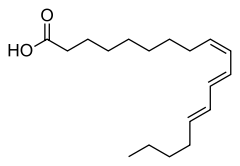
(9Z,11E,13E)-octadeca-9,11,13-trienoic acid (α-Eleostearic acid)
An octadecatrienoic acid is a chemical compounds with formula C
18H
30O
2, a polyunsaturated fatty acid with whose molecule has an 18-carbon unbranched backbone with three double bonds.
The name refers to many different structural and conformational isomers, that differ in the position of the double bonds along the backbone and on whether they are in cis ('Z') or trans ('E') conformation. Some isomers have considerable biological, pharmaceutical, or industrial importance, such as:
- α-Linolenic acid (9Z,12Z,15Z), found in many cooking oils
- γ-Linolenic acid (6Z,9Z,12Z), found in the evening primrose (Oenothera biennis)
- Pinolenic acid (5Z,9Z,12Z), found in the seeds of pines (Pinus species)
- Columbinic acid (5E,9Z,12Z), found in Thalictrum seed oils
- α-Eleostearic acid (9Z,11E,13E), the main component of tung oil, produced from the nuts of tung tree (Vernicia fordii)
- β-Eleostearic acid (9E,11E,13E)
- Catalpic acid (9E,11E,13Z), found in the seeds of yellow catalpa (Catalpa ovata) and southern catalpa (Catalpa bignonioides)
- Punicic acid (9Z,11E,13Z), found in pomegranate seed oil
- α-Calendic acid (8E,10E,12Z), found in the pot marigold (Calendula officinalis)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.