 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
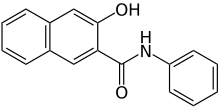
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-Hydroxy-N-phenylnaphthalene-2-carboxamide | |
| Other names
Naphtol AS, 3-hydroxy-2-naphthanilide, β-Hydroxynaphthoic anilide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.990 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H13NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 263.296 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Warning | |
| H302, H315, H317, H319, H332, H335, H411 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P272, P273, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P312, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P330, P332+P313, P333+P313, P337+P313, P362, P363, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Naphthol AS is an organic compound with the formula C10H6(OH)C(O)NHC6H5. It is the anilide of 3-hydroxy-2-carboxynaphthalene. Many analogous compounds are known, designated with a differing suffix. For example, in Naphthol AS-OL, the aryl substituent on nitrogen is C6H4-2-OCH3. These compounds are used as coupling partners in the preparation of some azo dyes.[1]
History
In 1911, it was found to be a good precursor to dyes for wool by chemists at K. Oehler Anilin- und Anilinfarbenfabrik Offenbach.[2][3]
References
- ↑ K. Hunger; W. Herbst (2012). "Pigments, Organic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a20_371. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ↑ Willy Herbst, Klaus Hunger (2009). Industrielle Organische Pigmente Herstellung, Eigenschaften, Anwendung (3. ed.). Wiley VCH. p. 201. ISBN 978-3-527-62496-6.
- ↑ US 0
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.