 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
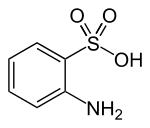
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Aminobenzene-1-sulfonic acid | |
| Other names
Orthanilic acid, 2-Aminobenzenesulfonic acid o-Aminobenzenesulfonic acid Aniline-2-sulfonic acid 88-21-1 Aniline-o-sulfonic acid[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.646 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H7NO3S | |
| Molar mass | 173.19 g·mol−1 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.46 (H2O)[2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Orthanilic acid (2-aminobenzenesulfonic acid) is a biological acid with roles in benzoate degradation and microbial metabolism in diverse environments.
Orthanilic acid promotes reverse turn formation in peptides, inducing a folded conformation[3][4] when incorporated into peptide sequences (Xaa-SAnt-Yaa), showing robust 11-membered-ring hydrogen-bonding.
Orthanilic acid is a structural component of some azo dyes which consequently have poor bacterial degradation.[5]
Orthanilic acids have also been found to affect cardiac tension.[6][7]
References
- ↑ "PubChem entry". Retrieved 2014-05-17.
- ↑ Haynes, William M., ed. (2016). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (97th ed.). CRC Press. pp. 5–88. ISBN 978-1498754286.
- ↑ Kale, Sangram S.; Priya, Gowri; Kotmale, Amol S.; Gawade, Rupesh L.; Puranik, Vedavati G.; Rajamohanan, P. R.; Sanjayan, Gangadhar J. (March 2013). "Orthanilic acid-promoted reverse turn formation in peptides". Chem. Commun. 49 (22): 2222–4. doi:10.1039/C3CC40522B. PMID 23392615.
- ↑ Kale, Sangram S.; Priya, Gowri; Kotmale, Amol S.; Gawade, Rupesh L.; Puranik, Vedavati G.; Rajamohanan, P. R.; Sanjayan, Gangadhar J. (2013). "Orthanilic acid-promoted reverse turn formation in peptides". Chemical Communications. 49 (22): 2222–4. doi:10.1039/C3CC40522B. PMID 23392615.
- ↑ Tan, Nico C. G.; Leeuwen, Annemarie van; Voorthuizen, Ellen M. van; Slenders, Peter; Prenafeta-Boldú, Francesc X.; Temmink, Hardy; Lettinga, Gatze; Field, Jim A. (2005). "Fate and biodegradability of sulfonated aromatic amines". Biodegradation. 16 (6): 527–37. doi:10.1007/s10532-004-6593-x. PMID 15865345. S2CID 5778950.
- ↑ Franconi, F; Bennardini, F; Campana, S; Failli, P; Matucci, R; Stendardi, I; Giotti, A (1990). "Effect of taurine, L-cysteic and orthanilic acids on cardiac tension". Progress in Clinical and Biological Research. 351: 175–84. PMID 2122477.
- ↑ Franconi, F; Bennardini, F; Campana, S; Failli, P; Matucci, R; Stendardi, I; Giotti, A (1990). "Effect of taurine, L-cysteic and orthanilic acids on cardiac tension". Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 351: 175–84. PMID 2122477.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.