 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
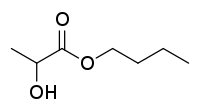
| Preferred IUPAC name
Butyl 2-hydroxypropanoate | |
| Other names
Butyl ester of 2-hydroxypropanoic acid Butyl ester of lactic acid Butyl 2-hydroxypropanoate Butyl α-hydroxypropionate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.834 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | C114966 |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H14O3 | |
| Molar mass | 146.186 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Clear, colorless to white liquid |
| Odor | Mild, transient |
| Density | 0.98 g/cm3 (20°C)[1] |
| Melting point | −43 °C; −45 °F; 230 K[1] |
| Boiling point | 188 °C; 370 °F; 461 K[1] |
| slightly soluble[1] | |
| Solubility | Soluble in ethyl ether, ethanol[2] |
| Vapor pressure | 0.4 mmHg (20°C)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 71 °C; 160 °F; 344 K[1] |
| 382 °C (720 °F; 655 K)[2] | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
>5 g/kg (oral, rabbit)[3] >2000 mg/kg (oral, rat)[3] |
LDLo (lowest published) |
11 g/kg (subcutaneous, mouse)[3] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
REL (Recommended) |
5 ppm (25 mg/m3)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
n-Butyl lactate is an industrial chemical and food additive.
Uses
In an industrial context, n-butyl lactate is used as a solvent and as a chemical feedstock. It is used as a dairy-related flavoring agent.[2]
Metabolism
It is metabolized to lactic acid, which is in turn metabolized to n-butanol, n-butyraldehyde, and n-butyric acid.[4]
Safety
n-Butyl lactate reacts with strong acids, strong bases, and oxidizers. It is also flammable. Exposure to dangerous amounts can occur through inhalation, ingestion, skin contact, or eye contact and causes irritation of the affected area, drowsiness, headache, central nervous system depression, nausea, and vomiting.[1] It is approved as a food additive by the US Food and Drug Administration.[4]