 1912 Multiplex Automobile brochure cover | |
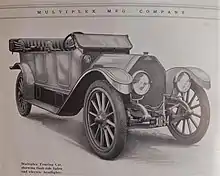 1912 Multiplex from brochure | |
| Type | Automobile manufacturer |
|---|---|
| Industry | Automotive |
| Founded | 1912 |
| Defunct | 1913 |
| Fate | ceased automobile manufacturing |
| Headquarters | , |
Key people | F. Bingaman, Crispin family |
| Products | Automobiles |
Production output | 14 (1912-1913) |
The Multiplex was an automobile built in Berwick, Pennsylvania by the Multiplex Manufacturing Company (today: Crispin Multiplex Manufacturing Company; Crispin Valve) from 1912 to 1913.
History
The Multiplex was a sporty, upper-priced and large car equipped with a four-cylinder engine, and offered as a Touring, a Roadster, and a Raceabout. A prototype "Sports" car with an 85 inches (2,200 mm) wheelbase, weighing in at just 980 pounds (440 kg) and allegedly capable of a top speed of 126 mph (203 km/h) was also built.[1]
The Multiplex 50 HP was claimed as the "highest expression of touring luxury". The car was developed by Fritz Bingaman in 1911, and offered for sale in 1912 and 1913. The wheelbase of the stock automobiles was 134 inches (3,400 mm), front tires were 38 × 4½ in, rear 39 × 5 in.[2]
The engine was a Waukesha.[1] It was a very large four cylinder unit with 5 inches (130 mm) bore and 6 inches (150 mm) stroke, giving it a volume of 471.2 c.i. (7722 cc.). It delivered 50 bhp,[2] and with this bore, the car had an ALAM rating of 40 hp.[3]
The Multiplex was expensive; $3,125 for the raceabout, $3,175 for the roadster, and $3,600 (equivalent to $109,167 in 2022) for the touring car.[1] Sales competition would have included Lozier, Mercer, Packard, Peerless, Thomas, and many others. The prototype sports model had an envisioned price tag of around $4,000.[1] In 2 years only 14 cars were built.[1]
The most remarkable success in motor sports was a victory in the Sealed bonnet road test, held by the Philadelphia Automobile Club in spring, 1913.[1]
After the failure of the car, Multiplex Manufacturing returned to making valves, which it did since 1905. There was a brief try with a sports car in 1954, but only prototypes of the Multiplex-Allied 186 with a Willys F-head six cylinder engine and coachwork copied straightaway from the Cisitalia 202 were actually built.
 1913 Multiplex Touring Car illustrated in the Automobile Trade Journal
1913 Multiplex Touring Car illustrated in the Automobile Trade Journal 1913 Multiplex Raceabout illustrated in the Automobile Trade Journal
1913 Multiplex Raceabout illustrated in the Automobile Trade Journal
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Kimes, Beverly Rae (1996). The Standard Catalog of American Cars: 1805-1942. Iola, Iowa: Krause Publications. p. 1009. ISBN 0873414284.
- 1 2 Dluhy, Robert (2013). American Automobiles of the Brass Era: Essential Specifications of 4,000+ Gasoline Powered Passenger Cars, 1906-1915, with a Statistical and Historical Overview. Jefferson, NC: McFarland. p. 102. ISBN 978-0786471362.
- ↑ National Automobile Chamber of Commerce (1970). Handbook of Automobiles 1915-1916. New York City, NY: Dover Publications, Inc.; Reprint. p. 12.