| Otto A.G.O. 50 hp | |
|---|---|
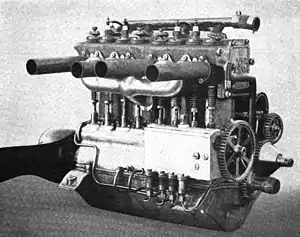 | |
| Aeromotor Gustav Otto 50 hp aircraft engine | |
| Type | Piston inline aero engine |
| National origin | Germany |
| Manufacturer | Gustav Otto Flugmaschinenwerke |
| First run | c.1911[1] |
| Developed into | Otto A.G.O. 70 hp |
The Otto A.G.O. 50 hp aircraft engine from 1911 was a four-cylinder, water cooled inline engine built by the German Gustav Otto Flugmaschinenwerke.
Design and development


The Otto A.G.O. (Aeromotor Gustav Otto) 50 hp engine was designed by Hans Geisenhof in 1911 at the Gustav Otto Flugmaschinenwerke. It had a bore and stroke of 110 mm × 150 mm (4.33 in × 5.91 in) and produced about 50 hp (37 kW) at 1,200 rpm.[2][3]
The cylinders were cast separately from iron and then machined. They were grouped together to a single block, joined at their cooling jackets by means of flanges and bolts. There were two side valves per cylinder, which were operated from the camshaft, which was located on the left side of the engine block and driven from the crankshaft by spur gears. All four cylinders were fed by a single carburettor. A single spark plug per cylinder was mounted above the inlet valve, with the magneto located at the control side of the engine, driven from the crankshaft via an intermediate spur gear.
The crankshaft was supported by one intermediate and two outer plain bearings, with two additional thrust ball bearings at the propeller end. Lubrication was pressure fed, with an oil pump feeding oil to the crankshaft bearings.[3]
Applications
- Otto Renn-Doppeldecker (1912) racing biplane[4]
Specifications
Data from Quittner[3]
General characteristics
- Type: four-cylinder, water-cooled in-line piston engine
- Bore: 110 mm (4.33 in)
- Stroke: 150 mm (5.91 in)
- Displacement: 5.7 L (348 cu in)
- Dry weight: 90 kg (198 lb)
- Designer: Hans Geisenhof
Components
- Valvetrain: one camshaft in the engine block, two Sidevalves per cylinder actuated via roller tappets
- Cooling system: Water-cooled
- Reduction gear: Direct-drive
Performance
- Power output: 50 hp (37 kW) at 1,200 rpm
See also
Related development
Related lists
References
Citations
- ↑ Illustrirte Mittheilungen des Oberrheinischen Vereins für Luftschiffahrt, issue 16/1911, p. 38, advertisement
- ↑ Angle 1921, pp. 372–373.
- 1 2 3 Quittner 1912, pp. 96–101.
- ↑ R. B. 1912, pp. 27–29.
Works cited
- Angle, Glenn Dale (1921). Airplane Engine Encyclopedia: An Alphabetically Arranged Compilation Of All Available Data On The World's Airplane Engines. Otterbein Press. pp. 372-373. OL 23525261M.
- Quittner, Victor (May 1912). "Die Flugmotorern auf der „ALA"". Der Oelmotor (in German). Berlin: Verlag für Fachliteratur G.m.b.H. I. Jahrgang 1912/13 (2): 96–101. OCLC 2449244.
- R. B. (1912). "Von den Otto-Flugzeugwerken in München". Deutsche Luftfahrt, Jahrgang 1912 (in German). 16: 27–29. OCLC 29889214.
Further reading
- Staff writer(s) (August 9, 1911). "Gustav Otto Flugmaschinen-Werke München (advertisement)". Illustrirte Mittheilungen des Oberrheinischen Vereins für Luftschiffahrt, Jahrgang 1911 (in German). 15 (16): 38. OCLC 19872940.
External links
 Media related to Otto A.G.O. 50 hp at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Otto A.G.O. 50 hp at Wikimedia Commons