| North Fork Feather River | |
|---|---|
 Freight train crossing the North Fork, 2017 | |
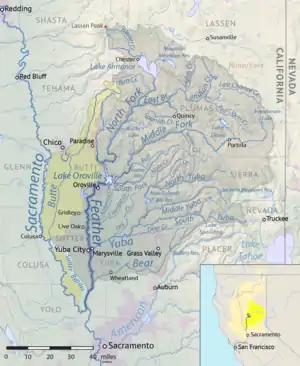 Map of the Feather River drainage basin. The North Fork flows from Lassen Peak southward to Lake Oroville. | |
| Location | |
| Country | United States |
| State | California |
| Region | North Fork Feather Watershed 1,090 sq mi (2,800 km2),[1] including the West Fork but not East Branch Watershed |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source confluence | Rice Creek (Feather River) & South Arm Rice Creek |
| • location | Feather River Meadows |
| Mouth | Lake Oroville, North ArmA |
| Length | 70 mi (110 km) |
| Basin size | 2,100 sq mi (5,400 km2)[1] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | mouth at north arm, Lake Oroville; max and min at Pulga[2] |
| • average | 2,930 cu ft/s (83 m3/s)[2] |
| • minimum | 5.4 cu ft/s (0.15 m3/s) |
| • maximum | 105,400 cu ft/s (2,980 m3/s) |
| APrior to Oroville Dam construction, the North Fork flowed to its former mouth[3] in the current lake's Main Basin.[4] | |
The North Fork Feather River is a watercourse of the northern Sierra Nevada and southern Cascades in the U.S. state of California. It flows generally southwards from its headwaters near Lassen Peak to Lake Oroville, a reservoir formed by Oroville Dam in the foothills of the Sierra, where it runs into the Feather River. The river drains about 2,100 square miles (5,400 km2) of the western slope of the Sierras. By discharge, it is the largest tributary of the Feather.
It rises at the confluence of Rice Creek and a smaller unnamed stream in the southern part of the Lassen Volcanic National Park. The river flows east, receiving Warner Creek from the left, and passes the town of Chester. It then empties into Lake Almanor, which is formed by the Canyon Dam. After leaving the dam the river cuts south into a gorge, and turns southwest to receive Butt Creek from the right. The East Branch North Fork Feather River, the North Fork's largest tributary, comes in next to Caribou Rd (40°00'49.9"N 121°13'32.4"W). It then flows southwards, through several hydroelectric dams, into the north arm of Lake Oroville.
The fork's portion of the Feather River Canyon is notable as part of the Feather River Route, and the railroad's North Fork Bridge near the river's mouth is the longest reinforced concrete bridge in the US.[5]
The North Fork is heavily developed for hydroelectricity generation and is impounded by five dams, as part of three hydroelectric projects – the Upper North Fork Feather River Project, the Rock Creek-Cresta Hydroelectric Project and the Poe Hydroelectric Project. The system is so extensive that it has been dubbed the "Stairway of Power".[6][7]


Watershed
The North Fork Feather Watershed (USGS Huc 18020121)[8] extends from the North Fork headwaters south-southwest to the Lower Feather Watershed.[9] The headwaters are in the Shasta Cascades and the northern Sierras along the Pit River and Eagle-Honey watersheds. The drainage divide for the headwaters begins in Shasta County at the Lassen Peak quadruple watershed point of East Sulpher Creek (Mill-Big Chico), Manzanita Creek (Upper Cow-Battle watershed), Lost Creek (Lower Pit River), and Kings Creek (North Fork Feather). The headwater divide extends in an arc east to Lassen County, then to the Great Basin Divide triple point of the Feather, Pit, and Susan Rivers. The divide arcs southeast to Pegleg Mountain and along 13 mi (21 km) of the Sierra Crest to the triple point with the East Branch North Fork Feather River on the east slope of Indicator Peak (40°00′43″N 120°11′15″W / 40.012069°N 120.187554°W).
Downstream of Shasta and Lassen counties, the majority of the North Fork Feather Watershed area is in Plumas County. The west divide of the watershed is along the Mill-Big Chico Watershed, southward to the West Branch Feather River triple point. The southeast divide of the North Fork Feather Watershed is the watershed of the East Branch to the triple point with the Middle Fork Feather River.
The lowest elevations of the North Fork Feather Watershed are in Butte County, with the emergency weir crest at 901 ft (275 m) and, at average storage capacity, the Lake Oroville level of 812 ft (247 m) .[10]
| description | coordinates | |
|---|---|---|
| headpoint | summit SSE of Mount Helen | 40°27′39″N 121°29′53″W / 40.460728°N 121.498103°W |
| Rice Creek | confluence, headwaters w/ Rice Cr | 40°27′19″N 121°29′08″W / 40.455242°N 121.485572°W |
| inflow to Crumbaugh Lake | 40.447829 121.488361 | |
| border, Shasta/Plumas counties | ||
| border, Stump Ranch Marsh Area | ||
| confluence, South Arm Rice Creek | 40°21′47″N 121°27′5″W / 40.36306°N 121.45139°W | |
| North Fork | source, North Fork | |
| confluence, flow from Buzzard Sprs | 40.354884 121.366396 | |
| confluence, Warner Creek | 40.333133 121.306529 | |
| diversion channel W of Lake Almanor | 40.302538 121.263914 | |
| road, CA 36 N of Chester | 40.310753 121.228638 | |
| inflow to Lake Almanor | 40.303225 121.212373 | |
| Canyon Dam | 40.174578 121.087017 | |
| confluence, Bear Creek | 40.107487 121.080408 | |
| dam, Belden ForeBay | 40.076167 121.160789 | |
| confluence, Mosquito Creek | 40.060731 121.200657 | |
| North Fork in Feather River Canyon[5] |
confluence, East Branch | 40°00′51″N 121°13′33″W / 40.014074°N 121.225934°W |
| confluence, Indian Creek | 40.005068 121.264 | |
| dam, Rock Creek Reservoir | 39.986919 121.28314 | |
| confluence, Rock Creek | 39.899959 121.359487 | |
| confluence, Jackass Creek | 39.937283 121.316013 | |
| road, Rock Creek Camp | 39.925535 121.316013 | |
| road, CA 70 | 39.918031 121.321507 | |
| confluence, Bucks Creek | 39.91418 121.326742 | |
| dam, Cresta Reservoir | 39.876118 121.373477 | |
| confluence, Mill Creek | 39.805008 121.440425 | |
| confluence, Flea Valley Creek | 39.802107 121.446948 | |
| North Fork | road, 1932 arch bridge (CA 70) | 39.79482 121.451669 |
| railroad, trestles S of CA 70 | 39.7948 121.451669 | |
| dam, Poe Reservoir | ||
| border, Plumas/Butte counties | ||
| mouth, North Fork (912 ft elevation)[3] | 39°43′27″N 121°28′19″W / 39.72417°N 121.47194°W | |
| Lake Oroville, North Arm |
railroad, 1962 North Fork Bridge | 39.716529 121.470551 |
| confluence, Rock Creek | 39.716034 121.455402 | |
| border, Lassen NF | 39.71336 121.468663 | |
| confluence, Chino Creek | 39.719005 121.422701 | |
| confluence, Mosquito Creek | 39.69705 121.406007 | |
| confluence, W of Stephens Ridge | 39.688101 121.400127 | |
| confluences, Berry & Frazier creeks | 39.670166 121.431456 | |
| confluence, West Arm | 39.666499 121.496773 | |
| former town, Big Ripple | 39°37′38″N 121°29′33″W / 39.62722°N 121.49250°W | |
| former town, Bloomer | 39°37′28″N 121°29′29″W / 39.62444°N 121.49139°W | |
| mouth, lower North Arm | 39°34′43″N 121°28′19″W / 39.57857°N 121.471882°W | |
| Lake Oroville, Main Basin |
inflow, lake's Main Basin[4] | |
| landing area for seaplane base | 39°33′59″N 121°28′07″W / 39.5662750°N 121.4685789°W | |
| former town, Bidwell | 39°33′25″N 121°27′56″W / 39.55694°N 121.46556°W | |
| former mouth,A North F w/ Feather R | 39°33′20″N 121°28′0″W / 39.55556°N 121.46667°W | |
| former town, Land | 39°33′13″N 121°28′04″W / 39.55361°N 121.46778°W) | |
| intake (main), Hyatt powerplant | ||
| Oroville Dam | road on crest (900 ft elevation)[3] | 39°32′20″N 121°29′08″W / 39.5387752°N 121.4855237°W |
| downstream dam face (702 ft) | 39°32′06″N 121°28′58″W / 39.5348863°N 121.4827459°W | |
| diversion, Palermo Canal (505 ft) | 39°31′59″N 121°28′58″W / 39.532942°N 121.482825°W | |
| road, Oro Powerhouse (360 ft) | 39°32′05″N 121°29′10″W / 39.534696°N 121.486216°W | |
| Feather River | source, downstream of dam[4] | 39°32′1.59″N 121°29′13.88″W / 39.5337750°N 121.4871889°W |
| former community, Quartz | 39°31′58″N 121°29′54″W / 39.5326641°N 121.4983018°W | |
| confluence, Oroville Spillway[11] | 39°32′08″N 121°30′06″W / 39.5356933°N 121.5016958°W | |
References
- 1 2 "Boundary Descriptions and Names of Regions, Subregions, Accounting Units and Cataloging Units". USGS.gov. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- 1 2 Wills, Leah. "upper Feather River Integrated Regional Water Management Plan" (PDF). Water.lgc.org. Plumas County. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 September 2011. Retrieved 4 August 2010.
- 1 2 3 "Query Form For The United States And Its Territories". U.S. Board on Geographic Names. Retrieved 2010-07-30.
- "North Fork Feather River (GNIS code 264163)". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved 2010-09-14. "Mouth formerly located at 393320N1212800W, now inundated by Lake Oroville. (US-T121) See Rice Creek, 1927 Board on Geographic Names (BGN) changed name and application of Rice Creek. South Arm Rice Creek and Rice Creek join to form North Fork Feather River (BGN 1950). Current maps, 1995, are mislabelled for South Arm, North Arm Rice Creek, Rice Creek and North Fork Feather River."
- "Palermo Canal (GNIS code 230252)". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved 2010-09-15.
- "Feather River (GNIS code 223423)". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved 2010-09-14. NOTE: The GNIS identifies the Feather River source at 39.5337752 -121.4871904, and Google maps depicts the source coordinates at the discharge flow point, downstream of the Oroville Dam. The National Elevation Dataset lists elevation of the source coordinates as 247.69853106321 ft) Archived 2012-03-01 at the Wayback Machine
- Lake Oroville (GNIS code 264404) NOTE: The GNIS page identifies the lake elevation as "935 ft", but the maximum water level at the Oroville Dam is 900 ft
- 1 2 3 "Section 2: Proposed Action and Alternatives". Final Environmental Impact Statement for the Oroville Facilities Project. Federal Energy Regulatory Commission. p. 17. Retrieved 2010-09-15.
- 1 2 Oxlade, John (31 December 2003). "Out-n-About - The Feather River Canyon, California, USA". WorldRailFans.info. Archived from the original on 28 July 2011. Retrieved 2010-09-11.
the actual "canyon" portion petween Pulga and Keddie is only approx. 42 miles
- ↑ "Rock Creek - Cresta, California : Pioneering Recreational Whitewater Flow Studies" (PDF). Npg.gov. Retrieved 20 January 2018.
- ↑ "NORTH FORK FEATHER RIVER PLANNING UNIT : Feather River Watershed" (PDF). Lcp.stewardshipcouncil.org. Retrieved 20 January 2018.
- ↑ "North Fork Feather Watershed -- 18020121 - Surf Your Watershed - US EPA". Cfpub.epa.gov. 17 March 2015. Retrieved 20 January 2018.
- ↑ "Lower Feather Watershed -- 18020106 - Surf Your Watershed - US EPA". Cfpub.epa.gov. 17 March 2015. Retrieved 20 January 2018.
- ↑ "Oroville Dam (ORO)". Retrieved 2010-09-15. NOTE: The 2010 measurements closest to average capacity (2,332,203 acre-feet (2.876730 km3)) were 2,331,494 acre-feet (2.875856 km3) & 2,342,112 acre-feet (2.888953 km3)
- ↑ "Oroville Dam". UCDavis.edu. Archived from the original on 2010-06-20. Retrieved 2010-09-15.
Oroville Spillway ... gated flood control outlet and emergency weir