.svg.png.webp) |
.svg.png.webp) |


 The American Civil War Portal
The American Civil War Portal


The American Civil War (1861–1865) was a sectional rebellion against the United States of America by the Confederate States, formed of eleven southern states' governments which moved to secede from the Union after the 1860 election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States. The Union's victory was eventually achieved by leveraging advantages in population, manufacturing and logistics and through a strategic naval blockade denying the Confederacy access to the world's markets.
In many ways, the conflict's central issues – the enslavement of African Americans, the role of constitutional federal government, and the rights of states – are still not completely resolved. Not surprisingly, the Confederate army's surrender at Appomattox on April 9,1865 did little to change many Americans' attitudes toward the potential powers of central government. The passage of the Thirteenth, Fourteenth and Fifteenth amendments to the Constitution in the years immediately following the war did not change the racial prejudice prevalent among Americans of the day; and the process of Reconstruction did not heal the deeply personal wounds inflicted by four brutal years of war and more than 970,000 casualties – 3 percent of the population, including approximately 560,000 deaths. As a result, controversies affected by the war's unresolved social, political, economic and racial tensions continue to shape contemporary American thought. The causes of the war, the reasons for the outcome, and even the name of the war itself are subjects of much discussion even today. (Full article)


 Featured article
Featured article
Dunderberg, which is a Swedish word meaning "thunder(ing) mountain", was an ocean-going casemate ironclad of 14 guns built for the Union Navy. She resembled an enlarged, two-masted version of the Confederate casemate ironclad CSS Virginia. She was originally designed to have both gun turrets and a casemate but the turrets were deleted while the ship was still being built. Construction began in 1862, but progress was slow and she was not launched until after the end of the American Civil War in 1865.
The ship was not accepted by the Union Navy so her builder began seeking buyers elsewhere; Otto von Bismarck expressed some interest, and the thought of Prussia armed with such a vessel prompted France to purchase her and commission her in 1867 with the name Rochambeau. She was initially placed in reserve, but was mobilized in 1870 to participate in the Franco-Prussian War. The ship saw no action and was decommissioned after the end of the war. Rochambeau was stricken from the Navy Directory in 1872 and scrapped in 1874. (Full article...)


 Grand Parade of the States
Grand Parade of the States


 Featured biography
Featured biography
John Milton Hay (October 8, 1838 – July 1, 1905) was an American statesman and official whose career in government stretched over almost half a century. Beginning as a private secretary and an assistant for Abraham Lincoln, he became a diplomat. He served as United States Secretary of State under Presidents William McKinley and Theodore Roosevelt. Hay was also a biographer of Lincoln, and wrote poetry and other literature throughout his life.
Born in Salem, Indiana to an anti-slavery family that moved to Warsaw, Illinois, Hay showed great potential from an early age, and his family sent him to Brown University. After graduation in 1858, Hay read law in his uncle's office in Springfield, Illinois, adjacent to that of Lincoln. Hay worked for Lincoln's successful presidential campaign and became one of his private secretaries in the White House. Throughout the American Civil War, Hay was close to Lincoln and stood by his deathbed after the President was shot. In addition to his other literary works, Hay co-authored, with John George Nicolay, a ten-volume biography of Lincoln that helped shape the assassinated president's historical image. (Full article...)


 WikiProjects
WikiProjects
- Military history WikiProject
- American Civil War task force
- United States military history task force
- United States WikiProject
- History WikiProject
- Biography WikiProject


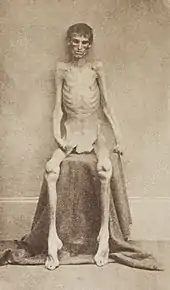
 Featured picture
Featured picture


 Did you know...
Did you know...
- ... that Colonel Bradley Winslow was brevetted by US president Abraham Lincoln for "brave and gallant conduct" during the siege of Petersburg in the American Civil War?
- ... that The Land We Love, a little magazine that merged into Southern Magazine, printed American Civil War recollections, poetry, agricultural material, and many works by female authors?
- ... that according to one historian, James S. Rains made a "significant contribution to the Confederate war effort" by getting drunk?
- ... that Romeo and Juliet both served in the Union Navy?
- ... that Emma Dean Powell received a pass from General Ulysses S. Grant to accompany her husband to battlefield camps during the American Civil War after he lost his arm?
- ... that Dubuque, Arkansas, was destroyed in the American Civil War and is now covered by the waters of Bull Shoals Lake?


 Subcategories
Subcategories


 American Civil War topics
American Civil War topics


 Related portals
Related portals


 Things you can do
Things you can do
- Attention needed
- ...to referencing and citation • ...to coverage and accuracy • ...to structure • ...to grammar • ...to supporting materials
- Popular pages
- Full list
- Cleanup needed
- The West Tennessee Raids
- Requested articles
- James Ashby (soldier) • Bluffton expedition • Benjamin D. Fearing • Charles A. Hickman • Richard Henry Jackson • James B. Speers • Charles S. Steedman • Battle of Barton's Station • Lawrence P. Graham • Thomas John Lucas • Daniel Henry Rucker • James Hughes Stokes • Frederick S. Sturmbaugh • Davis Tillson • Action at Nineveh (currently a redirect) • International response to the American Civil War • Spain and the American Civil War • Savannah Campaign Confederate order of battle • Native Americans in the American Civil War (currently disambiguation after deletion) • 1st Battalion, Mississippi Mounted Rifles (Union) • Battle of Lafayette • Requested American Civil War Medal of Honor recipients
- Expansion needed
- Battle of Boonsborough • Battle of Guard Hill • Battle of Rice's Station • Battle of Simmon's Bluff • Battle of Summit Point • Charleston Arsenal • Edenton Bell Battery • First Battle of Dalton • Blackshear Prison • Edwin Forbes • Hiram B. Granbury • Henry Thomas Harrison • Louis Hébert (colonel) • Benjamin G. Humphreys • Maynard Carbine • Hezekiah G. Spruill • Smith carbine • Edward C. Walthall • Confederate States Secretary of the Navy • Confederate States Secretary of the Treasury • David Henry Williams • Battle of Rome Cross Roads • Delaware in the American Civil War • Ironclad Board • United States Military Railroad • Kansas in the American Civil War • Rufus Daggett • Ebenezer Magoffin • Confederate Quartermaster-General's Department • First Corps, Army of Northern Virginia • Francis Laurens Vinton • Henry Maury • Other American Civil War battle stubs • Other American Civil War stubs
- Images needed
- Battle of Lone Jack • Preston Pond, Jr. • Melancthon Smith
- Merging needed
- 1st Regiment New York Mounted Rifles and 7th Regiment New York Volunteer Cavalry
- Citations needed
- 1st Alabama Cavalry Regiment (Union) • 4th Maine Battery • 33rd Ohio Infantry • 110th New York Volunteer Infantry • Battle of Hatcher's Run • Camp Dennison • Confederate colonies • CSS Resolute • Dakota War of 1862 • Florida in the American Civil War • Ethan A. Hitchcock (general) • Fort Harker (Alabama) • Gettysburg (1993 film) • Iowa in the American Civil War • Second Battle of Fort Sumter • Samuel Benton
- Translation needed
- Add an article here!


 Associated Wikimedia
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wikivoyage
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
-
 List of all portals
List of all portals -

-

-

-

-

-

-
-

-

-
 Random portal
Random portal -
 WikiProject Portals
WikiProject Portals
- Shortcuts to this page: Portal:ACW • P:ACW
_(14596346858)_The_steam_ram_'Dunderberg'_(cropped).jpg.webp)
















.jpg.webp)