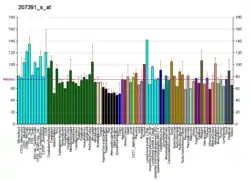
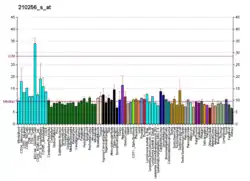
Phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase type-1 alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIP5K1A gene.[5][6][7]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000143398 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000028126 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Loijens JC, Anderson RA (Jan 1997). "Type I phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinases are distinct members of this novel lipid kinase family". J Biol Chem. 271 (51): 32937–43. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.51.32937. PMID 8955136.
- ↑ Xie Y, Zhu L, Zhao G (Jun 2000). "Assignment of type I phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase (PIP5K1A) to human chromosome bands 1q22--> q24 by in situ hybridization". Cytogenet Cell Genet. 88 (3–4): 197–9. doi:10.1159/000015545. PMID 10828584. S2CID 45527362.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: PIP5K1A phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase, type I, alpha".
Further reading
- Honda A, Nogami M, Yokozeki T, et al. (1999). "Phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinase alpha is a downstream effector of the small G protein ARF6 in membrane ruffle formation". Cell. 99 (5): 521–32. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81540-8. PMID 10589680. S2CID 10031591.
- Jones DH, Morris JB, Morgan CP, et al. (2000). "Type I phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinase directly interacts with ADP-ribosylation factor 1 and is responsible for phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate synthesis in the golgi compartment". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (18): 13962–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.C901019199. PMID 10747863.
- Divecha N, Roefs M, Halstead JR, et al. (2000). "Interaction of the type Ialpha PIPkinase with phospholipase D: a role for the local generation of phosphatidylinositol 4, 5-bisphosphate in the regulation of PLD2 activity". EMBO J. 19 (20): 5440–9. doi:10.1093/emboj/19.20.5440. PMC 314009. PMID 11032811.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Doughman RL, Firestone AJ, Wojtasiak ML, et al. (2003). "Membrane ruffling requires coordination between type Ialpha phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinase and Rac signaling". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (25): 23036–45. doi:10.1074/jbc.M211397200. PMID 12682053.
- Chang JD, Field SJ, Rameh LE, et al. (2004). "Identification and characterization of a phosphoinositide phosphate kinase homolog". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (12): 11672–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M309721200. PMID 14701839.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Kisseleva M, Feng Y, Ward M, et al. (2005). "The LIM protein Ajuba regulates phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate levels in migrating cells through an interaction with and activation of PIPKI alpha". Mol. Cell. Biol. 25 (10): 3956–66. doi:10.1128/MCB.25.10.3956-3966.2005. PMC 1087706. PMID 15870270.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. Bibcode:2005Natur.437.1173R. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514. S2CID 4427026.
- Gregory SG, Barlow KF, McLay KE, et al. (2006). "The DNA sequence and biological annotation of human chromosome 1". Nature. 441 (7091): 315–21. Bibcode:2006Natur.441..315G. doi:10.1038/nature04727. PMID 16710414.
- Halstead JR, van Rheenen J, Snel MH, et al. (2006). "A role for PtdIns(4,5)P2 and PIP5Kalpha in regulating stress-induced apoptosis". Curr. Biol. 16 (18): 1850–6. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2006.07.066. PMID 16979564. S2CID 15282445.
- Im YJ, Perera IY, Brglez I, et al. (2007). "Increasing plasma membrane phosphatidylinositol(4,5)bisphosphate biosynthesis increases phosphoinositide metabolism in Nicotiana tabacum". Plant Cell. 19 (5): 1603–16. doi:10.1105/tpc.107.051367. PMC 1913725. PMID 17496116.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.