| Mount Baden-Powell | |
|---|---|
 Mount Baden-Powell as seen from Blue Ridge | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 9,407 ft (2,867 m) NAVD 88[1] |
| Prominence | 2,799 ft (853 m)[2] |
| Parent peak | Mount San Antonio[2] |
| Listing | Hundred Peaks Section[3] |
| Coordinates | 34°21′30″N 117°45′53″W / 34.358441036°N 117.764615353°W[1] |
| Geography | |
 Mount Baden-Powell Location in California  Mount Baden-Powell Mount Baden-Powell (the United States) | |
| Location | Los Angeles County, California, U.S. |
| Parent range | San Gabriel Mountains |
| Topo map | USGS Crystal Lake |
| Climbing | |
| First ascent | 1933 by Weldon Heald[4] |
| Easiest route | Hike |
Mount Baden-Powell (/ˈbeɪdən ˈpoʊ.əl/) is a peak in the San Gabriel Mountains of California named for the founder of the World Scouting Movement, Robert Baden-Powell, 1st Baron Baden-Powell. It was officially recognized by the USGS at a dedication ceremony in 1931.[5] It was originally known as East Twin or North Baldy.[4]
Geography

At 9,407 feet (2,867 m) in elevation, Mount Baden-Powell is traditionally considered to be the 5th highest peak of the San Gabriel Range; however it is the second highest peak in the range with more than 1,000 feet (300 m) of prominence, and is the highest peak not part of the Mount San Antonio massif.
The peak is within the Angeles National Forest and San Gabriel Mountains National Monument.
Hiking
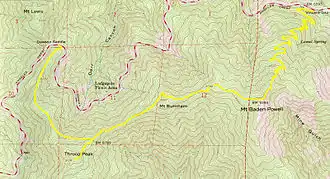
The Pacific Crest Trail reaches within 0.25 miles (0.40 km) of the summit; at 9,360 feet (2,850 m), this is the highest point of the trail south of the Sierra Nevada.
The summit has long been a favorite hiking excursion either from the Mount Islip Saddle near Little Jimmy Trail Camp, or the Vincent Gap Trail which leads up a moderate to strenuous set of switchbacks from Wrightwood. Mount Baden-Powell is also the high point along The Silver Moccasin Trail, a historic 53-mile (85 km) Boy Scout hiking trail, which connects this summit to Mount Burnham (less than 1 mile (1.6 km) away), Throop Peak, and Mount Hawkins. The Vincent Gap hike leads through a variety of forested areas consisting of Jeffrey Pine, Ponderosa Pine, Lodgepole Pine, Incense-cedar, and an ancient forest of Limber Pine some of which are more than 2,000 years old.
In 1957 several Southern California councils of the Boy Scouts of America placed a formal marker at the summit with a plaque dedicated to Lord Baden-Powell.
See also
- Baden-Powell Peak in Nepal
References
- 1 2 "Mt. Baden Powell". NGS Data Sheet. National Geodetic Survey, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, United States Department of Commerce. Retrieved 2008-12-03.
- 1 2 "Mount Baden-Powell, California". Peakbagger.com. Retrieved 2008-12-03.
- ↑ "Mount Baden-Powell". Hundred Peaks Section List. Angeles Chapter, Sierra Club. Retrieved 2019-07-09.
- 1 2 "Summit Signatures, Mount Baden-Powell". Hundred Peaks Section, Angeles Chapter, Sierra Club. Retrieved 2013-12-22.
- ↑ Burnham, Frederick; Everett, Mary Nixon (1944). Taking Chances. Haynes Corporation. xxv–xxix. OCLC 2785490.
External links
- "Mount Baden-Powell". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved 2010-05-17.
- "Dedication of Mount Baden-Powell". Pine Tree Web. Archived from the original on 2006-09-08. Retrieved 2008-12-03.
- "Mount Baden Powell". Digital-Desert.
- "Mount Baden Powell near Wrightwood, CA". WrightwoodCA.com. Retrieved 2011-06-30.
- "Guide to Mount Baden Powell Trail". WrightwoodCA.com. Retrieved 2011-06-30.