| Mount Bird | |
|---|---|
 Mount Bird Location in Antarctica | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 1,765 m (5,791 ft) |
| Coordinates | 77°16′S 166°45′E / 77.267°S 166.750°E |
| Geography | |
| Continent | Antarctica |
| Region | Ross Dependency |
| Geology | |
| Mountain type | Shield volcano |
| Volcanic belt | McMurdo Volcanic Group |
Mount Bird is a 1,765 m (5,791 ft) high shield volcano standing about 7 miles (11 km) south of Cape Bird, the northern extremity of Ross Island. It was mapped by the British National Antarctic Expedition, 1901–04, under Robert Falcon Scott, and apparently named by them after Cape Bird.[1] Endeavour Piedmont Glacier lies on its slopes.
There are several western lobes of the Mount Bird icecap. One of these is Quaternary Icefall, which descends steeply into Wohlschlag Bay 1 mile (1.6 km) south of Cinder Hill. The site was mapped and so named by the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition (NZGSAE), 1958–59, because of the Quaternary glacial period marine shells carried by the glacier and deposited in terminal moraines.[2] Another such lobe is Shell Glacier.[1]
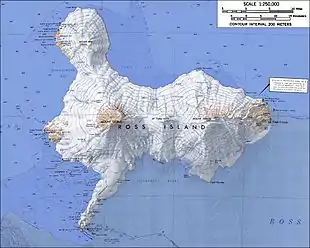
Mount Bird is in the upper left.
Mount Erebus is in the lower left.
Mount Terra Nova is in the middle.
Mount Terror is in the right.
See also
References
- 1 2 "Mount Bird". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved 2018-08-27.
- ↑ "Quaternary Icefall". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved 2018-08-27.
- Wright, A. C.; Kyle, P. R. (1990). "A.15. Mount Bird". In LeMasurier, W. E.; Thomson, J. W. (eds.). Volcanoes of the Antarctic Plate and Southern Oceans. American Geophysical Union. pp. 97–98. ISBN 0-87590-172-7.
- Mount Bird Archived 2013-10-29 at the Wayback Machine, Volcano World