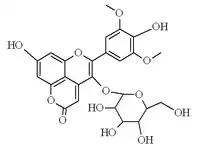
Chemical structure of oxovitisin A.
Oxovitisins are a type of pyranoanthocyanin with a pyranone (2-pyrone) component found in aged Port wines. They do not contain an oxonium ion component (flavylium cation), as anthocyanins do. Therefore, they do not have an absorption maximum at 520 nm. Oxovitisins are stable yellowish pigments with similar unique spectral features, displaying only a pronounced broad band around 370 nm in the UV−vis spectrum.[1]
Examples
- Pyranone-malvidin-3-glucoside (Oxovitisin A)
- Pyranone-malvidin-3-coumaroylglucoside[2]
References
- ↑ Oxovitisins: A New Class of Neutral Pyranone-anthocyanin Derivatives in Red Wines. Jingren He, Joana Oliveira, Artur M. S. Silva, Nuno Mateus and Victor De Freitas, J. Agric. Food Chem., 2010, 58 (15), pages 8814–8819, doi:10.1021/jf101408q
- ↑ Oxidative formation and structural characterisation of new α-pyranone (lactone) compounds of non-oxonium nature originated from fruit anthocyanins. Jingren He, Artur M.S. Silva, Nuno Mateus and Victor de Freitas, Food Chemistry, Volume 127, Issue 3, 1 August 2011, pages 984–992, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.01.069
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.