| Mount Robinson | |
|---|---|
 Southwest aspect, from Mt. Agassiz | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 12,967 ft (3,952 m)[1][2] |
| Prominence | 367 ft (112 m)[3] |
| Parent peak | Aperture Peak (13,265 ft)[4] |
| Isolation | 0.73 mi (1.17 km)[4] |
| Coordinates | 37°07′04″N 118°31′02″W / 37.1178726°N 118.5172677°W[5] |
| Naming | |
| Etymology | Douglas Robinson |
| Geography | |
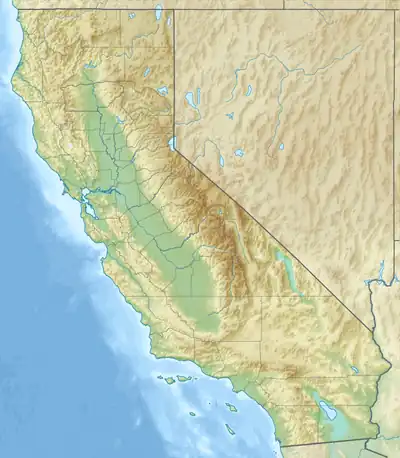 Mount Robinson Location in California  Mount Robinson Mount Robinson (the United States) | |
| Location | Inyo County, California, U.S. |
| Parent range | Sierra Nevada Inconsolable Range[3] |
| Topo map | USGS North Palisade |
| Geology | |
| Age of rock | Cretaceous |
| Mountain type | Fault block |
| Type of rock | Inconsolable Quartz Monzodiorite[6] |
| Climbing | |
| First ascent | 1930 Norman Clyde |
| Easiest route | class 3[2] |
Mount Robinson is a 12,967-foot-elevation (3,952 meter) mountain summit located in Inyo County, California, United States.[5]
Description
Mount Robinson is set within the John Muir Wilderness, on land managed by Inyo National Forest. It is situated one mile east of the crest of the Sierra Nevada mountain range in the Palisades area, just outside the boundary of Kings Canyon National Park. It is approximately 13 miles (21 km) west of the community of Big Pine, 0.8 miles (1.3 km) northeast of line parent Mount Agassiz, and 0.7 miles (1.1 km) east of proximate parent Aperture Peak. Mount Robinson ranks as the 156th-highest summit in California,[4] and the seventh-highest peak of the Inconsolable Range.[3] Topographic relief is significant as the summit rises 2,700 feet (820 meters) above the Big Pine Lakes in one mile. A rock glacier lies below the west slope.
History
The first ascent of the summit was made July 4, 1930, by Norman Clyde, who is credited with 130 first ascents, most of which were in the Sierra Nevada.[2][7] This landform's toponym was officially adopted by the U.S. Board on Geographic Names to honor Douglas Robinson whose career with the US Forest Service spanned 30 years.[5][8] In 1933, he authored "Inyo National Forest" which compiled valuable information about the forest.[9] As Chief Ranger, Robinson dispatched volunteers to search for Walter A. Starr Jr.[10]

Climate
According to the Köppen climate classification system, Mount Robinson is located in an alpine climate zone.[11] Most weather fronts originate in the Pacific Ocean, and travel east toward the Sierra Nevada mountains. As fronts approach, they are forced upward by the peaks (orographic lift), causing them to drop their moisture in the form of rain or snowfall onto the range. Precipitation runoff from this mountain drains into headwaters of North Fork Big Pine Creek.
See also
References
- ↑ United States Geological Survey topographical map - North Palisade
- 1 2 3 Secor, R.J. (2009). The High Sierra Peaks, Passes, and Trails (3rd ed.). Seattle: The Mountaineers. ISBN 978-0898869712.
- 1 2 3 "Mount Robinson, California". Peakbagger.com. Retrieved 2022-07-23.
- 1 2 3 "Robinson, Mount CA". ListsOfJohn.com. Retrieved 2022-07-23.
- 1 2 3 "Mount Robinson". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved 2022-07-23.
- ↑ Stratotype Inventory—Sequoia and Kings Canyon National Parks, California, nps.gov
- ↑ "Norman Clyde - Mountaineer". OwensValleyHistory.com. Retrieved 2022-07-23.
- ↑ Browning, Peter (1986). Place Names of the Sierra Nevada. Berkley: Wilderness Press. p. 185. ISBN 978-0899970479.
- ↑ Erwin G. Gudde, William Bright (2010), California Place Names: The Origin and Etymology of Current Geographical Names, University of California Press, ISBN 9780520266193, p. 460
- ↑ Robert C. Pavlik (2020), Norman Clyde: Legendary Mountaineer of California's Sierra Nevada, Yosemite Conservancy, ISBN 9781951179076
- ↑ "Climate of the Sierra Nevada". Encyclopædia Britannica.
External links
- Weather forecast: Mount Robinson