| Navicula | |
|---|---|
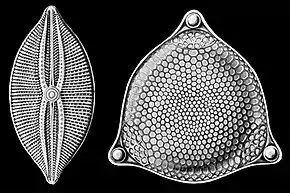 | |
| Navicula bullata (left) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Clade: | Diaphoretickes |
| Clade: | SAR |
| Clade: | Stramenopiles |
| Phylum: | Gyrista |
| Subphylum: | Ochrophytina |
| Class: | Bacillariophyceae |
| Order: | Naviculales |
| Family: | Naviculaceae |
| Genus: | Navicula Bory de Saint-Vincent, 1822 |
| Type species | |
| Navicula tripunctata | |
| Species | |
Navicula is a genus of boat-shaped diatom algae, comprising over 1,200 species.[1] Navicula is Latin for "small ship", and also a term in English for a boat-shaped incense-holder.[2]
Diatoms — eukaryotic, primarily aquatic, single-celled photosynthetic organisms — play an important role in global ecology, producing about a quarter of all the oxygen within Earth's biosphere, often serving as foundational organisms, or keystone species in the food chain of many environments where they provide a staple for the diets of many aquatic species.
Mobility
Navicula diatoms have been observed to possess a motile ability to glide over one another and on hard surfaces such as microscope slides.[3][4][5] Around the outside of the navicula's shell is a girdle of mucilage strands that can flow and thus act as a tank track.[6]
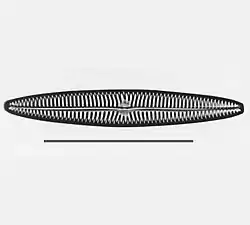
 Lyrella hennedy
Lyrella hennedy.jpg.webp) Navicula oblonga
Navicula oblonga.jpg.webp) Navicula oblonga
Navicula oblonga
References
- ↑ M.D. Guiry (2015). Guiry, M.D.; Guiry, G.M. (eds.). "AlgaeBase". World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. Retrieved 2015-08-15.
- ↑ Oxford English Dictionary, "Navicula. 3"
- ↑ Navicula Diatom: Youtube video
- ↑ Gupta, S; Agrawal, SC (2007). "Survival and motility of diatoms Navicula grimmei and Nitzschia palea affected by some physical and chemical factors". Folia Microbiol (Praha). 52 (2): 127–34. doi:10.1007/BF02932151. PMID 17575911. S2CID 20030370.
- ↑ J Microbiol Methods. 2013 Mar;92(3):349-54. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2013.01.006. Epub 2013 Jan 18. Semi-circular microgrooves to observe active movements of individual Navicula pavillardii cells. Umemura K1, Haneda T, Tanabe M, Suzuki A, Kumashiro Y, Itoga K, Okano T, Mayama S.
- ↑ Chen, Lei; Weng, Ding; Du, Chuan; Wang, Jiadao; Cao, Shan (14 May 2019). "Contribution of frustules and mucilage trails to the mobility of diatom Navicula sp". Scientific Reports. 9 (1): 7342. Bibcode:2019NatSR...9.7342C. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-43663-z. PMC 6517400. PMID 31089153.
External links
- Navicula Image (Missouri State University)
- Navicula sp. Diatoms from Guaíba island, Rio de Janeiro.
- Bacillariophyceae - Navicula Ohio University
- "Navicula". WoRMS. World Register of Marine Species.
 Media related to Navicula at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Navicula at Wikimedia Commons
