| |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | SEF-di-nir |
| Trade names | Cefzon, Omnicef, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a698001 |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 16% to 21% (dose-dependent) |
| Protein binding | 60% to 70% |
| Metabolism | Negligible |
| Elimination half-life | 1.7 ± 0.6 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.171.145 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H13N5O5S2 |
| Molar mass | 395.41 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 170 °C (338 °F) (dec.) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Cefdinir, sold under the brand name Omnicef among others, is an antibiotic used to treat pneumonia, otitis media, strep throat, and cellulitis.[1] It is a less preferred option for pneumonia, otitis media, and strep throat which may be used in those with a severe allergy to penicillin.[1] It is taken by mouth.[1]
Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, and a skin rash.[1] Serious side effects may include Clostridioides difficile infection, anaphylaxis, and Stevens–Johnson syndrome.[1] Use in pregnancy and breastfeeding is believed to be safe but has not been well studied.[2] It is a third-generation cephalosporin and works by interfering with a bacteria's ability to make a cell wall resulting in its death.[1]
It was patented in 1979 and approved for medical use in 1991.[3] It is available as a generic medication.[1] In 2020, it was the 228th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 2 million prescriptions.[4][5]
Medical uses
Therapeutic uses of cefdinir include otitis media, soft tissue infections, and respiratory tract infections, including sinusitis, strep throat (note: no documented resistance of Group A Streptococcus to penicillin has ever been reported, and penicillin or amoxicillin is preferred except in penicillin allergic patients), community-acquired pneumonia, and acute exacerbations of bronchitis.
Susceptible organisms
Cefdinir is a bactericidal antibiotic of the cephalosporin class of antibiotics. It can be used to treat infections caused by several Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria.
Bacterial susceptibility and resistance
Cefdinir is a broad-spectrum antibiotic and has been used to treat infections of the respiratory tract including pneumonia, sinusitis, and bronchitis. The following represents MIC susceptibility data for a few medically significant microorganisms.[6]
- Haemophilus influenzae: 0.05 - 4 μg/ml
- Streptococcus pneumoniae: 0.006 - 64 μg/ml
- Streptococcus pyogenes: ≤0.004 - 2 μg/ml
Side effects
Side effects include diarrhea, vaginal infections or inflammation, nausea, headache, and abdominal pain."[7]
It is also one of the medications that can cause toxic epidermal necrolysis or Stevens–Johnson syndrome.[8]
The pediatric version of cefdinir can bind to iron in the digestive tract; in rare cases, this causes a rust or red discoloration of the stool. Blood typically appears dark brown or black in stool, and testing may confirm which is present. If the reddish stool is accompanied by abdominal pain, weight loss, diarrhea, etc., a Clostridioides difficile infection caused by the antibiotic could be signified.
Mechanism of action
Society and culture
Economics
As of 2008, cefdinir was the highest-selling cephalosporin antibiotic in the United States, with more than $585 million in retail sales of its generic versions.[9]
Available forms
Cefdinir is administered orally. It is available as capsules and a suspension. Dosage, schedule, and duration of therapy varies according to the type of infection.
Warner-Lambert licensed the drug for marketing in US from Fujisawa.[10] Abbott obtained U.S. marketing rights to cefdinir in December 1998 through an agreement with Warner-Lambert Company.[11] It was approved by the FDA on December 4, 1997.[12] It is available in US as Omnicef by Abbott Laboratories and in India as Cednir by Abbott, Kefnir by Glenmark, Cefdair by Xalra Pharma and Cefdiel by Ranbaxy.
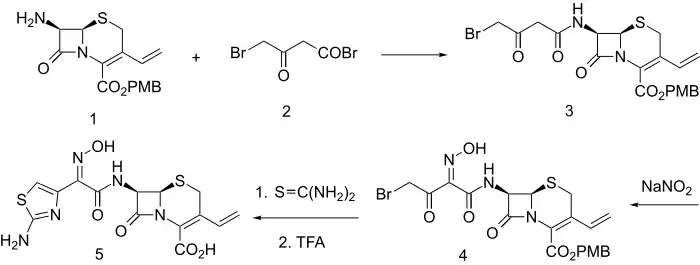
Synthesis
Acylation of the primary amine 1 with 4-bromo-3-oxobutanoyl bromide (2) leads to the amide (3). The active methylene group in that product is then nitrosated with sodium nitrite; the initial product spontaneously tautomerizes to afford the oxime (4). The bromoketone array in that intermediate constitutes a classical starting function for construction of thiazoles. Reaction of 4 with thiourea thus leads to formation of an aminothiazole moiety. Thus there is obtained the antibiotic cefdinir (5).
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "Cefdinir Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved 23 March 2019.
- ↑ "Cefdinir Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ↑ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 49X. ISBN 9783527607495.
- ↑ "The Top 300 of 2020". ClinCalc. Retrieved 7 October 2022.
- ↑ "Cefdinir - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Retrieved 7 October 2022.
- ↑ "Susceptibility and Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Data" (PDF). October 14, 2015. Retrieved 1 October 2015.
- ↑ "Omnicef capsules Patient Information" (PDF). Abbott Laboratories. February 2004. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2006-11-18. Retrieved 2006-11-24.
- ↑ "Omnicef manufacturer's packet insert" (PDF). FDA. Retrieved 2016-12-11.
- ↑ "2008 Top 200 generic drugs by retail dollars" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-01-12. (399.4 KB). Drug Topics (May 26, 2009). Retrieved on July 24, 2009.
- ↑ "Document". elsevierbi.com.
- ↑ "Medicis.com - Medicis Pharmaceutical Corporation". globenewswire.com. Archived from the original on 2014-07-14.
- ↑ "Cefdinir medical facts from Drugs.com". drugs.com.
- ↑ Takaya T, et al., BE 897864; eidem, U.S. Patent 4,559,334 (1984, 1985 both to Fujisawa Pharmaceuticals).
- ↑ Inamoto Y, Chiba T, Kamimura T, Takaya T (June 1988). "FK 482, a new orally active cephalosporin synthesis and biological properties". The Journal of Antibiotics. 41 (6): 828–30. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.41.828. PMID 3255303.
- ↑ Kamachi H, Narita Y, Okita T, Abe Y, Iimura S, Tomatsu K, et al. (November 1988). "Synthesis and biological activity of a new cephalosporin, BMY-28232 and its prodrug-type esters for oral use". The Journal of Antibiotics. 41 (11): 1602–16. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.41.1602. PMID 3198494.
- ↑ González M, Rodríguez Z, Tolón B, Rodríguez JC, Velez H, Valdés B, et al. (June 2003). "An alternative procedure for preparation of cefdinir". Farmaco. 58 (6): 409–18. doi:10.1016/S0014-827X(03)00063-6. PMID 12767379.
External links
- "Cefdinir". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.