Napakiak
Naparyarraq | |
|---|---|
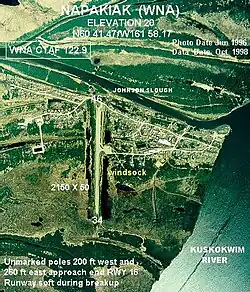 Aerial view of Napakiak | |
 Napakiak Location in Alaska | |
| Coordinates: 60°41′36″N 161°58′25″W / 60.69333°N 161.97361°W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Alaska |
| Census Area | Bethel |
| Incorporated | October 19, 1970[1] |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Elsie Chris |
| • State senator | Lyman Hoffman (D) |
| • State rep. | Conrad McCormick (D) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 2.11 sq mi (5.45 km2) |
| • Land | 2.01 sq mi (5.21 km2) |
| • Water | 0.10 sq mi (0.24 km2) |
| Elevation | 10 ft (3 m) |
| Population (2020) | |
| • Total | 358 |
| • Density | 178.02/sq mi (68.72/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC-9 (Alaska (AKST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-8 (AKDT) |
| ZIP code | 99634 |
| Area code | 907 |
| FIPS code | 02-52390 |
| GNIS feature ID | 1406829 |
Napakiak (Central Yupik: Naparyarraq) is a city in Bethel Census Area, Alaska, United States. At the 2010 census the population was 354,[3] up one resident from 353 since 2000.
Geography
Napakiak is located at 60°41′36″N 161°58′25″W / 60.69333°N 161.97361°W (60.693282, -161.973491),[4] on the north bank of the Kuskokwim River, approximately 10 miles (16 km) downriver (southwest) of Bethel.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 5.0 square miles (13.0 km2), of which 4.4 square miles (11.4 km2) is land and 0.62 square miles (1.6 km2), or 12.26%, is water.[3]
Demographics
| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1880 | 98 | — | |
| 1900 | 197 | — | |
| 1910 | 166 | −15.7% | |
| 1920 | 173 | 4.2% | |
| 1940 | 113 | — | |
| 1950 | 139 | 23.0% | |
| 1960 | 190 | 36.7% | |
| 1970 | 259 | 36.3% | |
| 1980 | 262 | 1.2% | |
| 1990 | 318 | 21.4% | |
| 2000 | 353 | 11.0% | |
| 2010 | 354 | [3] | 0.3% |
| 2020 | 358 | 1.1% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census[5] | |||
Napakiak first appeared on the 1880 U.S. Census as the unincorporated Inuit village of "Napahaiagamute."[6] All 98 residents were of the Inuit tribe.[7] It next returned in 1900 as the village of "Naparegarak." In 1910, it returned as Napakiak (with the alternative 1880 name of Napahaiagamute). In 1920, it returned as "Napakiakamute." It did not appear on the 1930 census. It next appeared again in 1940 and in every successive census to date as Napakiak. It formally incorporated in 1970.
As of the census[8] of 2000, there were 353 people, 90 households, and 71 families residing in the city. The population density was 75.2 inhabitants per square mile (29.0/km2). There were 101 housing units at an average density of 21.5 per square mile (8.3/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 1.42% White, 1.70% Black or African American, 96.03% Native American, and 0.85% from two or more races. 0.28% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race. Most of the residents are Yup'ik people. The sale, importation or possession of alcohol is forbidden in the village.
There were 90 households, out of which 48.9% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 53.3% were married couples living together, 18.9% had a female householder with no husband present, and 21.1% were non-families. 16.7% of all households were made up of individuals, and 4.4% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 3.92 and the average family size was 4.52.
In the city, the age distribution of the population shows 38.8% under the age of 18, 9.1% from 18 to 24, 27.8% from 25 to 44, 17.0% from 45 to 64, and 7.4% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 26 years. For every 100 females, there were 130.7 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 109.7 males.
The median income for a household in the city was $28,750, and the median income for a family was $29,167. Males had a median income of $26,250 versus $43,750 for females. The per capita income for the city was $7,319. About 16.2% of families and 20.2% of the population were below the poverty line, including 20.7% of those under age 18 and 9.1% of those age 65 or over.
Education
Lower Kuskokwim School District operates the William N. Miller School, PreK-12. As of 2018 it has 96 students.[9]
Health
Sale, importation and possession of alcohol are banned in the village.[10]
Miscellaneous
Napakiak is the terminus of a unique 8.5-mile (13.7 km) prototype single-wire earth return electrical intertie from Bethel, Alaska, constructed in 1981.[11]
References
- ↑ 1996 Alaska Municipal Officials Directory. Juneau: Alaska Municipal League/Alaska Department of Community and Regional Affairs. January 1996. p. 99.
- ↑ "2020 U.S. Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved October 29, 2021.
- 1 2 3 "Geographic Identifiers: 2010 Demographic Profile Data (G001): Napakiak city, Alaska". U.S. Census Bureau, American Factfinder. Archived from the original on February 12, 2020. Retrieved September 20, 2013.
- ↑ "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. February 12, 2011. Retrieved April 23, 2011.
- ↑ "Census of Population and Housing". Census.gov. Retrieved June 4, 2015.
- ↑ "Geological Survey Professional Paper". 1949.
- ↑ "Statistics of the Population of Alaska" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. 1880.
- ↑ "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- ↑ William N. Miller Memorial School." William N. Miller Memorial School. Retrieved on July 13, 2018.
- ↑ "Schedule of Local Option Communities" (PDF). Alcoholic Beverage Control Board. Retrieved May 3, 2023.
- ↑ "Reconnaissance Study of Energy Requirements and Alternatives" (PDF). Alaska Industrial Development and Export Authority. 1981.
