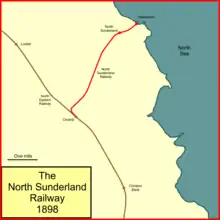
The North Sunderland Railway was a railway line in Northumberland, England. It was opened in 1898, and ran from Chathill to Seahouses, with an intermediate station at North Sunderland. Chathill was on the main line of the North Eastern Railway between Morpeth and Berwick. The branch was four miles in length and a single track with standard gauge track.
The line was built independently, and money was always scarce. In 1933 an early diesel shunting locomotive was acquired for the line, bought on the hire-purchase system.
After World War II the company's indebtedness and lack of income precipitated closure, which took place in 1951.
History
Before the railway
The community at Seahouses and North Sunderland was small, and dependent on fishing. In the middle decades of the nineteenth century the small harbour was of little commercial use except as a refuge for coastal vessels in bad weather.
In 1885 the estate of Lord Crewe obtained an Act of Parliament authorising the construction of a new north pier. It was to cost £30,000 and local stone was to be used. A short standard gauge tramway was laid on the pier as it extended, to handle the heavy stone. As the land-side communication was poor, it naturally occurred to the estate manager to enquire of the North Eastern Railway if they would construct a branch line: the NER main line was only four miles away at Chathill.[1]
An independent branch line
The North Eastern Railway made it plain that they were not interested in building a branch line, and the trustees of Lord Crewe decided that a locally promoted independent branch line was the way forward. A public meeting was held on 11 April 1891 and support for the scheme was expressed.
The cost of a railway line, even such a short one, was obviously a formidable obstacle, and a number of measures were examined in an attempt to reduce the cost of construction. Comparison was made with the Wisbech and Upwell Tramway, actually a railway with a substantial section of running in and alongside the public road. The option of building the branch on a narrow gauge was also examined. This would save a considerable sum, but had the disadvantage of preventing through-running of goods vehicles to and from the NER: transshipment would be unavoidable.
Finally a parliamentary bill was presented for a standard gauge branch line, and this was given royal assent in 1892; the capital was £21,000. The line would run from Chathill NER to Seahouses, with an intermediate station at North Sunderland.[1]
Construction and opening
Getting £21,000 of capital authorised was one thing; but the money had to be raised, and for some time this proved an insuperable obstacle. Lord Armstrong appears to have been persuaded to subscribe a considerable portion of the necessary capital, but then this was not forthcoming. A contractor was found who was willing to build the line in return for shares in the company, but then he was unable to raise the money. Finally on 13 November 1896 a contract was let for the work.
Meanwhile, the government had passed the Light Railways Act 1896; this was designed to enable the low-cost construction of lines that would otherwise not be viable. In July 1897, little construction having actually taken place, it was suggested that the branch line should be converted into light railway status. This appears not to have been done. The line opened for goods traffic on 1 August 1898.
On 5 October 1898 the Board of Trade inspecting officer visited the line to consider it for passenger operation. He was dissatisfied with a number of points, chief among them being the lack of continuous brakes on the passenger coaches, and the absence of proper interlocking at Chathill. These shortcomings were remarkably quickly dealt with, and the line opened to passengers on 18 December 1898.[1][2]
Operation
There were five passenger trains each way weekdays, and the journey time was 15 minutes. Branch trains used a bay platform at Chathill NER station. An 0-6-0 saddle tank locomotive was obtained from Manning Wardle on hire purchase as no money was available for an outright purchase. The locomotive was given the name Bamburgh. It was derailed at Chathill before the opening of the branch line.
The North Eastern Railway obtained an Act in 1898 authorising an extension to Bamburgh, which they wished to develop, and conversion of the original line to light railway status. These arrangements were never put into practice, however. The line was worked on the one engine in steam system.
The locomotive Bamburgh worked until 16 December 1902, when a NER locomotive took over. However Bamburgh was back on the line on 9 January 1903, and was still at work in 1941.[3]
During World War II there was heavy traffic on the line, and some modification to the working was introduced in order to permit two trains being on the line at once.[1]
Since 1923
The North Eastern Railway was a constituent of the new London and North Eastern Railway in 1923, following the Railways Act 1921. By January 1939 the LNER was owed £4,500 by the North Sunderland Railway in operating charges; by 1948, when the railways were nationalised, this had escalated to £14,941. Upgrade of the track and some structures to handle heavier vehicles was essential and the little company had no money to pay for this work.
Meanwhile, in the 1930s the engineering company Armstrong Whitworth had been experimenting with diesel traction, and as part of their development work they built a small four-wheeled 75 hp diesel shunting locomotive. In November 1933 this was allocated to the North Sunderland line. It was not possible to fit air brakes on the small locomotive, but the passenger trains on the branch were not fitted with continuous brakes anyway. The locomotive was purchased on hire purchase for £1,850.[1]
.jpg.webp)
Management of the line was taken over by the LNER in 1939. Trains took 20 minutes on the branch, with six trains a day before closure. It was initially operated by Manning Wardle 0-6-0 Bamburgh, which was scrapped about 1948. 'Bamburgh' was replaced by an 0-4-0 diesel electric locomotive, 'Lady Armstrong', delivered in 1934. They were replaced until closure by NER Class H (LNER Class Y7) and passenger trains had two Great Eastern Railway 6-wheel coaches.[4]
Closure
North Sunderland Railway | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Traffic on the impecunious line declined steeply in the 1930s, and following the establishment of British Railways on nationalisation of the railways, the decision was taken to close the line: it closed on 27 October 1951.
Station list
The line opened on 14 December 1898 and closed on 29 October 1951.
- Chathill; station on North Eastern Railway main line;
- North Sunderland;
- Seahouses.
References
Sources
- "North Sunderland Railway". Notes and News. The Railway Magazine. Vol. 87, no. 526. London: Tothill Press Limited. April 1941.
Further reading
- "North Sunderland Railway". Notes and News. The Railway Magazine. Vol. 82. London: Tothill Press Limited. December 1936.
- Barnett, A.L. (1992). The Light Railway King of the North. Mold: RCHS. ISBN 978-0-901461-15-5.
- Wright, Alan (1967). The North Sunderland Railway (1st ed.). Lingfield: Oakwood Press. OCLC 963635780. LP36.
External links
- Photo and short description of 'Bamburgh' 0-6-0 Paul Johnson
- A walk with description of the line Seahouses Community
- The line and its history LNER encyclopaedia
- North Sunderland Railway brief history Farne Co.
- Line history with plans and video footage LNER encyclopaedia
- The Four Mile Railway 1928 British Pathé
- British Railways Class Y7 at Seahouses Urban Ghosts
- The line on a navigable OS map National Library of Scotland
- The line with mileages Railway Codes