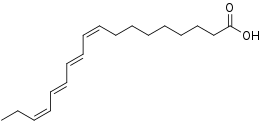
(9Z,11E,13E,15Z)-octadeca-9,11,13,15-tetraenoic acid (α-Parinaric acid)
An octadecatetraenoic acid is a chemical compound with formula C
18H
28O
2, a polyunsaturated fatty acid with whose molecule has an 18-carbon unbranched backbone with four double bonds.[1]
The name refers has different structural and conformational isomers, that differ in the position of the double bonds and on whether they are in cis ('Z') or trans ('E') conformation. Some isomers have considerable biological, pharmaceutical, or industrial importance, such as:
- α-Parinaric acid (9Z,11E,13E,15Z), found in the seeds of the makita tree (Parinari laurina)
- Stearidonic acid (6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z), an essential fatty acid
- Coniferonic acid (5Z,9Z,12Z,15Z), found in Larix decidua
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.