| Nanxiong Formation | |
|---|---|
| Stratigraphic range: Maastrichtian | |
| Type | Geological formation |
| Underlies | Shanghu Formation |
| Overlies | Jurassic granite basement, Changba Formation (Nanxiong Group) |
| Thickness | ~300 m (980 ft) Several kilometers (Nanxiong Group) |
| Lithology | |
| Primary | Sandstone, siltstone, mudstone |
| Other | Limestone, conglomerate |
| Location | |
| Coordinates | 23°30′N 114°54′E / 23.5°N 114.9°E |
| Approximate paleocoordinates | 23°48′N 110°30′E / 23.8°N 110.5°E |
| Region | Guangdong Province |
| Country | |
| Extent | Nanxiong Basin |
 Nanxiong Formation (China)  Nanxiong Formation (Guangdong) | |
The Nanxiong Formation (also known as Yuanpu Formation) is a Late Cretaceous geologic formation in Guangdong Province. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.
Description
It consists of continental siliciclastic red beds, with fauna which similar to that of the Nemegt Formation. It has been dated about 66.7 ± 0.3 million years ago.[1] It is the lowest unit of the Nanxiong Basin, a small graben created during Mesozoic rifting.[2] Buck et al. state that it overlies Jurassic granite basement, and is conformably overlain by the Shanghu Formation.[1] Alternative stratigraphic schemes for the Nanxiong basin have been proposed,[3] one of which refers to the Nanxiong succession as the Nanxiong Group, and dividing it into the Yuanfu, Zhutian and Zhenshui formations, and overlying the Albian to Turonian Changba Formation.[4]
Paleobiota of the Nanxiong Formation
Color key
|
Notes Uncertain or tentative taxa are in small text; |
Crocodilians
| Crocodilians | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Material | Notes | Images | ||
| Jiangxisuchus[5] | J. nankangensis | Nearly complete skull and mandible | A crocodyloid | |||
Lizards
| Lizards | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Material | Notes | Images | ||
| Chianghsia[6] | C. nankangensis | A partial skull and lower jaws | A monstersaurian lizard | |||
| Tianyusaurus[7] | T. zhengi | A skull, mandible, first eight cervical vertebrae and nearly complete pectoral girdles | A polyglyphanodontian lizard, also known from the Qiupa Formation |  | ||
Turtles
| Turtles | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Material | Notes | Images | ||
| Jiangxichelys[8] | J. ganzhouensis | A complete shell | A nanhsiungchelyid turtle | |||
| Nanhsiungchelys[9] | N. wuchingensis | A partial skeleton | A nanhsiungchelyid turtle[10] | |||
| Oolithes[11][10] | O. elongatus, O. nanhsiungensis, O. rugustus and O. spheroides. | Egg and egg clutches. Some of these were probably laid by Nanhsiungchelys.[11][10] | Turtle and/or theropod eggs. | .jpg.webp) | ||
Dinosaurs
| Genus | Species | Material | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Theropoda indet. |
Indeterminate | A maxillary tooth that differs from tyrannosaurid and carcharodontosaurid dentition.[12] | A notably large theropod. | |
| Indeterminate | Isolated dorsal vertebra.[11] | A theropod. | ||
Hadrosaurs
| Hadrosaurs | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Material | Notes | Images | ||
| Microhadrosaurus[11] | M. nanshiungensis | Partial lower jaw from a juvenile that was about 2.6 m long | A nomen dubium hadrosaur taxon.[4] | |||
| Hadrosauropodus isp.[4] | Indeterminate | Three-toed footprints[4] | A hadrosaur | |||
Oviraptorosaurs
| Oviraptorosaurs | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Material | Notes | Images | ||
| Banji[13] | B. long | Nearly complete skull and lower jaw | An oviraptorid |  | ||
| Corythoraptor[14] | C. jacobsi | Nearly complete skeleton including the skull and lower jaw | An oviraptorid with a distinct cassowary-like crest |  | ||
| Elongatoolithidae indet. | Indeterminate | Three eggs with embryonic remains.[15] | Oviraptorid eggs. | .png.webp) | ||
| Ganzhousaurus[16] | G. nankangensis | Lower jaw, leg bone, hip bone and caudal vertebrae | A transitional oviraptorid with both basal and derived traits |  | ||
| Huanansaurus[17] | H. ganzhouensis | Nearly complete skull, lower jaws, neck vertebrae, a humerus, arm fragments, lower part of the right thighbone, the upper part of the right shinbone, and parts of the right foot | An oviraptorid | 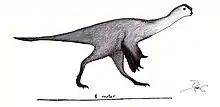 | ||
| Jiangxisaurus[18] | J. ganzhouensis | Incomplete skull, lower jaw, vertebrae, nearly complete pectoral girdle, the left forelimb, ribs, and a partially preserved pelvic girdle | An oviraptorid |  | ||
| Macroolithus | Indeterminate | Five egg clutches containing over 60 eggs.[19] | Oviraptorid eggs |  | ||
| Indeterminate | Three eggs with embryonic remains.[20] | Oviraptorid eggs | .png.webp) | |||
| M. yaotunensis | Two eggs with embryonic remains.[21] | Oviraptorid eggs. Skeletal proportions resemble Heyuannia huangi | ||||
| M. yaotunensis | A nest of 24 eggs associated with an adult oviraptorid.[22] | Oviraptorid eggs | ||||
| Nankangia[23] | N. jiangxiensis | A partial lower jaw, vertebrae, both scapulocoracoids, a nearly complete right humerus, pubic bones, and some dorsal ribs | An oviraptorid | 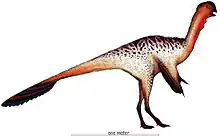 | ||
|
Oviraptoridae indet. |
Indeterminate | A female individual preserving the pelvic girdle, some caudals and two eggs inside the abdominal cavity.[24] | A pregnant oviraptorid | |||
| Indeterminate | A nesting adult over a nest of eggs, preserving cervical vertebrae, arms and the pelvic region.[22] | An oviraptorid that represents the fifth nesting taxon. | ||||
| Indeterminate | A female individual preserving a partial pelvic girdle, hindlimbs and some caudals with two eggs associated near the pelvic region.[25] | A pregnant oviraptorid. | ||||
| Shixinggia[26] | S. oblita | Sparse postcranial remains lacking the skull | An oviraptorid | |||
| Tongtianlong[27] | T. limosus | Almost complete skeleton, portions of the arms, right leg, and tail were destroyed by TNT blasts | An oviraptorid, the pose indicates that it may have died trying to free itself from mud |  | ||
Sauropods
| Sauropods | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Material | Notes | Images | ||
| Gannansaurus[28] | G. sinensis | A single, nearly complete dorsal vertebra and a mid-caudal vertebra | A sauropod closely related to Euhelopus | |||
| Jiangxititan[29] | J. ganzhouensis | The three posteriormost cervical vertebrae with two cervical ribs, articulated with the first four dorsal vertebrae with three dorsal ribs | A derived lognkosaurian likely closely related to Mongolosaurus, but not the coeval Gannansaurus | |||
Therizinosaurids
| Therizinosaurids | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Material | Notes | Images | ||
| Nanshiungosaurus | N. brevispinus | Eleven cervical vertebrae, ten dorsal vertebrae, six sacral vertebrae and the pelvis.[11][30] | A therizinosaurid. |  | ||
Tyrannosaurids
| Tyrannosaurids | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Material | Notes | Images | ||
| Qianzhousaurus[31] | Q. sinensis | A skull, lower jaw, vertebrae, both scapulocoracoids, a left femur and a left tibia | A tyrannosaurid, could represent a third species of Alioramus[32] |  | ||
|
Tyrannosauridae indet. |
Indeterminate | Two isolated teeth.[11] | A tyrannosaurid. | |||
| Indeterminate | Large and well-preserved tooth.[12] | A tyrannosaurid. | ||||
See also
References
- 1 2 Buck, B. J.; Hanson, A. D.; Hengst, R. A.; Shu-sheng, H. (2004). ""Tertiary Dinosaurs" in the Nanxiong Basin, Southern China, Are Reworked from the Cretaceous". The Journal of Geology. 112 (1): 111–118. Bibcode:2004JG....112..111B. doi:10.1086/379695. S2CID 12866840.
- ↑ Lucas, Spencer G.; Kirkland, James I.; Estep, John W. (1998). "Vertebrate biostratigraphy and biochronology of the Cretaceous of China". Lower and Middle Cretaceous Terrestrial Ecosystems: Bulletin 14. New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science. p. 14.
- ↑ Yan, Yi; Xia, Bin; Lin, Ge; Cui, Xuejun; Hu, Xiaoqiong; Yan, Pin; Zhang, Faqiang (April 2007). "Geochemistry of the sedimentary rocks from the Nanxiong Basin, South China and implications for provenance, paleoenvironment and paleoclimate at the K/T boundary" (PDF). Sedimentary Geology. 197 (1–2): 127–140. Bibcode:2007SedG..197..127Y. doi:10.1016/j.sedgeo.2006.09.004. ISSN 0037-0738. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2020-07-21.
- 1 2 3 4 Xing, L.; Lockley, M. G.; Li, D.; Klein, H.; Ye, Y.; Scott Persons IV, W.; Ran, H. (2017). "Late Cretaceous ornithopod-dominated, theropod, and pterosaur track assemblages from the Nanxiong Basin, China: New discoveries, ichnotaxonomy, and paleoecology" (PDF). Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 466: 303−313. Bibcode:2017PPP...466..303X. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2016.11.035.
- ↑ Chun Li; Xiao-chun Wu; Scott Rufolo (2018). "A new crocodyloid (Eusuchia: Crocodylia) from the Upper Cretaceous of China". Cretaceous Research. 94: 25–39. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2018.09.015. S2CID 133661294.
- ↑ Mo, J. Y.; Xu, X.; Evans, S. E. (2012). "A large predatory lizard (Platynota, Squamata) from the Late Cretaceous of South China". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 10 (2): 333. doi:10.1080/14772019.2011.588254. S2CID 85682211.
- ↑ Jun-chang Lü; Shu-an Ji; Zhi-ming Dong; Xiao-chun Wu (2008). "An Upper Cretaceous lizard with a lower temporal arcade". Naturwissenschaften. 95 (7): 663–669. Bibcode:2008NW.....95..663L. doi:10.1007/s00114-008-0364-1. PMID 18338150. S2CID 22544904.
- ↑ Haiyan Tong; Jinyou Mo (2010). "Jiangxichelys, a new nanhsiungchelyid turtle from the Late Cretaceous of Ganzhou, Jiangxi Province, China". Geological Magazine. 147 (6): 981–986. Bibcode:2010GeoM..147..981T. doi:10.1017/S0016756810000671. S2CID 131484464. Archived from the original on 11 July 2011. Retrieved 14 January 2011.
- ↑ H.-k. Yeh. 1966. A new Cretaceous turtle of Nanhsiung, northern Kwangtung. Vertebrata PalAsiatica
- 1 2 3 Tong, H.; Li, L. (2019). "A revision of the holotype of Nanhsiungchelys wuchingensis, Ye, 1966 (Testudines: Cryptodira: Trionychoidae: Nanhsiungchelyidae)". Cretaceous Research. 95: 151−163. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2018.11.003. hdl:311034/9424. S2CID 133937906.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dong, Z. (1979). "Cretaceous dinosaur fossils in southern China" [Cretaceous dinosaurs of the Huanan (south China)]. In Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology; Nanjing Institute of Paleontology (eds.). Mesozoic and Cenozoic Redbeds in Southern China (in Chinese). Beijing: Science Press. pp. 342–350. Translated paper
- 1 2 Mo, J.-Y.; Xu, X. (2015). "Large theropod teeth from the Upper Cretaceous of Jiangxi, southern China" (PDF). Vertebrata PalAsiatica. 53 (1): 63−72.
- ↑ Xu, X.; Han, F.-L. (2010). "A new oviraptorid dinosaur (Theropoda: Oviraptorosauria) from the Upper Cretaceous of China". Vertebrata PalAsiatica. 48 (1): 11–18.
- ↑ Lü, J.; Li, G; Kundrát, M.; Lee, Y.; Zhenyuan, S.; Yoshitsugu, K.; Caizhi, S.; Fangfang, T.; Hanfeng, L (2017). "High diversity of the Ganzhou Oviraptorid Fauna increased by a new "cassowary-like" crested species". Scientific Reports. 7 (1): 6393. Bibcode:2017NatSR...7.6393L. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-05016-6. PMC 5532250. PMID 28751667.
- ↑ Wang, S.; Zhang, S.; Sullivan, C.; Xu, X. (2016). "Elongatoolithid eggs containing oviraptorid (Theropoda, Oviraptorosauria) embryos from the Upper Cretaceous of Southern China". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 16 (67): 67. doi:10.1186/s12862-016-0633-0. PMC 4807547. PMID 27012653.
- ↑ Wang, S.; Sun, C.; Sullivan, C.; Xu, X. (2013). "A new oviraptorid (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the Upper Cretaceous of southern China". Zootaxa. 3640 (2): 242–57. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.3640.2.7. PMID 26000415. S2CID 28527553.
- ↑ Lü, Junchang; Pu, Hanyong; Kobayashi, Yoshitsugu; Xu, Li; Chang, Huali; Shang, Yuhua; Liu, Di; Lee, Yuong-Nam; Kundrát, Martin; Shen, Caizhi (2015). "A New Oviraptorid Dinosaur (Dinosauria: Oviraptorosauria) from the Late Cretaceous of Southern China and Its Paleobiogeographical Implications". Scientific Reports. 5 (11490): 11490. Bibcode:2015NatSR...511490L. doi:10.1038/srep11490. PMC 4489096. PMID 26133245.
- ↑ Wei Xuefang; Pu Hanyong; Xu Li; Liu Di; Lü Junchang (2013). "A New Oviraptorid Dinosaur (Theropoda: Oviraptorosauria) from the Late Cretaceous of Jiangxi Province, Southern China". Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition). 87 (4): 899–904. doi:10.1111/1755-6724.12098. S2CID 129797420.
- ↑ Yang, T.-R.; Wiemann, J.; Xu, L.; Cheng, Y.-N.; Wu, X.-C.; Sander, P. M. (2019). "Reconstruction of oviraptorid clutches illuminates their unique nesting biology". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 466: 581−596. doi:10.4202/app.00497.2018.
- ↑ Yang, T.-R.; Engler, T.; Lallensack, J. N.; Samathi, A.; Makowska, M.; Schillinger, B. (2019). "Hatching Asynchrony in Oviraptorid Dinosaurs Sheds Light on Their Unique Nesting Biology". Integrative Organismal Biology. 1 (1): obz030. doi:10.1093/iob/obz030. PMC 7671163. PMID 33791544.
- ↑ Cheng, Y.-N.; Ji, Q.; Wu, X.-C.; Shan, H.-Y. (2008). "Oviraptorosaurian Eggs (Dinosauria) with Embryonic Skeletons Discovered for the First Time in China". Acta Geologica Sinica. 82 (6): 1089–1094. doi:10.1111/j.1755-6724.2008.tb00708.x. S2CID 140202077.
- 1 2 Bi, S.; Amiot, R.; Peyre de Fabrègues, C.; Pittman, M.; Lamanna, M. C.; Yu, Y.; Yu, C.; Yang, T.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, Q.; Xu, X. (2020). "An oviraptorid preserved atop an embryo-bearing egg clutch sheds light on the reproductive biology of non-avialan theropod dinosaurs". Science Bulletin. 66 (9): 947–954. doi:10.1016/j.scib.2020.12.018. PMID 36654242.
- ↑ Lü, J.; Yi, L.; Zhong, H.; Wei, X. (2013). Dodson, Peter (ed.). "A New Oviraptorosaur (Dinosauria: Oviraptorosauria) from the Late Cretaceous of Southern China and Its Paleoecological Implications". PLOS ONE. 8 (11): e80557. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...880557L. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0080557. PMC 3842309. PMID 24312233.
- ↑ Sato, T.; Cheng, Y.-N.; Wu, X.-C.; Zelenitsky, D. K.; Hsiao, Y.-F. (2005). "A Pair of Shelled Eggs Inside A Female Dinosaur" (PDF). Science. 308 (5720): 375. doi:10.1126/science.1110578. PMID 15831749. S2CID 19470371.
- ↑ Jin, X.; Varricchio, D. J.; Poust, A. W.; He, T. (2020). "An oviraptorosaur adult-egg association from the Cretaceous of Jiangxi Province, China". Science. 39 (6): e1739060. doi:10.1080/02724634.2019.1739060. S2CID 219447073.
- ↑ Lü, J. C.; Zhang, B. K. (2005). "A new oviraptorid (Theropoda: Oviraptorosauria) from the Upper Cretaceous of the Nanxiong Basin, Guangdong Province of southern China". Acta Palaeontologica Sinica. 44: 412−422.
- ↑ Lü, J.; Chen, R.; Brusatte, S.L.; Zhu, Y.; Shen, C. (2016). "A Late Cretaceous diversification of Asian oviraptorid dinosaurs: evidence from a new species preserved in an unusual posture". Scientific Reports. 6: 35780. Bibcode:2016NatSR...635780L. doi:10.1038/srep35780. PMC 5103654. PMID 27831542.
- ↑ Junchang Lü; Laiping Yi; Hui Zhong; Xuefang Wei (2013). "A New Somphospondylan Sauropod (Dinosauria, Titanosauriformes) from the Late Cretaceous of Ganzhou, Jiangxi Province of Southern China". Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition). 87 (3): 678–685. doi:10.1111/1755-6724.12079. S2CID 140623061.
- ↑ Mo, Jin-You; Fu, Qiong-Yao; Yu, Yi-Lun; Xu, Xing (2023-09-21). "A New Titanosaurian Sauropod from the Upper Cretaceous of Jiangxi Province, Southern China". Historical Biology: 1–15. doi:10.1080/08912963.2023.2259413. ISSN 0891-2963.
- ↑ Zanno, L. E. (2010). "A taxonomic and phylogenetic re-evaluation of Therizinosauria (Dinosauria: Maniraptora)". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 8 (4): 503–543. doi:10.1080/14772019.2010.488045. S2CID 53405097.
- ↑ Lü, Junchang; Yi, Laiping; Brusatte, Stephen L.; Yang, Ling; Li, Hua; Chen, Liu (2014). "A new clade of Asian Late Cretaceous long-snouted tyrannosaurids". Nature Communications. 5: 3788. Bibcode:2014NatCo...5.3788L. doi:10.1038/ncomms4788. PMID 24807588.
- ↑ Carr, Thomas D.; Varricchio, David J.; Sedlmayr, Jayc C.; Roberts, Eric M.; Moore, Jason R. (2017). "A new tyrannosaur with evidence for anagenesis and crocodile-like facial sensory system". Scientific Reports. 7: 44942. Bibcode:2017NatSR...744942C. doi:10.1038/srep44942. PMC 5372470. PMID 28358353.