Ommen | |
|---|---|
 Ommen city centre with Vecht in the foreground | |
 Flag Coat of arms | |
.svg.png.webp) Location in Overijssel | |
| Coordinates: 52°31′N 6°25′E / 52.517°N 6.417°E | |
| Country | Netherlands |
| Province | Overijssel |
| Government | |
| • Body | Municipal council |
| • Mayor | Hans Vroomen |
| Area | |
| • Total | 182.01 km2 (70.27 sq mi) |
| • Land | 179.90 km2 (69.46 sq mi) |
| • Water | 2.11 km2 (0.81 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 6 m (20 ft) |
| Population (January 2021)[4] | |
| • Total | 18,295 |
| • Density | 102/km2 (260/sq mi) |
| Demonym(s) | Ommenaar, Ommer |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Postcode | 7685, 7730–7739, 8145–8149 |
| Area code | 0523, 0529, 0572 |
| Website | www |

Ommen (Dutch pronunciation: [ˈɔmə(n)] ⓘ) is a municipality and a Hanseatic city in the eastern Netherlands. It is located in the Vecht valley of the Salland region in Overijssel. Historical records first name Ommen in the early 12th century and it was officially founded as a city in 1248. The municipality had a population of 18,295 in 2021 and covers an area of 182.01 km2 (70.27 sq mi).
Population centres
Besides the city of Ommen (population: 8,710) and the town of Lemele (population: 570), the municipality consists of the following hamlets and villages:[5]
History
The emergence of Ommen
The first inhabitants of the area around Ommen were probably semi-nomadic hunter-gatherers. Flint from the Mesolithic period found in between Ommen and Mariënberg indicates the presence of humans around 9,000 BCE, but there seems to have been hardly any cultivation or permanent settlement during this period.[6]
The Vecht (sometimes called the Overijsselse Vecht, to avoid confusion with its namesake in Utrecht) and Regge rivers determined the first settlements in the area that is now the municipality of Ommen. Most of the Salland region was marshy but the higher banks along the Vecht and Regge provided fertile soil for agriculture. Moreover, good roads were rare, so for trade, transport and travel the rivers provided a vital infrastructure. The first sporadic agricultural settlements in Salland therefore arose along the riverbanks of the Vecht and the Regge around 5,000 BCE. Indeed, all early population centres in the current municipality of Ommen were originally built on riverbanks — with the exception of the town of Lemele, which was situated on the lower slopes of the Lemelerberg, free from flooding by the Regge.
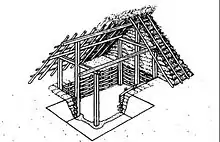
The location of Ommen itself proved particularly suitable for settlement — not only because of the fertile river soil and the higher ground of the river dune (even today the church square is visibly higher than the streets to its east and south), but also because of the ford in the Vecht facilitating trade routes between the Frisian north and Twente to the south. Archeological discoveries indicate that the first settlement in Ommen itself emerged during the 8th century CE, and by the end of the 11th century a veritable town had developed — among the first in Overijssel.[7] The first permanent settlers in Ommen were mixed crop-livestock farmers who also engaged in river trade and innkeeping. Most of these first settlers were probably of Saxon origin, though the Salians who dominated the banks of the IJssel also influenced the region economically, politically and religiously. The first houses in Ommen were hutkommen: wooden houses of which the ground floor was typically around half a meter below the ground. A church was built at the heart of Ommen around 1150 and was soon after replaced by a stone church, indicating further growth of the settlement. Written records first mention Ommen as de Vmme in 1133 and as Ummen in 1227.[8]

This gradual growth, however, did not mean Ommen could also dominate the surrounding area politically, as there were many other powers in the land. Above all, the Prince-Bishop of Utrecht, who had obtained dominion over all of Oversticht from Henry II, Holy Roman Emperor, in 1010, repeatedly attempted to increase and centralise his authority over the towns and estates of Salland. The burghers of nearby cities — especially Zwolle — were also known to interfere in the region. More locally, farming communities in the eastern Netherlands organised themselves into markes (autonomous areas) where a buurschap (rule by neighbours) formed a unique kind of grassroots local government. Last but not least, havezates (or castles) arose in the area surrounding Ommen — especially at strategic points such as the banks of the Vecht (the Arendshorst on the northern bank and Beerze on the southern bank), the banks of the Regge (most notably at Eerde) or both banks ('t Laer) — from which robber barons dominated the surrounding area and could levy tolls on river commerce in defiance of the authority of the bishop.[9] These robber barons and the buurschappen formed a check on the influence of Ommen on the surrounding region — yet it was ironically due to one such robber baron that Ommen grew to become an outright city.
Development into a city

On 25 August 1248, Ommen received city rights and fortification rights from Otto III, the Prince-Bishop of Utrecht, after the town was pillaged by local robber baron Rudolf of Coevorden and his militia of freemen in both 1215 and in the aftermath of the Battle of Ane of 1227. Ommen's location at the confluence of two rivers at the heart of the region made it the bishop's strategic and logistic basis in the defence of his domain Oversticht against the rebellious Drents.[10] Ommen thus became the 4th-oldest officially recognised city in Overijssel, after Deventer (956 A.D.), Zwolle and Rijssen.
A wall was soon erected around Ommen, including three gates: the Vechtpoort or Voorbruggenpoort (on the bank of the Vecht), the Varsenerpoort (on the western wall for traffic with Varsen) and the Arriërpoort (on the northern wall for traffic with Arriën). Even to this day, the two bells in the church's belltower, named Maria and Salvator and cast in 1517 by Hendrick de Tremonia of Dordrecht, are rung every evening at nine o'clock. These so-called Ave-Maria peals form a custom which traces its origin to the tradition of ringing the bell at the closing of the gates. Ommen never received a moat, even though it was permitted one.
Ommen soon became a regional port and market for agricultural products. Due to this commercial growth and strategic commercial position, Ommen eventually joined the Hanseatic League as a smaller port, so most of its trade was not directly with the Baltic Sea region, but with fellow Hanseatic cities Zwolle, Kampen, Zutphen and especially Deventer, of which it was a subsidiary city. A toll bridge across the Vecht (first built in 1492) further increased its wealth and commercial importance, even though the toll bridge across the Vecht was destroyed by ice floes three times through the centuries. The toll levy was usually auctioned off to private tax collectors, who resided in the toll house (built in 1531) next to the bridge. A bridge toll would be levied until 1925.[11]
For centuries during the Middle Ages, the Estates of Oversticht, a diet or feudal parliament representing the quarters of Salland, Twenthe and Vollenhove (and until 1527 also Drenthe) and the cities of Zwolle, Deventer and Kampen, convened just outside the city of Ommen at Nieuwebrug (or New Bridge), named after the bridge over the Regge on the road between Ommen and Hellendoorn. Following a feud between Kampen and Zwolle in 1519, however, a gathering of the Estates was attacked by citizens of neighbouring Zwolle, who abducted three noblemen and pillaged nearby Eerde castle. During the years that followed, conflict escalated in Overijssel.[12]
War and disaster

In 1522, citizens of Zwolle attacked and pillaged Ommen with the aid of Duke Charles of Guelders who thus conquered the city from Utrecht. Only the church and women's home de Heilige Geest (the Holy Spirit) survived the pillage and fire.[13]
Ommen remained part of Guelders until 1528, when emperor Charles V inherited authority over the entire Duchy of Guelders, including Overijssel. A new city hall was built in 1531 in between the church and the Vrijthof square. The city was pillaged again in 1568 by Spanish troops under the 'Iron' Duke of Alba, fighting for Charles's successor, Philip II of Spain. This time, the pillage was not as devastating: Ommen's church, city hall and several other main buildings were spared. In 1581, the Estates of Overijssel convened outside Ommen to depose Philip and proclaim the independence of the Netherlands.

Though a 'Golden Age' for the young Dutch Republic, the 17th century proved rather devastating for Ommen. A great fire in 1624 inflicted serious damage on the church, of which only the foundations and a few walls remained. To control traffic and to prevent military invasions from the north, the fortification of Ommerschans was constructed. In 1672, one of the most severe fires in Ommen's history raged through the entire city, destroying everything but the church. In that same year, the aptly named 'Rampjaar' (disaster year), the Franco-Dutch War broke out, and until 1674 foreign troops (especially from Münster) frequently marched through Ommen, demanding passage, payment, food and lodging. It was not until 1753 that Ommen had sufficiently recovered to afford a new city hall, built at the Vrijthof square, on the same location as the previous building.
During the so-called 'periwig era' of decline in the Netherlands, discontent with oligarchical rule also increased in Ommen. In 1732, the citizens of Ommen rose up against the city council. A petition was handed to the Magistrate on May 31, in which a large share of the citizenry rejected its authority and asked it to resign. The council refused and severe riots ensued, but eventually order was restored. In 1762, a night guard was installed to maintain public order, but the unrest would remain until the Batavian Revolution of 1795.
Ommen in modern times
On March 2, 1809, the municipal authorities prepared a welcome for the visit of Lodewijk Napoleon, king of the short-lived Kingdom of Holland. They were disappointed when they found out the king had already passed Ommen the day before. The three burgomasters quickly pursued the king and met with his party near Gramsbergen, still receiving a gift of 1000 Dutch guilders for the well-intended preparations for his visit.
When his brother Napoleon Bonaparte annexed the Kingdom of Holland into the French Empire in 1810, he had all local government radically reformed to become compatible with French structures. Ommen too was affected: the separate jurisdictions of Stad Ommen (composed of the city of Ommen and the Ommerschans) and Ambt Ommen (which comprised most of the rest of the current municipality, Avereest and Den Ham as well) were merged into one Mairie Ommen (though Den Ham became a separate municipality).[14] This caused much controversy and discontent locally because the marke communities thus lost their ancient rights of self-governance. In 1818, shortly after Dutch independence, Mairie Ommen was once more decentralised into the municipalities Stad Ommen, Ambt Ommen and Avereest. To ensure good coordination, one burgomaster was appointed over both Stad and Ambt from 1851 onwards.[15]
To safeguard the eastern borders of the newly established Kingdom of the Netherlands, plans were drawn by order of Baron Krayenhoff in 1819 to convert Ommen into a city with fortifications. However, these radical plans (Ontwerp ter bevestiging van Ommen 1819) were not carried out in the end, as the IJssel river to the west was considered a more natural line of defence.[16]
Although renovated and expanded in 1758, the toll house next to the bridge (also called the bridge master's house) was torn down in 1827 to be replaced by a new city hall, designed by the architect J.P. Orentzburg. This new building, situated on the bank of the Vecht, housed all offices of the municipal authorities — including the city council, the court, the tax and toll office, the Gentlemen's Society and the home of the burgomaster. The court moved to a new building in 1882. The burgomaster and the Gentlemen's Society moved soon afterwards. The city hall was renovated and expanded in 1925 and again in 1955. The municipal authorities left the building in 1982. It has since been converted into a museum and a restaurant.

In 1923, the municipalities of Stad Ommen and Ambt Ommen were once again merged. The borders of the municipality have remained unchanged since, with the exception of the eastern part of Lemelerveld which came under the municipality of Dalfsen in 1997.
On the night of 6 February 1972, a Palestine terrorist organisation named Black September attempted to blow up a natural gas pipeline at a distribution hub near Ommen, but not all explosives were detonated. A blue bag filled with explosives was found after the explosion, next to a three-meter-wide (9.8 ft) crater. During the same night there were also attacks in Hamburg and the Dutch village of Ravenstein — and later that year, Black September also caused the Munich Massacre.[17]
Eerde

About four kilometres (2.5 miles) south-east of Ommen and adjacent to the hamlet of Eerde lies the castle Eerde, a castle in the Dutch-classical style from 1715, surrounded by a 1,667 hectare estate in the Baroque style managed by the Natuurmonumenten foundation since 1965.[18]
The name "Eerde" is a Saxon word meaning "earth". The first castle on this site was built in the 14th century, but was soon destroyed by the bishop's men in 1380 — along with the fortifications of the town of Ommen. In the centuries since, the Van Twickelo, Van Renesse and Van Pallandt families have lived in castles on this site. The castle was used by the famous philosopher and spiritual teacher Jiddu Krishnamurti, of whom Baron Philip van Pallandt was an avid follower, from about 1924 to just before the start of the Second World War. Van Pallandt granted Krishnamurti a territory at the Besthemerberg, north of Eerde. There Krishnamurti held his Order of the Star in the East lectures and meetings in front of audiences of thousands of people from dozens of countries.[6]
During the Second World War, a Nazi concentration camp, Kamp Erika, was situated at the Besthemerberg. Only eight Jews were detained here; the camp was designated mostly for Dutchmen convicted of black market trade or resistance to the occupational authorities. The camp was notorious for the brutal behaviour of its personnel, leading Dutch judges to refuse to send convicts there in 1943. The camp was turned into an Arbeitserziehungslager mostly for those refusing to do forced labour, but in the fall of 1944 it once again became a penal camp. The camp was liberated on 11 April 1945. From 1945 to 1946, the camp was instead used to detain Dutchmen who had collaborated with the German occupiers. Their treatment was not much better.[19]
Nowadays the castle houses the private international boarding school Eerde, which offers the IB programme.[20]
Ommerschans
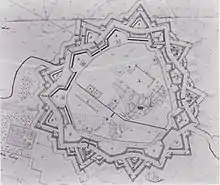
About ten kilometres (6.2 miles) due north of Ommen lies the former Ommerschans fortification.[21] The Ommerschans was a fortress built in 1628 as part of a defence line to defend the northern provinces of Groningen and Friesland from the marauding count Hendrik van den Bergh (in Spanish service) after the expiration of the Twelve Years' Truce. Hendrik, a nephew of William of Orange, then defected to the Dutch Republic in 1633.
The defences of the Ommerschans were restrengthened in the middle of the 17th century to deter and halt a possible invasion from the German states. Despite these new fortifications, the Ommerschans was captured without any resistance when Prince-Bishop Bernhard von Galen of Münster and Archbishop-Elector Maximilian Henry of Cologne invaded in 1672, the so-called rampjaar (or disaster year) that started the Franco-Dutch War. The 146 musketeers and 55 pikemen stationed at the Ommerschans fled north, only to return later that year when the bishops retreated after their failed siege of the northern city of Groningen.
Under pressure from the citizens of Ommen and after the Peace of Utrecht of 1713, the fortress was closed down in 1715, only to be reinstated as a fortified arsenal in 1740 when war reignited in Continental Europe. During the Patriot Revolt of 1787, militias from Zwolle, Kampen and Vollenhove conquered and pillaged the Ommerschans, stealing all its weaponry to help them in their paramilitary struggle against the regime. The Ommerschans fortification became abandoned and would never again be used for military purposes.

In the early 19th century, the Dutch government changed it into a resocialisation institution and labour camp for beggars, prostitutes and alcoholics from Amsterdam and other western cities. They were supposed to learn farming and morals by experience so they could reintegrate into society. In reality the beggars were used for semi-forced and all-but-unpaid labour to reclaim the wetlands surrounding Ommerschans, eventually reclaiming an area of 4 by 2+1⁄2 kilometres. Politician and novelist Jacob van Lennep visited Ommerschans during his walking tour with Dirk van Hogendorp across the newly independent United Kingdom of the Netherlands in the summer of 1823, and documented his shock at the conditions at the labour camp: "These hours are certainly among the saddest I have lived through."
When the institution went bankrupt in 1859 the Dutch government managed the labour camp until 1889, when it was finally closed down. During its years in operation, between several hundred and two thousand workers would live at Ommerschans at any one time, and an estimated 5448 workers died whilst interned there.
The city of Ommen
Location, economy and infrastructure

Ommen lies 20 kilometres (12 miles) east of the provincial capital of Zwolle and 35 kilometres (22 mi) north-east of fellow Hanseatic city Deventer. It lies on the north bank of the Vecht river, not far from where the Regge river merges with this stream. Only smaller ships and yachts can use these waterways.
Because Ommen is a rural municipality, tourism and agriculture are the pillars of the local economy. The forests and hilly heathlands of Ommen attract many nature-seeking visitors. The city of Ommen has several hotels and in the surrounding area there are fifteen campgrounds. Gilwell Ada's Hoeve on the left bank of the Vecht was the first Scouting campground in the Netherlands. Ommen also has a small marina.
Since 15 January 1903, Ommen has had a railway station designed by Eduard Cuypers. It is situated one kilometre (0.6 miles) from the centre on the opposite side of the Vecht. The station is on the (minor) Zwolle-Emmen line and trains stop roughly twice an hour. Ommen also used to have direct railway links to Stadskanaal and to Deventer via Raalte, which were abandoned when they lost their importance due to the emergence of the automobile. Early plans to establish railway lines from Ommen to Hoogeveen and to Hellendoorn were abandoned for that same reason.
An important infrastructural problem is the N34 road from Zwolle via Emmen to Groningen, which crosses the city of Ommen. One of its main crossroads, near the Vecht bridge is a bottleneck that causes frequent traffic congestion. The government is rerouting the N34 road north of the city, in order to reduce crosstown traffic.
Local politics
The current mayor of Ommen is Hans Vroomen. He started his tenure on December 18, 2017
The last municipal elections were in March 2022. The seventeen seats in Ommen's municipal council are divided as follows:
- Local Party Ommen (LPO): 4 seats
- CDA: 4 seats
- People's party Ommen Forward (VOV): 3 seats
- ChristianUnion: 3 seats
- PvdA: 1 seat
- D66: 1 seat
- VVD: 1 seat
International relations
Twin towns — Sister cities
Ommen is twinned with:
|
Culture
Bissing

Ommen is famous for its Bissing fair and markets. These yearly markets have been organised on the second Tuesday of July since at least 1557. The Bissing lasted three days from Monday till Wednesday. Its success was based on the wide array of products on offer and a relaxation of excises and regulation on alcoholic consumption, attracting merchants and consumers to Ommen from far and wide. In the 19th century it became one of the main markets in the province of Overijssel, and there would often be brawls and riots. In 1918, the council of Dutch Reformed Church asked the town council to end the public events surrounding the Bissing for moral reasons. The town council complied and the Bissing activities were suspended until 1958, although the market continued.
Nowadays the Bissing has become a major tourist attraction, lasting for five consecutive Wednesdays after the initial market and comprising a wide array of ceremonies, fairs, concerts, funfairs and activities.
The etymology of the word Bissing is widely discussed. Some believe it is derived from 'Bishop's day', in recognition of the granting of Ommen's town rights, whilst others believe the Low-Saxon word is related to the English word business.
Language
Most inhabitants of Ommen speak Dutch, but many will also speak Low Saxon or Plat — an ancient language related to Low German and Old English which is indigenous to the north-east of the Netherlands. The dialect of Plat spoken in Ommen is Sallands. Although both the national government and the European Union recognise Plat as a regional language, it is considered by many to be a mere dialect of Dutch, and its popularity is waning rapidly, even compared to Twents.
The poet Johanna van Buren died in Ommen in 1962. Her Plat poetry in the Salland and Twents dialect is still popular throughout Overijssel. The Johanna van Buren Cultural Prize is awarded once every three years to a person who contributed to the regional culture of the Eastern Netherlands.[22]
Religion
Ommen has a reasonable mix of Christian churches, with sizable Roman Catholic, Dutch Protestant and Liberated Reformed (Gereformeerd Vrijgemaakt) congregations.
Ommen was built around the old church at its centre, built around 1150, first mentioned in 1238 and severely damaged by fires in 1330 and 1624.[6] The church was converted to Calvinism during the Reformation of the 16th century, and it was not until the constitutional reforms of 1853 that the Roman Catholicism was once again openly practiced in Ommen and not until 1860 that a new Roman Catholic church was founded in the centre of Ommen. The village of Vilsteren to the west of Ommen, however, had remained entirely Roman Catholic throughout the centuries.
The famous preacher and dissenter Albertus van Raalte lived and worked in Ommen between 1839 and 1844, before he and his congregation moved to America to found the Christian Reformed Church in North America and the city of Holland, Michigan.
Jews in the Ommen area often were small-scale butchers. Most of Ommen's Jewish community was murdered during the Holocaust or left soon after the Nazi occupation of the Netherlands.[23] The synagogue building was demolished in 1956. Jewish graveyards still exist.
Sights

- The church in the centre, built in 1150 but rebuilt and renovated regularly, is by far the oldest building in Ommen.
- The National Tin Figurine Museum in the former Town Hall has over 200,000 figurines and panoramas, including four panoramas of the Battle of Ane.[24]
- Ommen has five windmills, of which three are in the town itself: the Lelie (1846, still in full operation), Den Oordt (1842, operates weekly) and the Konijnenbelt (1806, out of commission). Vilsteren has its own windmill (1858, recently recommissioned), as does the hamlet of Besthem (1862, recently renovated). The Besthemermolen also houses the Nature Information Centre with expositions about Ommen's diverse landscape and ecosystems.
- The small Regional Museum in Ommen explains Ommen's customs and history.[25]
- The estates of the Vilsteren and Eerde castles are open to the public.[18][26]
- The Pieterpad rambling trail (the most popular trail in the Netherlands) passes through Ommen.[27]
Notable inhabitants of Ommen

- Albertus van Raalte (1811 in Wanneperveen – 1876) preacher and founder of Holland, Michigan
- August van Groeningen (1866 in Ommen – 1894) writer
- Johanna van Buren (1881 in Hellendoorn – 1981) poet
- Gerrit Bouwhuis (1888 in Ommen – 1957) a Dutch sports shooter, competed at the 1924 Summer Olympics
- Philip baron van Pallandt (1889–1979), pioneer of Dutch Scouting
- J. H. A. Lokin (born 1945 in Ommen) jurist and academic
- Edward Top (born 1972 in Ommen), composer
- Malik Azmani (born 1976 in Heerenveen) is a Dutch politician and Member of the European Parliament
References
- ↑ "College van Burgemeester en Wethouders" [Board of mayor and aldermen] (in Dutch). Gemeente Ommen. Archived from the original on 10 May 2014. Retrieved 31 March 2014.
- ↑ "Kerncijfers wijken en buurten 2020" [Key figures for neighbourhoods 2020]. StatLine (in Dutch). CBS. 24 July 2020. Retrieved 19 September 2020.
- ↑ "Postcodetool for 7731EE". Actueel Hoogtebestand Nederland (in Dutch). Het Waterschapshuis. Retrieved 31 March 2014.
- ↑ "Bevolkingsontwikkeling; regio per maand" [Population growth; regions per month]. CBS Statline (in Dutch). CBS. 1 January 2021. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ↑ Central Bureau for Statistics (CBS), January 1, 2006
- 1 2 3 Gerrit Nevenzel, Kasteel Eerde Archived 2001-08-21 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Willem Bemboom, Het maritieme cultuurlandschap van Regge en Vecht (2007), Rijksuniversiteit Groningen, Afdeling Maritieme Archeology. (in Dutch)
- ↑ Steen, G. en W. Veldsink, 1948 – De geschiedenis van Ommen. (in Dutch)
- ↑ The History of 't Laer Archived 2009-01-20 at the Wayback Machine (in Dutch)
- ↑ Unknown author, Quedam narracio de Groninghe de Trentis de Covordia et diversis alliis sub episcopis Traiectensibis (a.k.a. Narracio), published by Vereniging Herdenking Slag bij Ane (2000), folder.
- ↑ The historical sources about Ommen differ on many of the dates before the 17th century. Usually the difference is only one or two years, but sometimes as much as a decade. The most commonly quoted dates are used on this page.
- ↑ Dieks Horsman, "Nieuwebrug, geen echte buurtschap... en toch een gezellige buurt" in De Darde Klokke, No. 117, page 28 (in Dutch)
- ↑ Jan Lucas, The Town Hall (in Dutch)
- ↑ Ad van der Meer and Onno Boonstra, "Repertorium van Nederlandse gemeenten" (2006) Koninklijke Nederlandse Akademie van Wetenschappen, ISBN 90-6984-495-8.
- ↑ Harry Woertink, Burgemeesters van Ommen, in Ommen Historisch Belicht (2006), Historische Kring Ommen. (In Dutch)
- ↑ "Plans for the fortification of Ommen in the Dutch National Archives". Archived from the original on 2010-11-08. Retrieved 2010-02-07.
- ↑ Andere Tijden, Aanslagen in Ravenstein en Ommen: De grootste sabotage-daad van na de oorlog, October 16, 2001. (In Dutch)
- 1 2 Stichting Natuurmonumenten, Natuurgebied Eerde Archived 2006-09-30 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Guusta Veldman Knackers achter prikkeldraad : kamp Erika bij Ommen, 1941–1945 (1993) ISBN 90-5345-037-8 (in Dutch)
- ↑ "International School Eerde -". eerde.nl.
- ↑ Vereniging De Ommerschans, History of the Ommerschans Archived 2007-02-08 at the Wayback Machine (in Dutch)
- ↑ Streektaalzang, Johanna van Buren (in Dutch)
- ↑ "Ommen - Joods Cultureel Kwartier".
- ↑ National Tin Figurine Museum, National Tin Figurine Museum Archived 2013-06-18 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Regional Museum Ommen (in Dutch), Regional Museum Ommen
- ↑ Landgoed Vilsteren, Landgoed Vilsteren Archived 2006-09-30 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Pieterpad (in Dutch) www site: http://www.pieterpad.nl/
External links
- Official website (Dutch)
- Ommen Regional Museum (Dutch)
- Ommen Historical Society (Dutch)
