In Old English poetry, many descriptive epithets for God were used to satisfy alliterative requirements. These epithets include:
List
| Main | Name (Old English) | Name meaning | Attestations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cyning "King" |
wuldres Cyning | "King of Glory" | The Dream of the Rood[1] |
| Dryhten[2] "Lord" |
ece Dryhten | "eternal Lord" | Cædmon's hymn[3] |
| dryhntes dreamas | "the joys of the Lord" | The Seafarer[4] | |
| heofones Dryhten | "heaven's Lord" | The Dream of the Rood[5] | |
| Ealdor[6] "Prince" |
wuldres Ealdor | "Prince of Glory" | The Dream of the Rood[7] |
| Fæder "Father" |
Heahfæder | "Highfather" | The Dream of the Rood |
| Wuldorfæder | "Glorious Father" | Cædmon's hymn | |
| Frea[8] "Lord" |
Frea ælmihtig | "Master almighty" | Cædmon's hymn |
| Frea mancynnes | "Mankind's Master" | The Dream of the Rood[9] | |
| God "God" |
God ælmihtig | "God almighty" | The Dream of the Rood[10] |
| weruda God | "God of hosts" | The Dream of the Rood | |
| Hælend[11] "Healer" |
Hælend | "Healer" | The Dream of the Rood |
| Metod[12] "Maker" |
Metod | "Maker" | Beowulf (110) [13] |
| eald Metod | "Old Maker" | Beowulf (945)[14] | |
| Wealdend[15] "Ruler" |
Wealdend | "Ruler" | The Dream of the Rood[16] |
| Al-wealda | "all-ruler" | Meters of Boethius (11) | |
| wuldor alwealda | "Glorious all-ruler" | Codex Exoniensis | |
| fæder alwealda | "Father all-ruler" | Beowulf (630) | |
| Weard[17] "Guard" |
heofonrices Weard[18] | "the heavenly kingdom's Guard" | Cædmon's hymn |
| Beowulf[19] |
 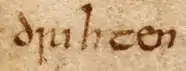  |
| "Ælmihtiga," "Drihten," "Metod," as they appear in the Beowulf. |
See also
Notes
- ↑ Swanton, p. 133
- ↑ Derived from dryht ("troop", "company"), emphasizing a noble's role as lord of a band of warriors.
- ↑ Whallon
- ↑ Godden, p. 188
- ↑ Swanton, p. 138
- ↑ Derived from eald "old". ealdor can also mean "elder" (but "elder" derives from ealdra "older" rather than from ealdor).
- ↑ Swanton, p. 138
- ↑ From Proto-Germanic *frauwaz; emphasizes a lord's domestic rulership. In later Old English, it becomes a word for husband.
- ↑ Swanton, p. 139
- ↑ Swanton, p. 95
- ↑ From hælan ("heal"); often translated "Saviour".
- ↑ Also meotod cf. Old Norse mjötuðr ("god", "fate"). Also translated as 'creator' and often used for the concept of "fate" (also known in O.E. as wyrd). The word is possibly from a root meaning "measurer" or "one who measures" related to the O.E. metan ("measure") and its descendant the Mod.E. mete in the term "to mete out".
- ↑ Whallon
- ↑ Whallon
- ↑ From wealdan ("rule", "control"; cf. modern English wield).
- ↑ Swanton, p. 146
- ↑ Emphasizes both guardianship and ownership.
- ↑ Heofon is "Heaven", and rice is "kingdom" (cf. the German reich).
- ↑ Whallon
References
- Whallon, William (1965). "The Idea of God in Beowulf". PMLA. Modern Language Association. 80 (1): 19–23. doi:10.2307/461121. JSTOR 461121.
- Swanton, Michael James, The Dream of the Rood.
- Godden, Malcolm, Michael Lapidge. The Cambridge companion to Old English literature. 2002. University of Cambridge Press. ISBN 0-521-37794-3
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.