольха noun means alder) with autumn/winter inspired colours.
- Kosino (2019) uses high-tech style with the addition of thin LED lights.
Some bleak, bland-looking "centipedes" like Akademicheskaya and Yugo-Zapadnaya have undergone renovations in the 21st century (new blue-striped white walls on Akademicheskaya, aqualine glassy, shiny walls on Yugo-Zapadnaya).
Moscow Central Circle urban railway (Line 14)

.jpg.webp)
A new circle metro line in Moscow was relatively quickly made in the 2010s. The Moscow Central Circle line (Line 14) was opened for use in September 2016 by re-purposing and upgrading the Maloe ZheleznoDorozhnoe Kol'tso. A proposal to convert that freight line into a metropolitan railway with frequent passenger service was announced in 2012. The original tracks had been built in pre-revolutionary Moscow decades before the creation of Moscow Metro; the tracks remained in place in one piece as a non-electrified line until the 21st century. Yet the circle route was never abandoned or cut. New track (along the existing one) was laid and all-new stations were built between 2014 and 2016. MCC's stations got such amenities as vending machines and free water closets.
Line 14 is operated by Russian Railways and uses full-sized trains (an idea, somewhat similar to S-Train). The extra resemblance to an S-Train line is, the 1908 line now connects modern northern residential districts to western and southern downtown area, with a station adjacent to Moscow International Business Center.

There is a noticeable relief of congestion, decrease in usage of formerly overcrowded Koltsevaya line since the introduction of MCC. To make line 14 attractive to frequent Koltsevaya line interchanges users, upgrades over regular comfort of Moscow Metro were made. Use of small laptops/portable video playing devices and food consumption from tupperwares and tubs was also improved for Line 14: the trains have small folding tables in the back of nearly every seat, while the seats are facing one direction like in planes or intercity buses - unlike side-against-side sofas typical for Metro.
Unlike MCD lines (D1, D2 etc.) MCC line accepts "unified" tickets and "Troika" cards just like Moscow Metro and buses of Moscow do. Free transfers are permitted between the MCC and the Moscow Metro if the trip before the transfer is less than 90 minutes.[32] It's made possible by using same "Ediny", literally "unified" tickets instead of printing "paper tickets" used at railroads.
- To interchange to line 14 for free, passenger must keep their freshly used ticket after entering Moscow Metro to apply it upon entering any line 14 station (and vice versa, keep their "fresh" ticket to enter underground Metro line after leaving Line 14 for an interchange).
MCD (D lines)
In 2019, new lines of Russian Railways got included in the map of Metro as "line D1" and "line D2". Unlike Line 14, the MCD lines actually form S-Train lines, bypassing the "vokzals", terminus stations of respective intercity railways. Line D3 is planned to be launched in August 2023, while D4 will be launched in September of that year. The schedule for the development of the infrastructure of the Central Transport Hub in 2023 was signed by the Moscow Mayor Sergei Sobyanin and the head of Russian Railways Oleg Belozerov in December 2022.[33]
As for the fees, MCD accepts Moscow's "Troika" cards. Also, every MCD station has printers which print "station X – station Y" tickets on paper. Users of the D lines must keep their tickets until exiting their destination stations: their exit terminals require a valid "... to station Y" ticket's barcode.
Big Circle Line (line 11)
After upgrading the railway from 1908 to a proper Metro line, the development of another circle route was re-launched, now adjusted for the pear-shaped circle route of line #14.
Throughout the late 2010s, Line 11 was extended from short, tiny Kakhovskaya line to a half-circle (from Kakhovskaya to Savyolovskaya. In early 2023, the circle was finished.[34]
- Similarly made Shelepikha, Khoroshovskaya, CSKA and Petrovsky Park stations have lots of polished granite and shiny surfaces, in contrast to Soviet "centipedes". Throughout 2018–2021, these stations were connected to line 8A.
- Narodnoye Opolcheniye (2021) features lots of straight edges and linear decorations (such as uninterrupted "three stripes" style of the ceiling lights and rectangular columns).
As for the spring of 2023, the whole circle route line is up and running, forming a circle stretching to the southern near-MKAD residential parts of the city (Prospekt Vernadskogo, Tekstilshchiki) as opposed to the MCC's stretching towards the northern districts of Moscow. In other words, it "mirrors" Line 14 rather than forming a perfect circle around the city centre. While being 70 km long, the line is now the longest subway line in the world, 13 kilometres ahead of the previous record holder - the line 10 of Beijing Subway.[35]
Logo
The first line of the Moscow Metro was launched in 1935, complete with the first logo, the capital M paired with the text "МЕТРО". There is no accurate information about the author of the logo, so it is often attributed to the architects of the first stations – Samuil Kravets, Ivan Taranov and Nadezhda Bykova. At the opening in 1935, the M letter on the logo had no definite shape.[36]
Today, with at least ten different variations of the shape in use, Moscow Metro still does not have clear brand or logo guidelines. An attempt was made in October 2013 to launch a nationwide brand image competition, only to be closed several hours after its announcement. A similar contest, held independently later that year by the design crowdsourcing company DesignContest, yielded better results, though none were officially accepted by the Metro officials.[37][38]
Ticketing

_(7221508840).jpg.webp)
Moscow Metro underground has neither "point A – point B" tariffs nor "zone" tariffs. Instead, it has a fee for a "ride", e.g. for a single-time entry without time or range limit. The exceptions "only confirm the rule": the "diameters" (Dx lines) and the Moscow Central Circle (Line 14) are Russian Railways' lines hence the shared yet not unified tariff system.
As for October 2021, one ride costs 60 rubles (approx. 1 US dollar). Discounts (up to 33%) for individual rides are available upon buying rides "in bulk" (buying multiple-trip tickets (such as twenty-trip or sixty-trip ones)), and children under age seven can travel free (with their parents). Troika "wallet" (a card, similar to Japanese Suica card) also offers some discounts for using the card instead of queueing a line for a ticket. "Rides" on the tickets available for a fixed number of trips, regardless of distance traveled or number of transfers.
- An exception in case of MCC e.g. Line 14: for a free interchange, one should interchange to it/from it within 90 minutes after entering the Metro. However, one can ride it for hours and use its amenities without leaving it.
There are tickets without "rides" as well: – a 24-hour "unified" ticket (265 rub in 2022), a 72-hour ticket, a month-long ticket, and a year-long ticket.
Fare enforcement takes place at the points of entry. Once a passenger has entered the Metro system, there are no further ticket checks – one can ride to any number of stations and make transfers within the system freely. Transfers to other public-transport systems (such as bus, tram, trolleybus/"electrobus") are not covered by the very ride used to enter Metro. Transfer to monorail and MCC is a free addition to the ride (available up to 90 minutes after entering a metro station).
In modern Metro, turnstiles accept designated plastic cards ("Troika", "social cards") or disposable-in-design RFID chip cardboard cards. Unlimited cards are also available for students at reduced price (as of 2017, 415 rubles—or about $US6—for a calendar month of unlimited usage) for a one-time cost of 70 rubles. Transport Cards impose a delay for each consecutive use; i.e. the card can not be used for 7 minutes after the user has passed a turnstile.
History of smart ticketing
Soviet era turnstiles simply accepted N kopeck coins.
In the early years of Russian Federation (and with the start of a hyperinflation) plastic tokens were used. Disposable magnetic stripe cards were introduced in 1993 on a trial basis, and used as unlimited monthly tickets between 1996 and 1998. The sale of tokens ended on 1 January 1999, and they stopped being accepted in February 1999; from that time, magnetic cards were used as tickets with a fixed number of rides.
On 1 September 1998, the Moscow Metro became the first metro system in Europe to fully implement "contactless" smart cards, known as Transport Cards. Transport Cards were the card to have unlimited amount of trips for 30, 90 or 365 days, its active lifetime was projected as 3½ years. Defective cards were to be exchanged at no extra cost.
- In August 2004, the city government launched the Muscovite's Social Card program. Social Cards are free smart cards issued for the elderly and other groups of citizens officially registered as residents of Moscow or the Moscow region; they offer discounts in shops and pharmacies, and double as credit cards issued by the Bank of Moscow. Social Cards can be used for unlimited free access to the city's public-transport system, including the Moscow Metro; while they do not feature the time delay, they include a photograph and are non-transferable.
- Since 2006, several banks have issued credit cards which double as Ultralight cards and are accepted at turnstiles. The fare is passed to the bank and the payment is withdrawn from the owner's bank account at the end of the calendar month, using a discount rate based on the number of trips that month (for up to 70 trips, the cost of each trip is prorated from current Ultralight rates; each additional trip costs 24.14 rubles).[39] Partner banks include the Bank of Moscow, CitiBank, Rosbank, Alfa-Bank and Avangard Bank.[40]
In January 2007, Moscow Metro began replacing limited magnetic cards with contactless disposable tickets based on NXP's MIFARE Ultralight technology. Ultralight tickets are available for a fixed number of trips in 1, 2, 5, 10, 20 and 60-trip denominations (valid for 5 or 90 days from the day of purchase) and as a monthly ticket, only valid for a selected calendar month and limited to 70 trips. The sale of magnetic cards ended on 16 January 2008 and magnetic cards ceased to be accepted in late 2008, making the Moscow metro the world's first major public-transport system to run exclusively on a contactless automatic fare-collection system.[41]
On 2 April 2013, Moscow Transport Department introduced a smartcard-based transport electronic wallet, named Troika. Three more smart cards have been launched:
- Ediniy's RFID-chip card, a "disposable"-design cardboard card for all city-owned public transport operated by Mosgortrans and Moscow Metro;
- 90 minutes card, an unlimited "90-minute" card
- and TAT card for surface public transport operated by Mosgortrans.[42]
One can "record" N-ride Ediniy ticket on Troika card as well in order to avoid carrying the easily frayed cardboard card of Ediniy for weeks (e.g. to use Troika's advanced chip). The turnstiles of Moscow Metro have monochrome screens which show such data as "money left" (if Troika is used as a "wallet"), "valid till DD.MM.YYYY" (if a social card is used) or "rides left" (if Ediniy tariff ticket is used).
Along with the tickets, new vending machines were built to sell tickets (1 or 2 rides) and put payments on Troika cards. At that time, the machines were not accepting contactless pay. The same machines now have tiny terminals with keypads for contactless payments (allowing quick payment for Troika card).
In 2013, as a way to promote both the "Olympic Games in Sochi and active lifestyles, Moscow Metro installed a vending machine that gives commuters a free ticket in exchange for doing 30 squats."[43]
Since the first quarter of 2015, all ticket windows (not turnstiles) at stations accept bank cards for fare payment. Passengers are also able to pay for tickets via contactless payment systems, such as PayPass technology. Since 2015, fare gates at stations accept mobile ticketing via a system which the Metro calls Mobilny Bilet (Мобильный билет) which requires NFC-handling smartphone (and a proper SIM-card). The pricing is the same as Troika's. Customers are able to use Mobile Ticket on Moscow's surface transport.[44] The Moscow Metro originally announced plans to launch the mobile ticketing service with Mobile TeleSystems (MTS) in 2010.[45]
In October 2021, the Moscow Metro became the first metro system in the world to offer Face-Pay to their customers. In order to use this system, passengers will need to connect their photo, bank card and metro card to the service through the metro’s mobile app. For this purpose, the metro authorities plan to equip over 900 turnstiles in over 240 stations with biometric scanners. This enables passengers to pay for their ride without taking out their phone, metro or bank card and therefore increasing passenger flow at the station entrances. In 2022, Face-Pay was used over 32 million times over the course of the year.
Fares
| Trip limit | Cost for central zone | Cost for suburban zone |
|---|---|---|
| Ediny ticket. Valid for metro, monorail, MCC and ground transport. Not valid for MCD. | ||
| 1 ride | 62 | - |
| 2 rides | 124 | - |
| Koshelek ticket on the Troika card. Valid for all public transport in Moscow (Metro, MCC, all surface transport, suburban electric trains). | ||
| 1 ride | 50 | 65 |
| 90 minutes | 75 | - |
| Ediny ticket on the Troika card. Valid for all metro, monorail, MCC, MCD zones "Central", "Suburban" or land transport. | ||
| 60 trips | 2.730 | – |
| 1 day | 285 | – |
| 3 nights | 540 | – |
| 30 days | 2.540 | 3.010 |
| 90 days | 6.150 | 7.800 |
| 365 days | 19.500 | 24.450 |
MCD network is divided between the "Central" and "Suburban" zone. Metro (with the monorail and the MCC) is completely within the Central zone.
| Effective date | Price | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| 1935-05-15 | 50 kopecks | |
| 1935-08-01 | 40 kopecks | with season ticket – 35 kopecks |
| 1935-10-01 | 30 kopecks | with season ticket – 25 kopecks |
| 1942-05-31 | 40 kopecks | |
| 1948-08-16 | 50 kopecks | Banknotes were cut in value to one-tenth but most prices stayed the same |
| 1961-01-01 | 5 kopecks | redenomination; turnstiles accepted 5 kopek coins |
| 1991-04-02 | 15 kopecks | Turnstiles accepted three 5 kopeck coins (written 5+5+5) |
| 1992-03-01 | 50 kopecks | 5 kopeck coins were replaced by turnstile tokens |
| 1992-06-24 | 1 ruble | |
| 1992-12-01 | 3 rubles | |
| 1993-02-16 | 6 rubles | |
| 1993-06-25 | 10 rubles | |
| 1993-10-15 | 30 rubles | |
| 1994-01-01 | 50 rubles | |
| 1994-03-18 | 100 rubles | |
| 1994-06-23 | 150 rubles | |
| 1994-09-21 | 250 rubles | |
| 1994-12-20 | 400 rubles | |
| 1995-03-20 | 600 rubles | |
| 1995-07-21 | 800 rubles | |
| 1995-09-20 | 1,000 rubles | |
| 1995-12-21 | 1,500 rubles | |
| 1997-06-11 | 2,000 rubles | |
| 1998-01-01 | 2 rubles | Redenomination due to post-Soviet inflation |
| 1998-09-01 | 3 rubles | |
| 1999-01-01 | 4 rubles | |
| 2000-07-15 | 5 rubles | |
| 2002-10-01 | 7 rubles | |
| 2004-04-01 | 10 rubles | |
| 2005-01-01 | 13 rubles | Monorail fare is 50 rubles (25 rubles discount fare), no other tickets are valid on monorail |
| 2006-01-01 | 15 rubles | |
| 2007-01-01 | 17 rubles | |
| 2008-01-01 | 19 rubles | Monorail fare is equal to the metro fare (reduced to 19 rubles), and only special monthly tickets also available and valid on this line |
| 2009-01-01 | 22 rubles | |
| 2010-01-01 | 26 rubles | |
| 2011-01-01 | 28 rubles | Russian Railways fare in Moscow fare principles are separated and the fare did not increase (26 rubles) unlike in earlier years. |
| 2013-01-01 | 28 rubles | minor change: Monorail fare included in all metro fares, first transfer in 90 minutes does not charge |
| 2013-04-02 | 30 rubles | Single journey fare increased. Most other kinds of fares are lowered. New: 90 minute fare. |
| 2014-01-01 | 30–40 rubles | Single and double fare increased. 5–60 pass fare, and all 90 minute fare are stayed. Russian railway fare in Moscow increased to 28 rubles. |
| 2016-01-01 | 32–50 rubles | All ticket fares increased. Single fare increased to 50 rubles or 32 rubles (by Troika e-wallet). All unlimited fare are stayed.[46] |
| 2017-01-01 | 35–55 rubles | All ticket fares increased. Single fare increased to 55 rubles or 35 rubles (by Troika e-wallet). All |-unlimited fare are stayed. |
| 2018-01-02 | 36–55 rubles | Single fare increased by 1 ruble, only while paying by Troika e-wallet. 90 minutes fare increased from 54 to 56 rubles. |
| 2019-01-02 | 38–55 rubles | Single fare increased by 2 rubles, while paying Troika card. 90 minutes tickets increased by 3 rubles. |
| 2019-12-09 | 38–55 rubles | 4 of 10 railway lines included in metro fare; central zone does not require (0–2 zones), surburbian +7RUR (but 7 RUR is difference only, 2–3 zones cost 23 RUR as earlier) |
| 2020-02-01 | 40–57 rubles | fares increased by 2 rubles, season tickets stayed. Also opened Ostafievo in zone 5 that caused to lower some fares is you set as destation and course of another ticket |
| 2020-04-21 | 40 rubles | Till 2010-06-09 COVID-19 restriction: single fare tickets are eliminated, bank cards disabled till June 9, some discount ticked also blocked (dates non shown) |
| 2020-02-01 | 42–60 rubles | fares raised except 90/365 days |
Expansions
Since the turn of the 2nd millennium several projects have been completed, and more are underway. The first was the Annino-Butovo extension, which extended the Serpukhovsko-Timiryazevskaya Line from Prazhskaya to Ulitsa Akademika Yangelya in 2000, Annino in 2001 and Bulvar Dmitriya Donskogo in 2002. Its continuation, an elevated Butovskaya Line, was inaugurated in 2003. Vorobyovy Gory station, which initially opened in 1959 and was forced to close in 1983 after the concrete used to build the bridge was found to be defective, was rebuilt and reopened after many years in 2002. Another recent project included building a branch off the Filyovskaya Line to the Moscow International Business Center. This included Vystavochnaya (opened in 2005) and Mezhdunarodnaya (opened in 2006).
The Strogino–Mitino extension began with Park Pobedy in 2003. Its first stations (an expanded Kuntsevskaya and Strogino) opened in January 2008, and Slavyansky Bulvar followed in September. Myakinino, Volokolamskaya and Mitino opened in December 2009. Myakinino station was built by a state-private financial partnership, unique in Moscow Metro history.[47] A new terminus, Pyatnitskoye Shosse, was completed in December 2012.
After many years of construction, the long-awaited Lyublinskaya Line extension was inaugurated with Trubnaya in August 2007 and Sretensky Bulvar in December of that year. In June 2010, it was extended northwards with the Dostoyevskaya and Maryina Roscha stations. In December 2011, the Lyublinskaya Line was expanded southwards by three stations and connected to the Zamoskvoretskaya Line, with the Alma-Atinskaya station opening on the latter in December 2012. The Kalininskaya Line was extended past the Moscow Ring Road in August 2012 with Novokosino station.
In 2011, works began on the Third Interchange Contour that is set to take the pressure off the Koltsevaya Line.[48] Eventually the new line will attain a shape of the second ring with connections to all lines (except Koltsevaya and Butovskaya).[49]
In 2013, the Tagansko-Krasnopresnenskaya Line was extended after several delays to the south-eastern districts of Moscow outside the Ring Road with the opening of Zhulebino and Lermontovsky Prospekt stations. Originally scheduled for 2013, a new segment of the Kalininskaya Line between Park Pobedy and Delovoy Tsentr (separate from the main part) was opened in January 2014, while the underground extension of Butovskaya Line northwards to offer a transfer to the Kaluzhsko-Rizhskaya Line was completed in February. Spartak, a station on the Tagansko-Krasnopresnenskaya Line that remained unfinished for forty years, was finally opened in August 2014. The first stage of the southern extension of the Sokolnicheskaya Line, the Troparyovo station, opened in December 2014.
Current plans
In addition to major metro expansion the Moscow Government and Russian Railways plans to upgrade more commuter railways to a metro-style service, similar to the MCC. New tracks and stations are planned to be built in order to achieve this.
| Line | Terminals | Length (km) | Stations | Status | Planned opening | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Novatorskaya | Kommunarka | 19 | 7 | Under construction | 2024 | |
| Kommunarka | Potapovo | 2.4 | 1 | Under construction | 2024 | |
| Novatorskaya | ZIL | 8.5 | 4 | Under construction | 2025 | |
| Shelepikha | Bulvar Karbysheva | 3.7 | 3 | Under construction | ||
| Suvorovskaya | 0 | 1 | Under construction | |||
| ZIL | Biryulyovo | 22.2 | 10 | Under Construction | ||
| Yuzhny Port | 0 | 1 | Planned | |||
| Shchyolkovskaya | Golyanovo | 1.5 | 1 | Planned | ||
| Kommunarka | Troitsk | 6 | Planned | |||
| Bulvar Karbysheva | Ilyinskaya | 5 | Planned | |||
| Tretyakovskaya | Delovoy Tsentr | 5.1 | 3 | Planned | ||
Metro 2
Conspiracy theorists have claimed that a second and deeper metro system code-named "D-6",[50] designed for emergency evacuation of key city personnel in case of nuclear attack during the Cold War, exists under military jurisdiction. It is believed that it consists of a single track connecting the Kremlin, chief HQ (General Staff –Genshtab), Lubyanka (FSB Headquarters), the Ministry of Defense and several other secret installations. There are alleged to be entrances to the system from several civilian buildings, such as the Russian State Library, Moscow State University (MSU) and at least two stations of the regular Metro. It is speculated that these would allow for the evacuation of a small number of randomly chosen civilians, in addition to most of the elite military personnel. A suspected junction between the secret system and the regular Metro is supposedly behind the Sportivnaya station on the Sokolnicheskaya Line. The final section of this system was supposedly completed in 1997.[51]
Statistics
.jpg.webp)
| Ridership statistics | |
|---|---|
| Passengers (2018) | 2,500,400,000 passengers[1] |
| —— full-fare | 1,812,900,000 passengers |
| —— privileged category | 473,500,000 passengers |
| —— pupils and students | 214,000,000 passengers |
| Maximum daily ridership | 9,715,635 passengers |
| Revenue from fares (2005) | 15.9974 billion rubles |
| Average passenger trip | 14.93 kilometres (9.28 mi) |
| Line statistics | |
| Total lines length | 333.3 kilometres (207.1 mi) |
| Number of lines | 15 |
| Longest line | Arbatsko-Pokrovskaya Line (43.5 kilometres (27.0 mi)) |
| Shortest line | Kakhovskaya Line (3.3 kilometres (2.1 mi)) |
| Longest section | Strogino–Krylatskoye (6.7 kilometres (4.2 mi)) |
| Shortest section | Vystavochnaya–Mezhdunarodnaya (502 metres (1,647 ft)) |
| Station statistics | |
| Number of stations | 228 |
| — transfer stations | 68 |
| — transfer points | 29 |
| — surface/elevated | 16 |
| Deepest station | Park Pobedy (84 metres (276 ft)) |
| Shallowest underground station | Pechatniki |
| Station with the longest platform | Vorobyovy Gory (Metro) (282 metres (925 ft)) |
| Number of stations with a single entrance | 73 |
| Infrastructure statistics | |
| Number of turnstiles with automatic control on entrances | 2,374 |
| Number of stations with escalators | 125 |
| Number of escalators | 631 |
| — including Monorail stations | 18 |
| Longest escalator | 126 metres (413 ft) (Park Pobedy) |
| Total number of ventilation shafts | 393 |
| Number of local ventilation systems in use | 4,965 |
| Number of medical assistance points (2005) | 46 |
| Total length of all escalators | 65.4 kilometres (40.6 mi) |
| Rolling stock statistics | |
| Number of train maintenance depots | 16 |
| Total number of train runs per day | 9,915 |
| Average speed: | |
| — commercial | 41.71 kilometres per hour (25.92 mph) |
| — technical (2005) | 48.85 kilometres per hour (30.35 mph) |
| Total number of cars (average per day) | 4,428 |
| Cars in service (average per day) | 3,397 |
| Annual run of all cars | 722,100,000 kilometres (448,700,000 mi) |
| Average daily run of a car | 556.2 kilometres (345.6 mi) |
| Average passengers per car | 53 people |
| Timetable fulfillment | 99.96% |
| Minimum average interval | 90 sec |
| Staff statistics | |
| Total number of employees | 34,792 people |
| — males | 18,291 people |
| — females | 16,448 people |
Notable incidents
1977 bombing
On 8 January 1977, a bomb was reported to have killed 7 and seriously injured 33. It went off in a crowded train between Izmaylovskaya and Pervomayskaya stations.[52] Three Armenians were later arrested, charged and executed in connection with the incident.[53]
1981 station fires
In June 1981, seven bodies were seen being removed from the Oktyabrskaya station during a fire there. A fire was also reported at Prospekt Mira station about that time.[54]
1982 escalator accident
A fatal accident occurred on 17 February 1982 due to an escalator collapse at the Aviamotornaya station on the Kalininskaya Line. Eight people were killed and 30 injured due to a pileup caused by faulty emergency brakes.[55]
1996 murder
In 1996, an American-Russian businessman Paul Tatum was murdered at the Kiyevskaya Metro station. He was shot dead by a man carrying a concealed Kalashnikov gun.[56]
2000 bombings
On 8 August 2000, a strong blast in a Metro underpass at Pushkinskaya metro station in the center of Moscow claimed the lives of 12, with 150 injured. A homemade bomb equivalent to 800 grams of TNT had been left in a bag near a kiosk.[57]
2004 bombings
On 6 February 2004, an explosion wrecked a train between the Avtozavodskaya and Paveletskaya stations on the Zamoskvoretskaya Line, killing 41 and wounding over 100.[58] Chechen terrorists were blamed. A later investigation concluded that a Karachay-Cherkessian resident had carried out a suicide bombing. The same group organized another attack on 31 August 2004, killing 10 and injuring more than 50 others.
2005 Moscow blackout
On 25 May 2005, a citywide blackout halted operation on some lines. The following lines, however, continued operations: Sokolnicheskaya, Zamoskvoretskaya from Avtozavodskaya to Rechnoy Vokzal, Arbatsko-Pokrovskaya, Filyovskaya, Koltsevaya, Kaluzhsko-Rizhskaya from Bitsevskiy Park to Oktyabrskaya-Radialnaya and from Prospekt Mira-Radialnaya to Medvedkovo, Tagansko-Krasnopresnenskaya, Kalininskaya, Serpukhovsko-Timiryazevskaya from Serpukhovskaya to Altufyevo and Lyublinskaya from Chkalovskaya to Dubrovka.[59] There was no service on the Kakhovskaya and Butovskaya lines. The blackout severely affected the Zamoskvoretskaya and Serpukhovsko-Timiryazevskaya lines, where initially all service was disrupted because of trains halted in tunnels in the southern part of city (most affected by the blackout). Later, limited service resumed and passengers stranded in tunnels were evacuated. Some lines were only slightly impacted by the blackout, which mainly affected southern Moscow; the north, east and western parts of the city experienced little or no disruption.[59]
2006 billboard incident

On 19 March 2006, a construction pile from an unauthorized billboard installation was driven through a tunnel roof, hitting a train between the Sokol and Voikovskaya stations on the Zamoskvoretskaya Line. No injuries were reported.[60]
2010 bombing
On 29 March 2010, two bombs exploded on the Sokolnicheskaya Line, killing 40 and injuring 102 others. The first bomb went off at the Lubyanka station on the Sokolnicheskaya Line at 7:56, during the morning rush hour.[61] At least 26 were killed in the first explosion, of which 14 were in the rail car where it took place. A second explosion occurred at the Park Kultury station at 8:38, roughly forty minutes after the first one.[61] Fourteen people were killed in that blast. The Caucasus Emirate later claimed responsibility for the bombings.
2014 pile incident
On 25 January 2014, at 15:37 a construction pile from a Moscow Central Circle construction site was driven through a tunnel roof between Avtozavodskaya and Kolomenskaya stations on the Zamoskvoretskaya Line. The train operator applied emergency brakes, and the train did not crash into the pile. Passengers were evacuated from the tunnel, with no injures reported. The normal line operation resumed the same day at 19:50.[62]
2014 derailment
On 15 July 2014, a train derailed between Park Pobedy and Slavyansky Bulvar on the Arbatsko-Pokrovskaya Line, killing 24 people and injuring dozens more.[63][64]
In popular culture
The Moscow Metro is the central location and namesake for the Metro series, where during a nuclear war, Moscow's inhabitants are driven down into the Moscow Metro, which has been designed as a fallout shelter, with the various stations being turned into makeshift settlements.
In 2012, an art film was released about a catastrophe in the Moscow underground.[65]
See also
Notes
- ↑ Russian: Московский метрополитен, IPA: [mɐˈskofskʲɪj mʲɪtrəpəlʲɪˈtɛn])
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Метрополитен в цифрах [Metropolitan in figures] (in Russian). Moscow Metro. Archived from the original on 26 December 2018. Retrieved 17 March 2018.
- ↑ "Как выглядят новые станции Большой кольцевой линии метро". MSK News. March 2023.
- ↑ "The best places to visit in Moscow". Expatica.
- ↑ "Москва первой в мире снизила интервал движения поездов метро до 90 секунд". Moscow 24.
- ↑ "Имя Ленина оставят в названиях станций московского метро Подробнее". MОСКВА24. 18 May 2016. Retrieved 2 February 2023.
- 1 2 Metro.ru Original order on naming the Metro after Kaganovich. Retrieved Archived 10 July 2001 at archive.today 19 October 2007
- ↑ Корябкин, Андрей (1 June 2020). "Московское метро: Лазарю – Лазарево, Ленину – ленинское". vgudok Light. Retrieved 2 February 2023.
- ↑ "Московский метрополитен".
- ↑ "Lines and stations". Moscow Metro website. Archived from the original on 30 December 2014. Retrieved 22 January 2015.
- ↑ See this image as an example
- ↑ "Режим работы станций и вестибюлей". Moscow Metro. Archived from the original on 17 November 2011. Retrieved 17 January 2015.
- ↑ "С сегодняшнего дня сеть Wi-Fi стала доступна на всех линиях Московского метрополитена". 1tv.ru (in Russian). Channel One Russia. 2 December 2014. Retrieved 12 April 2021.
- ↑ "The people's palace: exploring Moscow Metro's evolving designs". railway-technology.com. 10 December 2018. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- 1 2 Голоса в метро. Official blog of Moscow Metro (in Russian). 26 November 2010. Archived from the original on 24 January 2015. Retrieved 22 January 2015.
- ↑ "Ликсутов: После полного запуска БКЛ пассажиры уже совершили по новому кольцу 53,4 миллиона поездок". msk.kp.ru (in Russian). 3 May 2023. Retrieved 6 May 2023.
- ↑ Wilson, Vicky (2018). London's Oddities. Metro Publications Ltd. p. 310. ISBN 978-1-902910-53-6.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 25 March 2009. Retrieved 20 October 2008.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ Lawrence, David (1994). Underground Architecture. Harrow: Capital Transport. ISBN 1-85414-160-0.
- ↑ Michael Robbins, "London Underground and Moscow Metro," Journal of Transport History, (1997) 18#1 pp 45–53.
- ↑ Gordon W. Morrell, "Redefining Intelligence and Intelligence-Gathering: The Industrial Intelligence Centre and the Metro-Vickers Affair, Moscow 1933," Intelligence and National Security (1994) 9#3 pp 520–533.
- ↑ Sachak (date unknown). История создания Московского метро (History of Moscow Metro) (in Russian)
- 1 2 3 4 5 Jenks, Andrew (October 2000). "A Metro on the Mount: The Underground as a Church of Soviet Civilization". Technology and Culture. 41 (4): 697–724. doi:10.1353/tech.2000.0160. JSTOR 2517594. S2CID 108455892.
- ↑ Moscow Metro / Moscow Metro / General Information / Key Performance Indicators Archived 10 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine. Engl.mosmetro.ru. Retrieved on 17 August 2013.
- ↑ First Metro map. Retrieved from "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 25 March 2009. Retrieved 19 February 2009.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link). - ↑ Isabel Wünsche, "Homo Sovieticus: The Athletic Motif in the Design of the Dynamo Metro Station," Studies in the Decorative Arts (2000) 7#2 pp 65–90
- ↑ Andrew Jenks, "A Metro on the Mount," Technology & Culture (2000) 41#4 pp 697–723
- ↑ Voyce, Arthur (January 1956). "Soviet Art and Architecture: Recent Developments". Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science. Russia Since Stalin: Old Trends and New Problems. 303: 104–115. doi:10.1177/000271625630300110. JSTOR 1032295. S2CID 144177034.
- 1 2 Cooke, Catherine (1997). "Beauty as a Route to 'the Radiant Future': Responses of Soviet Architecture". Journal of Design History. Design, Stalin and the Thaw. 10 (2): 137–160. doi:10.1093/jdh/10.2.137. JSTOR 1316129.
- 1 2 Bowlt, John E. (2002). "Stalin as Isis and Ra: Socialist Realism and the Art of Design". The Journal of Decorative and Propaganda Arts. Design, Culture, Identity: The Wolfsonian Collection. 24: 34–63. doi:10.2307/1504182. JSTOR 1504182.
- 1 2 3 Damsky, Abram (Summer 1987). "Lamps and Architecture 1930–1950". The Journal of Decorative and Propaganda Arts. 5 (Russian/Soviet Theme): 90–111. doi:10.2307/1503938. JSTOR 1503938.
- ↑ O'Mahoney, Mike (January 2003). "Archaeological Fantasies: Constructing History on the Moscow Metro". The Modern Language Review. 98 (1): 138–150. doi:10.2307/3738180. JSTOR 3738180. S2CID 161592843.
- ↑ Бесплатные пересадки Московского центрального кольца, MCC official Facebook group
- ↑ "D3 and D4 will be launch in 2023". Kommersant. 26 December 2022.
- ↑ Она имеет протяженность 70 км и насчитывает 31 станцию ([The line has the length of 70 km and counts 31 station)]
- ↑
- ↑ "У московского метро нет логотипа". ADME. Archived from the original on 23 February 2014.
- ↑ "Проект DesignContest проводит конкурс на новый логотип столичного метро". Алиса По. The Vilarge. 2013. Retrieved 12 February 2014.
- ↑ "Moscow Metro 2014". DesignContest. 2013.
- 1 2 "Table of tariffs" (in Russian). City of Moscow.
- ↑ "Безналичная система оплаты проезда". Moscow metro. Archived from the original on 27 July 2011. Retrieved 20 September 2010.
- ↑ "Moscow Metro: the World's First Major Transport System to operate fully contactless with NXP's MIFARE Technology". NXP Semiconductors. Retrieved 26 January 2009.
- ↑ "Troika official site". City of Moscow. Retrieved 2 April 2013.
- ↑ "30 squats gets you a subway ride in Russia". Mother Nature Network. Archived from the original on 20 March 2014. Retrieved 22 December 2013.
- ↑ Московское метро ввело оплату с мобильного телефона. BBC Русская служба (in Russian). 4 September 2015.
- ↑ Moscow Metro / Public Relations Department / News Archived 7 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine. Engl.mosmetro.ru (24 November 2010). Retrieved on 2013-08-17.
- ↑ "На сколько в 2016 году подорожает проезд в московском метро?". 7 December 2015.
- ↑ "Крокус" сдал "частную" станцию метро. bn.ru (in Russian). Archived from the original on 13 January 2010. Retrieved 27 January 2010.
- ↑ "Третий пересадочный контур метро разгрузит Кольцевую ветку на 20%". RIA Novosti. 10 March 2009.
- ↑ "Власти Москвы утвердили план развития столичного метро с 2012 года". RIA Novosti. 22 March 2010.
- ↑ "Moscow Metro 2 – The dark legend of Moscow". Moscow Russia Insider's Guide. Archived from the original on 23 June 2011. Retrieved 6 March 2011.
- ↑ "Метро-2".
- ↑ "Terrorism: an appetite for killing for political purposes". Pravda.ru. 11 September 2006. Retrieved 19 October 2007.
- ↑ Взрыв на Арбатско-Покровской линии в 1977г.. metro.molot.ru (in Russian). Retrieved 31 August 2010.
- ↑ "7 Die in Moscow Subway Fire". The New York Times. UPI. 12 June 1981. Retrieved 19 March 2010.
- ↑ Авария эскалатора на станции "Авиамоторная". metro.molot.ru (in Russian). Archived from the original on 30 August 2010. Retrieved 31 August 2010.
- ↑ "Slaying Could Chill Business with Moscow Oklahoman in Hotel Dispute". 5 November 1996.
- ↑ "In pictures: Moscow's bomb horror". BBC News.
- ↑ Взрыв на Замоскворецкой линии. metro.molot.ru (in Russian).
- 1 2 Grashchenkov, Ilya (25 May 2005). Как работает московское метро. Список закрытых станций (in Russian). Yтро.ru. Archived from the original on 19 July 2011. Retrieved 18 March 2010.
- ↑ Moscow Metro Tunnel Collapses on Train; Nobody Hurt Archived 6 February 2006 at the Wayback Machine
- 1 2 "38 killed in Moscow metro suicide attacks". RTÉ. 29 March 2010. Retrieved 29 March 2010.
- ↑ "Движение на "зеленой ветке" московского метро восстановлено после аварии". Interfax.ru (in Russian). 22 January 2014. Retrieved 29 June 2021.
- ↑ "Число жертв аварии в московском метро увеличилось до 24 человек". ТАСС. Retrieved 16 November 2020.
- ↑ Alla Eshchenko, Laura Smith-Spark and Holly Yan (15 July 2014). "Report: 22 killed in Moscow train derailment". CNN. Retrieved 16 November 2020.
- ↑ "КиноПоиск.ru". www.kinopoisk.ru (in Russian). Retrieved 27 July 2017.
Further reading
- Winchester, Clarence, ed. (1936), "Moscow's underground", Railway Wonders of the World, pp. 894–899 illustrated contemporary description of the Moscow underground
- Sergey Kuznetsov/ Alexander Zmeul/ Erken Kagarov: Hidden Urbanism: Architecture and Design of the Moscow Metro 1935–2015. Berlin 2016, ISBN 978-3869224121.
External links
- Official website
- List of famous Moscow Metro stations
- Geographically precise Moscow Metro map (in Russian)

.jpg.webp)
