
Energy in Belarus describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in Belarus. Belarus is a net energy importer. According to IEA, the energy import vastly exceeded the energy production in 2015, describing Belarus as one of the world's least energy sufficient countries in the world.[1] Belarus is very dependent on Russia.[2]
Total energy consumption (measured by total primary energy supply) in Belarus was 27.0 Mtoe in 2018, similar to consumption in Norway and Hungary.[1] Primary energy use in Belarus was 327 TWh or 34 TWh per million persons in 2008.[3]
Primary energy use per capita in Belarus in 2009 (34 MWh) was slightly more than in Portugal (26 MWh) and about half of the use in Belgium (64 MWh) or Sweden (62 MWh).[3]
Electricity consumed in 2021 was 32.67 billion kWh, 3,547 kWh per capita.[4]
Overview
| Population (million) |
Prim. energy (TWh) |
Production (TWh) |
Import (TWh) |
Electricity (TWh) |
CO2-emission (Mt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2004 | 9.82 | 311 | 42 | 272 | 30.9 | 60.6 |
| 2007 | 9.70 | 326 | 47 | 276 | 32.5 | 62.7 |
| 2008 | 9.68 | 327 | 47 | 287 | 33.2 | 64.2 |
| 2009 | 9.66 | 311 | 47 | 258 | 31.4 | 60.8 |
| 2012 | 9.47 | 343 | 50 | 286 | 34.4 | 66.0 |
| 2012R | 9.46 | 355 | 47.9 | 309 | 35.0 | 71.1 |
| 2013 | 9.47 | 317 | 46.4 | 274 | 34.5 | 58.3 |
| Change 2004-09 | -1.6% | -0.1% | 11.9% | -5.0% | 1.6% | 0.2% |
| Mtoe = 11.63 TWh, Prim. energy includes energy losses
2012R = CO2 calculation criteria changed, numbers updated | ||||||
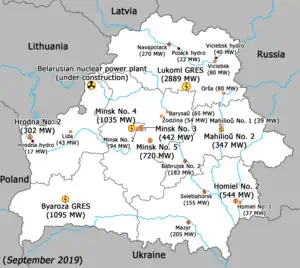
Power plants
| Name | Region/city | Capacity, MW[6] |
|---|---|---|
| Lukoml GRES | Vitebsk Region | 2,889 |
| Byaroza GRES | Brest Region | 1,095 |
| Minsk thermal No. 4 | Minsk city | 1,035 |
| Minsk thermal No. 5 | Minsk Region | 719.6 |
| Gomel thermal No. 2 | Gomel city | 544 |
| Minsk thermal No. 3 | Minsk city | 442 |
| Mogilev thermal No. 2 | Mogilev city | 347 |
| Grodno thermal No. 2 | Grodno city | 302.5 |
| Novopolotsk thermal | Novopolotsk city | 270 |
| Mazyr thermal | Mazyr city | 205 |
| Babruysk thermal No. 2 | Babruysk city | 182.6 |
| Svietlahorsk thermal | Svietlahorsk city | 155 |
| Minsk thermal No. 2 | Minsk city | 94 |
| Viciebsk thermal | Vitebsk city | 80 |
| Orsha thermal | Orsha city | 79.8 |
| Barysaw thermal | Barysaw city | 65 |
| Zhodzina thermal | Zhodzina city | 54 |
| Lida thermal | Lida city | 43 |
| Vitebsk hydro | Vitebsk Region | 40 |
| Mogilev thermal No. 1 | Mogilev city | 38.5 |
| Gomel thermal No. 1 | Gomel city | 37.3 |
| Zhlobin thermal | Zhlobin city | 26.2 |
| Pinsk thermal | Pinsk city | 22 |
| Polotsk hydro | Vitebsk Region | 21.7 |
| Mogilev thermal No. 3 | Mogilev city | 19.5 |
| Baranavichy thermal | Baranavichy city | 18 |
| Grodno hydro | Grodno Region | 17 |
| Brest thermal | Brest city | 12 |
| Babruysk thermal No. 1 | Babruysk city | 12 |
The Astravets Nuclear Power Plant is under construction, with the first unit of two expected to come online in 2020.[7]
Natural gas
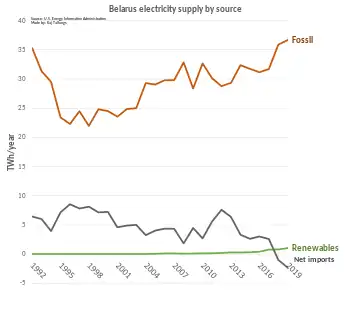
The country is one of the world’s largest importers of natural gas with estimates for 2018 being about 17 Mtoe (20 billion cubic metres [bcm]) of natural gas, making it the leading importer among the so-called EU4Energy countries: Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Moldova, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Ukraine and Uzbekistan. In 2018 almost all generated electricity came from natural gas (97%, or 39 terawatt hours [TWh]).[1] In 1990, the IEA reported natural gas as constituting 52% of electricity generation, with oil generating 48%.[8]
There are two large gas pipes running through Belarus, the Yamal–Europe pipeline and Northern Lights. In addition there is the Minsk–Kaliningrad Interconnection that connects to Kaliningrad.
In 2021 18.64 billion m3 were consumed with 0.06 billion produced, the rest imported.[4]
Oil

Belarus is a large oil refiner, listed 36th in the world, at 19 Mt of oil products in 2018 by the IEA.[1] It has two refineries and oil pipelines built during the Soviet era including the Mozyr Oil Refinery.
Oil consumed in 2021 amounted to 49.13m barrels with 12.52 m barrels produced, the rest imported.[4]
Renewable energy
Renewable energy generation accounted for 6% of Belarus’s energy in 2018, rising to 8% in 2020, mostly from biofuels and waste. Renewables share in electricity generation was 2% in 2018 (0.8 TWh).[1]
| Achievement | Year | Achievement | Year | Achievement | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4% | 1999 | 6% | 2001 | 8% | 2020 |
Renewable energy includes wind, solar, biomass and geothermal energy sources.
Storage
Because non-nuclear thermal power plants are ramped up and down depending on heat requirements, and nuclear is not very flexible, increased battery storage has been suggested.[9]
Subsidies
Fossil fuelled heat is heavily subsidized.[10]: 62
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Belarus energy profile, International Energy Agency, retrieved May 26, 2021
- ↑ The Economic Aspects of the Energy Sector in CIS Countries (PDF), European Commission, retrieved May 26, 2021
- 1 2 IEA Key energy statistics 2010 Archived 2010-10-11 at the Wayback Machine Page: Country specific indicator numbers from page 48
- 1 2 3 4 "Energy consumption in Belarus". Retrieved 11 November 2023.
- ↑ IEA Key World Energy Statistics Statistics 2015 Archived 2016-03-04 at the Wayback Machine, 2014 (2012R as in November 2015 Archived 2015-04-05 at the Wayback Machine + 2012 as in March 2014 is comparable to previous years statistical calculation criteria, 2013 Archived 2014-09-02 at the Wayback Machine, 2012 Archived 2013-03-09 at the Wayback Machine, 2011 Archived 2011-10-27 at the Wayback Machine, 2010 Archived 2010-10-11 at the Wayback Machine, 2009 Archived 2013-10-07 at the Wayback Machine, 2006 Archived 2009-10-12 at the Wayback Machine IEA October, crude oil p.11, coal p. 13 gas p. 15
- ↑ Установленная мощность, кВт (in Russian)
- ↑ "Hot tests completed at Ostrovets unit 1". World Nuclear News. 16 April 2020. Retrieved 3 May 2020.
- ↑ IEA statistics: Belarus 1990, archived from the original on 2014-10-22
- ↑ "How the energy system of Belarus should develop in order to stay beneficial. Forecast". ecoidea.me. Retrieved 2021-12-23.
- ↑ "Renewables Readiness Assessment: Belarus". /publications/2021/Jul/Renewables-Readiness-Assessment-Belarus. Retrieved 2021-12-23.

.svg.png.webp)