| New Wolfstein Castle | |
|---|---|
Burg Neu-Wolfstein Burg Neuwolfstein | |
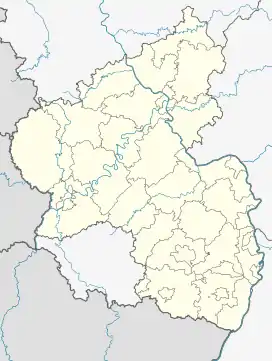
| Wolfstein | |
 | |
 New Wolfstein Castle  New Wolfstein Castle | |
| Coordinates | 49°35′8.42″N 7°36′17.39″E / 49.5856722°N 7.6048306°E |
| Type | hill castle |
| Code | DE-RP |
| Height | 238 m above sea level (NN) |
| Site information | |
| Condition | Wall remains |
| Site history | |
| Built | c. 1300 |
| Garrison information | |
| Occupants | counts |

New Wolfstein Castle (German: Burg Neu-Wolfstein) is a ruined hill castle on a 238-metre-high hill above the town of Wolfstein in the county of Kusel in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate. Today the ruins are a cultural monument[1]
History
Not much is known about the origins of the castle. It was probably built by Rudolph of Habsburg between 1275 and 1324 in connexion with the founding of the town of Wolfstein, as part of the town's defences. It is first recorded in 1324 as Hus zu Wolvenstein.[2]
In 1503, during the War of the Succession of Landshut, the castle was badly damaged. In 1609 it was demolished and rebuilt. In 1688 it was destroyed by the French and rebuilt yet again in order to serve as a barracks for French soldiers. This was in turn partly destroyed by cannon fire in 1713 on the orders of Marshal Villar and the Kingdom of Bavaria then used the ruins as a quarry. From 1720 to 1771, St. George's Chapel at the castle was used by the borough of Wolfstein as a church. In 1792 the site was recorded as being in a poor state. Two years later French soldiers used the castle as a chapel and medical post. Until 1798 the building was still used as a vicarage. After that the castle was left to fall into ruins.[3]
Present use
The ruins are used today as a war memorial. Since 1963, they have belonged to the state of Rhineland-Palatinate.
Description
Of the old castle, the remains of the neck ditch, the 1.2-metre-thick enceinte, the shield wall, the castle gate and the foundations of the palas have survived.
Legend
According to legend there was a deep well at New Wolfstein that has long since been filled in. French cavalry are supposed to have fallen into it one after another when they left their route at night. Reportedly, 30 troopers met their death.[4]
Literature and sources
- ↑ Landesamt für Vermessung und Geobasisinformation Rheinland-Pfalz: Kaiserslautern-Nord - ISBN 3-89637-280-7
- ↑ Magnus Backes: Staatliche Burgen, Schlösser und Altertümer in Rheinland-Pfalz - ISBN 3-7954-1566-7
- ↑ Manfred Czerwinski: Burgen - stolze Zeugen einer großen Zeit - ISBN 3-936216-07-X
- ↑ Viktor Carl: Pfälzer Sagen und Legenden - ISBN 3-9804668-3-3